Media monopoly
Explore the implications of corporate media control on politics, culture, and democracy. Analyze the challenges faced in contemporary debates about media control. Assess the role of new communication technologies in reshaping media power dynamics. Understand the transformation of the U.S. media syst
2 views • 47 slides
Dominate Your Career Ace L3M1 Procurement & Supply Environments Exam with Confidence
Achieve success in the L3M1 Procurement and Supply Environments exam with confidence. Prepare effectively with comprehensive study materials and practice tests. Gain expertise in procurement processes, supply chain management, and industry environments. Validate your skills and enhance your career p
1 views • 4 slides
Alternatives to Regulation in the Market: Public Enterprise and Franchise Bidding
Understanding the concept of natural monopoly problem and exploring the alternatives to market regulation such as public enterprise and franchise bidding, with a focus on cable television. Delve into the challenges and benefits of each approach, including the potential of franchise bidding to achiev
6 views • 22 slides
Environments,Tuples,& Dictionaries
Explore the concepts of environments, tuples, and dictionaries in Python through visual diagrams and explanations. Learn about how Python interprets programs, assignments, functions, and function calls within different frames and environments. Discover the rules for name lookup in user-defined funct
2 views • 27 slides
The Evolution of Online Casinos in Singapore A Decade in Review
The initial years saw a clear distinction between online and offline gambling. The Singapore Pools monopoly dominated the market, offering legal avenues for Singapore sport bet and Singapore horse racing live odds. Online casinos, however, operated in a grey area.\nFor more information about online
6 views • 4 slides
Market Structures and Competition Overview
Market structures in economics define the competitive characteristics of different markets. Perfect competition features many small firms producing identical products as price takers. Monopoly has one seller with significant market power, while monopolistic competition involves firms with some marke
4 views • 5 slides
Market Structures: Perfect Competition vs Monopoly
Perfect competition features identical products, many sellers, and low barriers to entry, promoting efficiency. Monopolies, with one seller, can abuse power but are allowed in select industries. Understanding market structures is crucial for economic analysis and policy-making.
0 views • 23 slides
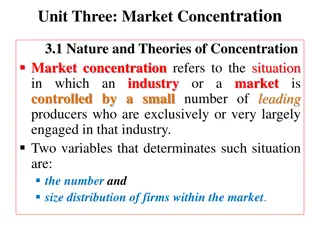
Understanding Market Concentration and Its Implications
Market concentration refers to industries controlled by a small number of leading producers, impacting pricing and output decisions. Various theories, measurement methods, and implications on firm behavior and performance are discussed, highlighting the relationship between monopoly power and market
0 views • 62 slides
Law, Strategy, and Human Rights in Global Sports Industry
The content delves into the legal aspects and strategic considerations within the globalized sports industry with a focus on monopolization, abuse of dominant position, and human rights constraints on sporting entities. It discusses the implications of attaining monopoly power, abuse by National Gov
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Profit: The Entrepreneur's Reward
Profit is the reward for entrepreneurial functions and differs from returns on other factors due to its uncertain and residual nature. Various theories such as Frictional, Monopoly, Compensatory, and Innovation shed light on the complexities of profit generation in business.
