Set Transformer: A Framework for Attention-Based Permutation-Invariant Neural Networks
Explore the Set Transformer framework that introduces advanced methods for handling set-input problems and achieving permutation invariance in neural networks. The framework utilizes self-attention mechanisms and pooling architectures to encode features and transform sets efficiently, offering insig
9 views • 21 slides
Self-Supervised Learning of Pretext-Invariant Representations
This presentation discusses a novel approach in self-supervised learning (SSL) called Pretext-Invariant Representations Learning (PIRL). Traditional SSL methods yield covariant representations, but PIRL aims to learn invariant representations using pretext tasks that make representations similar for
0 views • 8 slides
Stretches and Shears in Geometry
Learn about the concepts of stretches and shears in geometry through visual representations and explanations. Discover how to identify stretches and shears, understand the role of invariant lines, determine scale factors, differentiate between the two transformations, and plot points in different sc
3 views • 11 slides
Fixed Effects Regression for Causal Inference in Social Research
Explore the concept of fixed effects regression for obtaining causal estimates with observational data, focusing on the association between social participation and depressive symptoms. Discover how this method controls for time-invariant factors and eliminates confounding variables, providing a clo
1 views • 49 slides
Myhill-Nerode Theorem in Automata Theory
Myhill-Nerode theorem states that three statements are equivalent regarding the properties of a regular language: 1) L is the union of some equivalence classes of a right-invariant equivalence relation of finite index, 2) Equivalence relation RL is defined in a specific way, and 3) RL has finite ind
2 views • 20 slides
Introduction to Quantum Chromodynamics & Field Theories in High-Energy Physics
Explore the fundamentals of Quantum Chromodynamics and Classical Field Theories in this informative lecture, covering topics such as global and local symmetries, Lagrangians, actions, and dynamics. Understand the significance of global and local symmetries in classical field theories, along with exa
5 views • 17 slides
SCET: Effective Theory of QCD
SCET, a soft collinear effective theory, describes interactions between low energy, soft partonic fields, and collinear fields in QCD. It helps prove factorization theorems and identifies relevant scales. The SCET Lagrangian is formed by gauge invariant building blocks, enabling gauge transformation
1 views • 38 slides
Unlabeled Certificates in Decision Tree Model
Dive into the concept of unlabeled certificates in the decision tree model, exploring their significance in minimizing queries to adjacency matrices for graph properties. Learn about the difference between labeled and unlabeled certificates, their relevance in invariant functions, and the complexiti
1 views • 31 slides
C Program Refinement Types with Liquid Types and Invariant Discovery
Discover the integration of Liquid Types and Refinement Types in C programming through Invariant Discovery, leading to automatically adapting C programs to fit Liquid Types. Explore challenges and solutions in expressing invariants, handling unknown aliasing, and implementing strong updates within t
0 views • 24 slides
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence Kernels and Clustering at UC Berkeley
Explore the world of Artificial Intelligence through CS188 course slides by Dan Klein and Pieter Abbeel at the University of California, Berkeley. Dive into topics like Case-Based Learning, Nearest-Neighbor Classification, Parametric vs. Non-Parametric models, Similarity Functions, and more. Discove
0 views • 41 slides
Exploring Transverse Momentum Distributions (TMDs) at the GDR PH-QCD Annual Meeting
The Annual Meeting of the GDR PH-QCD focused on discussing Transverse Momentum Distributions (TMDs) and their significance at small kT and small x values. Topics covered include gauge-invariant correlators, PDFs, and PFFs, as well as the utilization of color gauge links in describing partonic transv
1 views • 33 slides
Formal Verification of Flash Memory Reading Unit
Perform formal verification of a flash memory reading unit by demonstrating correctness using randomized testing and exhaustive testing. Randomly select physical sectors to write characters and set corresponding Security Assertion Markup (SAM) structures. Create a total of 43,680 distinct test cases
0 views • 5 slides
Maximum Likelihood Estimation in Physics
Maximum likelihood estimation (MLE) is a powerful statistical method used in nuclear, particle, and astro physics to derive estimators for parameters by maximizing the likelihood function. MLE is versatile and can be used in various problems, although it can be computationally intensive. MLE estimat
