Viral Vectors in Gene Delivery: Safety and Considerations
Exploring the mechanisms of gene delivery via viral vectors, this content delves into the basics of viral structure, infection, and replication. It discusses common viral vector systems like Adenoviral and Lentiviral vectors, highlighting safety considerations and the production processes involved.
1 views • 19 slides
Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
2 views • 19 slides
Introduction to Cartesian Components of Vectors in Two-Dimensional Space
Exploring Cartesian components of vectors in a two-dimensional coordinate frame using unit vectors i and j. Learn how to express vectors, add them using the triangle law, use column vector notation, and find resultant vectors. Understand position vectors in terms of coordinates. Examples and diagram
0 views • 16 slides
Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Amity School of Engineering & Technology Vectors in Java
Amity School of Engineering & Technology Vectors provide a flexible way to manage dynamic arrays in Java programming. With capabilities to store objects of any type and accommodate dynamic resizing, these vectors offer optimized storage management through capacity and capacity increment settings. Co
0 views • 18 slides
Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
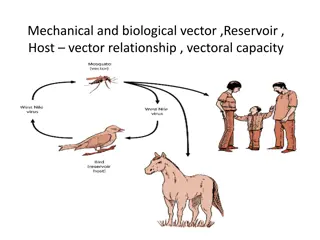
Vector Relationships and Pathogen Transmission
Understanding mechanical and biological vectors, reservoir hosts, and their role in disease transmission is crucial for effective disease control. Mechanical vectors like flies can transfer pathogens without getting infected, while biological vectors like mosquitoes carry pathogens that reproduce in
1 views • 5 slides
Curvilinear Motion with Cylindrical Coordinates in Physics
Cylindrical coordinates, specifically the r- coordinate system, are useful in describing curvilinear motion. This system helps explain motion in relation to a fixed origin, making it ideal for scenarios involving rotation or changes in angle. By using radial and transverse unit vectors, positions, v
1 views • 16 slides
Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
2 views • 25 slides
Vectors and Velocity in Physics and Game Programming
Exploring the concepts of vectors, velocity, and positional vectors in both physics and game programming. Learn about key properties, conversion formulas, and the application of velocity vectors to positional vectors using examples and visual representations.
3 views • 32 slides
Vectors and Motion Control Systems in Industrial Machinery
Vectors play a crucial role in machine control systems, particularly in programming and motion control. This article explores the concept of vectors, their application in two and three-dimensional machines, and their significance in physics. It also delves into the use of vectors for controlling mov
0 views • 6 slides
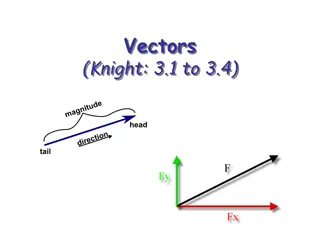
Exploring Vectors: Magnitude, Direction, and Operations
Delve into the world of vectors, understanding their properties, how to add and subtract them, and determining their components in different coordinate systems. Learn about scalar quantities, vector quantities, the tip-to-tail rule, and the role of unit vectors in calculations.
0 views • 19 slides
Cloning Vectors and Recombinant DNA Technology
Genetics Engineering Lecture-2 delves into the concept and basic steps of recombinant DNA technology and gene cloning, highlighting different types of cloning vectors like plasmids, bacteriophages, bacterial artificial chromosomes, yeast artificial chromosomes, and mammalian artificial chromosomes.
1 views • 13 slides
Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
Motion in Computer Games: Lecture #11 Movement
Explore the fundamentals of motion in computer games through Lecture #11 Movement. Delve into concepts like Newton's Laws, vectors, motion terms, and handling various forces to enhance your grasp on gaming physics. Discover how to apply basic rules of motion, obtain continuous input from keyboards,
0 views • 81 slides
Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Trigonometry and Vector Illustrations in Physics
Explore applications of trigonometry and vectors in solving real-world problems such as directing a helicopter pilot to a stranded camper, measuring the height of a tree, analyzing displacement vectors, and adding vectors using graphical and component methods.
0 views • 10 slides
Acceleration Due to Gravity Vectors
Discover the direction of acceleration due to gravity vectors for various scenarios such as a pebble dropped from a bridge, a baseball tossed up in the air, a football thrown at a 45-degree angle, and more. Explore how vectors can be represented to show both magnitude and direction, helping in visua
0 views • 18 slides
Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
3 views • 12 slides
Four-Vectors in 4D Space
Explore the concept of four-vectors in four-dimensional space, covering topics such as radius vectors, general 4-vectors, contravariant and covariant components, summation conventions, scalar products, and the components of a general 4-vector. Learn how these vectors transform under rotations and Lo
0 views • 42 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
1 views • 17 slides
Phage Vectors in Genetic Engineering
Phage vectors, utilized in genetic engineering, are bacteriophages capable of incorporating genes of interest into their genome. They have a higher DNA capacity compared to plasmids, making them ideal for creating genomic libraries. Bacteriophages like Lambda and M13 are commonly used for cloning ve
0 views • 17 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
MATLAB Basics for Electrical Engineering Students
In this instructional content from the Government Polytechnic West Champaran Department of Electrical Engineering, students are introduced to the fundamentals of MATLAB. Topics covered include transposing matrices, concatenating matrices, matrix generators, arrays, entering matrices, and manipulatin
0 views • 48 slides
Vectors in AP Physics C: Mechanics
Explore the fundamental concepts of vectors in AP Physics C: Mechanics, including scalar vs. vector quantities, vector operations, and vector multiplication. Discover the significance of vectors in explaining and predicting physical phenomena through graphical methods and mathematical equations. Div
0 views • 28 slides
Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Vector Mathematics for Geometric Problem Solving
Learn how to use vectors to solve geometric problems, including finding position vectors of points dividing line segments in given ratios. Explore concepts such as position vectors, ratios, trigonometry, and Pythagoras' theorem to determine angles and side lengths in triangles using vector methods.
0 views • 9 slides
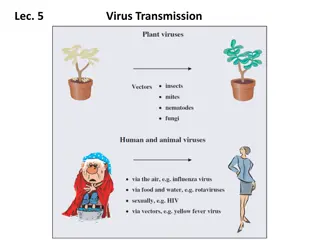
Virus Transmission via Vectors
Viruses must be transmitted to new hosts for their survival. This transmission occurs through vectors like arthropods, which acquire and transmit viruses during feeding. The mechanism involves viruses attaching to the vectors' mouthparts or entering their circulatory system to reach salivary glands
0 views • 14 slides
Dynamic Systems in Simulink: A Cannon Ball Example
Explore the vertical motion of a cannon ball under gravity in Simulink, starting with basic equations and progressing to modeling air resistance. Learn how to analyze two-dimensional motion using vectors and avoid hidden errors related to vectors in your simulations.
0 views • 10 slides
Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
1 views • 18 slides
Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Vectors: Concepts, Operations, and Applications
Vectors are quantities defined by magnitude and direction, essential in various fields like physics and mathematics. Learn about vector properties, examples, operations like addition and multiplication, as well as applications such as understanding displacement, velocity, and acceleration. Dive into
0 views • 20 slides
Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Cloning in Yeasts: Vectors and Selectable Markers
Yeasts like Saccharomyces cerevisiae and Schizosaccharomyces pombe are valuable organisms for eukaryotic gene expression. They offer easy growth like bacteria and are genetically well-characterized. Yeast selectable markers and vectors enable efficient cloning and expression of genes. The use of shu
0 views • 16 slides
Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
0 views • 20 slides