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Revenue Concepts in Different Market Conditions
Explore revenue concepts like Total Revenue (TR), Marginal Revenue (MR), and Average Revenue (AR) along with elasticity of demand in various market structures such as perfect competition, monopoly, monopolistic competition, and oligopoly. Learn about short and long-run equilibrium conditions and the
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Monopoly Power and Regulation in Economics
Degree of Monopoly Power is measured by the difference between marginal cost and price, with a greater difference signifying larger monopoly power. Prof. Abba P. Lerner's formula for monopoly power emphasizes the gap between price and marginal cost. Monopoly power can also be assessed using price el
0 views • 4 slides
Top WHO-GMP-ISO Certified Monopoly Pharma Franchise Company
Top WHO-GMP-ISO Certified Monopoly Pharma Franchise Company in India. Contact Unibiotech Formulations At 917814301804, 919216901651
1 views • 5 slides
Understanding Monopolistic Competition in Market Structures
Monopolistic competition lies between perfect competition and monopoly, where many sellers offer similar but non-identical products. This type of market allows for new firms to enter freely in the long run, enabling product differentiation and individual pricing strategies. Learn about the main feat
0 views • 37 slides
Understanding Oligopoly in Microeconomics
Introduction to oligopoly, a market structure between perfect competition and pure monopoly. In oligopoly, only a few sellers offer similar or identical products, leading to a balance between cooperation and self-interest. Characteristics of an oligopoly market include interdependence among firms an
0 views • 46 slides
Understanding Markets with Market Power
Explore the dynamics of markets characterized by market power through a detailed analysis of topics such as monopoly profit maximization, welfare analysis, price discrimination, and competitive firm entry effects. Delve into concepts like payoff matrices, the prisoner's dilemma, and industry concent
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Monopoly in Microeconomics
A comprehensive discussion on the concept of monopoly, its sources of power, short-run and long-run equilibrium of a monopoly firm, price discrimination, and the social cost of monopoly. It also covers practical aspects like measuring monopoly power and the social implications of monopoly behavior s
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding the Cournot Duopoly Model in Advanced Microeconomics
The Cournot Duopoly Model, named after Augustin Cournot, is an economic model where competing firms independently choose quantities to produce simultaneously. It strikes a balance between monopoly and competition, resulting in stable Nash Equilibrium. While advantageous, it has limitations due to un
8 views • 5 slides
Understanding Oligopoly Market Structure
This content delves into oligopoly, a market structure characterized by high concentration ratios and strategic interactions among a few sellers. It explores market concentration ratios in various U.S. industries, strategic behavior in oligopoly, and the challenges of collusion. Through examples lik
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Monopolistic Competition and Price Discrimination
Explore the market structures between perfect competition and monopoly, focusing on monopolistic competition. Learn how firms in monopolistic competition set prices and quantities, and examine their ability to earn economic profit. Understand the effects on society's welfare and the implications of
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Patentable Inventions: Requirements and Anticipation
Patentable inventions must be new, useful, and inventive. Anticipation plays a crucial role in determining patent validity, requiring clear claims and not covering old or useless ideas. The Canadian legal perspective on anticipation and old patent definitions provide insights into establishing the n
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding Antitrust Laws: Market Definition and Power Analysis
The economic purpose of antitrust laws is to ensure overall economic efficiency by focusing on whether a practice benefits or harms consumers. Antitrust cases involve defining relevant markets and assessing market power, distinguishing between market power and monopoly power. Understanding these con
0 views • 20 slides
Factors Leading to Singapore's Selection as a Trading Settlement by the British
The British chose Singapore as a trading settlement due to the need to break the Dutch monopoly, Singapore's strategic location, and its natural harbor. By establishing Singapore, the British could bypass Dutch interference and have a friendly port to support their trade routes. This essay explains
0 views • 29 slides
America Between the World Wars: Innovations and Impacts
Explore the era between World War I and World War II, discovering the origins of various innovations like radar, nylon, Monopoly, and more. Delve into the economic, social, and political effects of World War I, the Russian Revolution, and the Influenza Pandemic, along with Woodrow Wilson's decisions
0 views • 45 slides
Antitrust and Price Discrimination: Robinson-Patman Act Overview
The Robinson-Patman Act, a significant antitrust statute, aims to prevent price discrimination that harms competition, particularly targeting sellers granting discriminatory prices. While some price discrimination can enhance efficiency, predatory discrimination poses a serious threat to competition
0 views • 30 slides
Worcestershire West Weekly Physical Activity Programme