1 views • 22 slides
Fundamentals of Computer Vision and Image Processing
Fundamentals of computer vision cover topics such as light, geometry, matching, and more. It delves into how images are recorded, how to relate world and image coordinates, measuring similarity between regions, aligning points/patches, and grouping elements together. Understanding concepts like shad
1 views • 29 slides
Object-Oriented Python Code for WIMP Direct Detection Signals
Calculating signals for Weakly Interacting Massive Particle (WIMP) direct detection using an object-oriented Python code called WimPyDD. WimPyDD provides accurate predictions for expected rates in WIMP direct detection experiments within the framework of Galilean invariant non-relativistic effective
0 views • 24 slides
Radiometric Calibration Methods for Remote Sensing Applications
Techniques for radiometric calibration in remote sensing include vicarious approaches utilizing invariant desert sites, in-situ methods characterizing surfaces and atmospheres, and SI-traceable measurements for intercomparisons between sensors. The repeatability of in-situ results and comparison wit
3 views • 20 slides
Submission to Governmental Authorities in the Bible
The Bible emphasizes the importance of honoring and submitting to governmental authorities as they are appointed by God. Passages from 1 Peter and Romans instruct believers to obey rulers, governors, and kings, not using freedom as a pretext for wrongdoing. By following these teachings, individuals
0 views • 26 slides
Lazy Code Motion and Partial Redundancy Elimination in Optimizing Compiler
Lazy code motion, partial redundancy elimination, common subexpression elimination, and loop invariant code motion are optimization techniques used in compilers to improve code efficiency by eliminating redundant computations and moving code blocks to optimize performance. These techniques aim to de
2 views • 35 slides
Loop Invariant Code Motion in Frequent Paths for Optimization
Loop Invariant Code Motion (LICM) is a key optimization technique that identifies and moves code operations whose operands remain constant within a loop to improve performance. The process involves careful consideration of memory operations and operations not executed every iteration. The assignment
0 views • 20 slides
Challenges in Object Recognition for Machine Learning
Understanding the complexities of object recognition is crucial in machine learning. Real scenes present challenges like cluttered backgrounds, varied lighting, deformation, and affordances. Viewpoint changes and input dimension hopping further complicate recognition tasks. Different approaches, suc
1 views • 30 slides
Unraveling Collider Physics: Investigations, Interpretations, and Accelerations
Dive into the world of collider physics with a focus on LHC results, future collider projects, and experiments from the Baikal Summer School 2021. Explore topics like invariant mass calculations, Higgs boson decays, particle acceleration in the LHC tunnel, and particle velocity considerations. Engag
0 views • 10 slides
Impairments in Wireline Communication Channels
Wireline communication channels can experience various impairments such as linear time-invariant effects like attenuation and spreading, as well as linear time-varying effects like phase jitter, nonlinear effects, additive noise, and interference. These impairments can affect the quality of transmit
1 views • 16 slides
Distributed Transactions in Spanner: Insights and Mechanisms
Spanner, a strictly serializable system, leverages TrueTime for timestamping to enforce the invariant between transactions. It ensures efficient read-only transactions and multi-shard transactions. Mechanisms like 2PL, 2PC, and (Multi)Paxos contribute to Spanner's fault tolerance and scalability. Le
1 views • 21 slides
Loop Invariant Code Motion (LICM) in LLVM
Loop Invariant Code Motion (LICM) is a technique used in LLVM to move operations that do not change within a loop outside of the loop, improving performance by executing them only once per loop iteration. This process must be done carefully to handle memory operations and operations that are not exe
0 views • 19 slides
Fundamentals of Block Diagram Algebra
Graphical representation illustrating the functional relationships among components in a system. It serves as a cause-and-effect pictorial shorthand, showcasing the relationship and flow of signals. The diagram features various components such as single blocks, summing points, and pick-off points, e
0 views • 24 slides
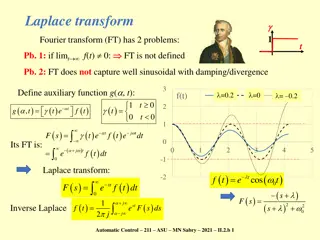
Solving LTI ODE Using Laplace and Fourier Transforms
Application of Laplace and Fourier transforms to solve Linear Time-Invariant Ordinary Differential Equations (LTI ODEs) with specific functions and parameters. Learn how to find the inverse transform using partial fractions and handle complex solutions.