The Worcestershire West Weekly Physical Activity Programme offers a variety of fun fitness activities for school children, including games like Snakes & Ladders, Fit Dice, Monopoly Fitness, Bingo, UNO, and more. The schedule includes exercises such as sit-ups, lunges, star jumps, jumping jacks, and
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Section 2 of the Sherman Act
Section 2 of the Sherman Act addresses unilateral conduct related to monopolization and anti-competitive behavior. It focuses on the possession or acquisition of monopoly power, predatory conduct, and the intent to monopolize. The key principle under US law governing single firm conduct is the proof
0 views • 16 slides
Action for Economic Reforms in Rice Sector and Bus Transport
Madeiline Joy Aloria implemented actions for economic reforms in the rice sector and bus transport in November 2014. The main issues identified were the trade monopoly of the National Food Authority in the rice sector and traffic congestion in bus transport due to cut-throat competition. Activities
0 views • 9 slides
Challenges and Solutions in Consumer Protection within Monopoly Environments
Consumer protection in the context of monopoly environments presents unique challenges and requires specific actions. Professor Stephen Littlechild highlights the importance of competition as the most effective means of protecting consumers. In situations where there is a single supplier, such as in
0 views • 9 slides
Mathematical Discoveries at PMEG 2023
Explore the world of math through workshops, activities, and project presentations at PMEG 2023. Dive into Euclidean Geometry, straight lines, Monopoly, Fibonacci, Cartesian Planes, linear equations, and binary code with our dynamic teams. Unveil the possibilities of mathematical exploration!
0 views • 5 slides
The South Sea Bubble: A Historical Overview
The South Sea Bubble was a significant financial crisis in early 18th-century England, involving the South Sea Company and key individuals like Robert Harley, Eustace Budgell, Charles Spencer, Sir Robert Walpole, and King George I. The company was founded to trade slaves with Spanish America but eve
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Monopolies in Economics
Monopolies are considered inefficient because they can earn long-term profits. In a monopoly equilibrium, the relationship between price, marginal revenue, and marginal cost differs. Natural monopolies can supply goods at lower costs. Compared to perfectly competitive firms, monopolies charge higher
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Public Goods and Market Imperfections
Public goods are non-rival and non-excludable in consumption, posing challenges for free market provision due to free-riding. Market imperfections like monopoly and externalities deviate from perfect competition assumptions, impacting economic efficiency. Government intervention can address public g
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Market Structure and Power in Economics
Market structure defines the environment in which firms operate, based on factors like the number and type of buyers and sellers, products offered, barriers to entry, and information symmetry. Market power, on the other hand, refers to a firm's ability to control output and pricing. The relationship
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Market: Meaning and Classification
Market signifies a space where buyers and sellers interact to exchange goods for money. In economics, it refers to the entire region where such transactions occur. Markets can be classified based on geographical location, period of existence, and the number of buyers and sellers. Various market type
0 views • 8 slides
Exploring Virtual Environments in Computing: An Overview
Virtual environments in computing encompass a range of technologies, from virtual memory to virtual machines and virtual execution environments. These environments allow software to run in a different setting than originally designed, minimizing complexities. Key components include virtual memory, m
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding Market Structures and Business Ownership
Explore the characteristics of different market structures like pure competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Learn about types of business ownership such as sole proprietorships, partnerships, and corporations. Discover the regulations affecting businesses and the economic ri
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Price Discrimination in Monopoly Markets
Price discrimination under monopoly occurs when businesses charge different prices to different consumer groups for the same product or service. Conditions for price discrimination include monopoly power, market segmentation, ability to separate consumer groups, and prevention of resale. Examples of
0 views • 12 slides
Education Meeting Highlights and Updates - February 2015
Highlights from the BCIC meeting in February 2015 include discussions on assessment decisions, important updates, and news on various educational initiatives such as Capitol News on ending the public school monopoly. The meeting also covered plans for Higher Education Panel Presentation and Regional
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding the State and Law: Key Concepts and Perspectives
The discussion delves into the essence of the state and law, exploring various theoretical approaches such as social, Marxist, and political-legal perspectives. It defines the state as the main institution of the political system integrating social classes, powers, and politics, with persistent feat
1 views • 30 slides