0 views • 5 slides
Symbolic Loop Bound Analysis: Art of Invariant Generation
Innovative techniques for computing symbolic loop bounds through invariant generation. Learn about applications, challenges, and examples in this cutting-edge research field.
0 views • 33 slides
Welcome to Inflation
Inflation in the very early Universe and the goal to detect the large-scale B-mode pattern originating from primordial gravitational waves, a key signature of inflation. Single-field slow-roll inflation produces nearly scale-invariant perturbations. Explore the landscape of super-Planckian scenarios
0 views • 6 slides
Complete theory for martensitic transformations
Unlock the intricate world of martensitic transformations with in-depth insights into the Bain strain, lattice-invariant deformation, transformation twins, athermal transformation, and more. Dive into the fundamentals of martensite and austenite structures, encompassing observations of macroscopic s
1 views • 45 slides
Operator Scaling by Yuanzhi Li and Collaborators: Group Actions & Orbit Intersection Problems
This paper delves into the fascinating realm of operator scaling discussed by Yuanzhi Li from Princeton University in collaboration with other researchers. The focus is on group actions and problems related to orbit intersection, offering insight into graph isomorphism, complexity levels, and an eff
0 views • 60 slides
Anonymous Questions and Answerable Topics
In the realm of physics research, the Anonymous Questions BFYS Workshop of 2008 sparked interest with thought-provoking inquiries on particle decays. Moving to 2019, the focus shifted to Answerable Questions, delving into topics like open charm mesons, invariant mass distributions, and the usage of
0 views • 25 slides
Fifteen Puzzle Invariant Method: Understanding Parity in Solvability
Delve into the intricacies of the Fifteen Puzzle using the Invariant Method to analyze the solvability based on the concept of parity. Explore how the parity of states remains unchanged through moves, leading to the conclusion of solvability impossibility.
0 views • 40 slides
Chessboard Problems and Domino Puzzles
Solve chessboard problems and domino puzzles using the invariant method. Discover the logic behind bishop movements, chessboard filling, and domino placements. Learn how invariants provide solutions to complex challenges in chess-related scenarios.
0 views • 38 slides
RIDE: Reversal Invariant Descriptor Enhancement
Enhance your understanding of the RIDE algorithm presented at ICCV 2015, focusing on reversal invariance and image classification. Dive deep into image-level vector spatial pooling, geometric phrase pooling, and compact feature coding methods. Explore gradient-based local descriptors like SIFT and H
1 views • 41 slides
Quantization of 10D Massless Superparticle by Lado Razmadze
Delve into the fascinating world of quantizing gauge theories and relativistically invariant theories in curved spacetime through the study of 10D massless superparticles. Explore the algebraic approach using the Faddeev-Jackiw method, covariant quantization principles, and the use of Darboux's theo
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Channel Estimation and Impulse Response Identification
Learn about channel estimation and impulse response identification from data, including techniques for linear time-invariant systems and linear time-varying channels. Explore examples using MATLAB/Simulink and Stanford University Interim (SUI) Channel Models.
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Convolution and Correlation in Digital Image Analysis
Explore the key concepts of convolution and correlation in digital image analysis, including mask processing, interpolation techniques, and the advantages of understanding linear-shift-invariant systems. Learn about the relationship of pixels within their neighborhoods and how these operations can b
0 views • 20 slides
Differential Equations and Laplace Transforms in Signal Processing
Explore the computation of output signal transfer functions using differential equations and Laplace transforms in the context of first-order, second-order, and higher-order systems. Understand the implications of initial conditions and stability on the system's response characteristics. Gain insigh
1 views • 15 slides
Understanding LTI Systems and Signals
Explore the concept of Linear Time-Invariant (LTI) systems and signals through convolutions, impulse responses, and more in this lecture series. Discover the equivalence between linear and time-invariant systems and delve into topics like BIBO stability, correlation functions, z-transform, and Fouri
0 views • 53 slides
Understanding Linear Shift-Invariant Filtering in Computer Vision
Explore the concepts of linear shift-invariant filtering, derivative filtering, and the significance of derivative computation in computer vision. Discover how these filters are utilized to extract features like edges and corners from images, along with the precautions to take to avoid false edges d
1 views • 33 slides