Knowledge and Curriculum
Various forms of curriculum, the importance of curriculum, new trends in education, and the relationship between power and ideology in curriculum development. Understand the role of the state in curriculum development and the impact of meritocracy on the curriculum.
2 views • 16 slides
Angela Carter and Her Influential Works: A Contextual Analysis
Angela Carter, an English novelist known for her feminist and magical realism works, was influenced by her personal experiences and feminist ideologies. Her notable works include "The Bloody Chamber" and "The Sadeian Woman and the Ideology of Pornography". Carter's unique perspective on women's role
1 views • 26 slides
The Significance of Media in Language Learning
Media plays a crucial role in language learning by raising awareness of the ideology behind linguistic structures and providing valuable information on society and culture. Linguists are drawn to media language for research purposes and to understand its impact on language use and attitudes. Media s
12 views • 5 slides
Approaches to the study of Human Rights
The Marxist perspective on human rights emphasizes social rights over individual rights, viewing the full realization of self within society. Marx connects bourgeois society with human rights, highlighting how exploitation under capitalism alienates individuals. In contrast, the Third World perspect
5 views • 19 slides
A.R. Desai: Contributions to Indian Nationalism and Sociology
A.R. Desai, a prominent figure in the field of sociology, made significant contributions to Indian nationalism and the study of society in India. His works focused on topics such as the social background of Indian nationalism, peasant movements, path of development, and Marxist democratic rights. De
5 views • 14 slides
The Development Pattern and Rationale Behind Economic Nationalism in India
Three core elements - economic planning, autarchy, and building socialism - define India's development pattern focused on self-sufficiency and state ownership of industries. The rationale behind this approach is debated between economic theory influences and Marxist perspectives, reflecting a commit
6 views • 14 slides
Mahatma Gandhi and His Ideology in Indian History
Mahatma Gandhi, a pivotal figure in India's freedom struggle, advocated for non-violence, truth, and self-realization. He reshaped the Indian National Congress and empowered the masses to fight against injustice through civil disobedience. Gandhi's ideologies of swadeshi, local democracy, and truste
0 views • 28 slides
Objectives and Aims of Teaching Pakistan Studies in Education
Understanding the objectives and aims of teaching Pakistan Studies is essential for educators. Objectives serve as guiding points in the teaching-learning process, providing a framework for evaluation and development. On the other hand, aims are broader and philosophical, focusing on the purpose and
0 views • 48 slides
Understanding Religious Conflict: Definition and Types Explored
Religious conflict is a complex and recurring concept throughout history. Scholars have defined it as disagreements between religious groups. This conflict arises from contentious issues touching on ideology, morality, power, and identity, influenced by various socio-political, economic, and cultura
1 views • 13 slides
European Imperialism in the Late 19th Century
European nations in the late 1800s pursued imperialism to expand their empires for economic, political, and social reasons. Motives included economic interests, political and military ambitions, and the ideology of Social Darwinism. The Industrial Revolution fueled the need for resources and markets
1 views • 14 slides
Terrorism: A Global Threat in International Politics
The rise of terrorism as a global menace is a significant factor in contemporary international politics. Fueled by advancements in technology and ideology, terrorism poses a formidable challenge, exemplified by events like the 9/11 attacks. Efforts are needed to combat terrorism on both national and
0 views • 24 slides
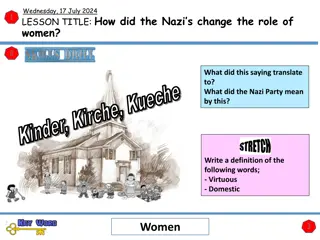
Women's Role in Nazi Germany: Impact and Ideology
Explore how the Nazis shaped the role of women through policies and propaganda, emphasizing domesticity and motherhood. Analyze key figures like Joseph Goebbels and Hitler's perspectives on women's place in society. Understand the contrast between women's lives in Weimar and Nazi Germany.
0 views • 18 slides
Insights into Manik Bandopadhyay’s Works and Ideologies
Manik Bandopadhyay, an eminent Indian writer, delved into the complexities of human psyche and societal issues in his novels and short stories. Influenced by Marxist philosophy and Freudian principles, he portrayed ordinary individuals enduring extraordinary circumstances during the colonial era. Hi
4 views • 11 slides
Understanding Class Struggle in Animal Farm through Marxist Ideology
Animal Farm, written by George Orwell, explores the concept of class struggle through the lens of Marxist ideology. The novel depicts the conflict between the bourgeoisie, represented by characters like Mr. Jones, and the proletariat, symbolized by the other animals on the farm. Through the story of
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Literary Criticism: A Comprehensive Overview
Literary criticism involves the study, evaluation, and interpretation of literature, focusing on themes, styles, settings, and historical contexts. This discipline explores the meanings, workings, and values of literary works through interpretation, analysis, and evaluation. Various types of literar
2 views • 20 slides
Understanding Liberalism: Key Ideas and Historical Context
Liberalism, a prominent political ideology, emerged in the 19th century and is closely linked to capitalism. It stands against absolutism and feudal privileges, advocating for individualism, freedom, reason, equality, toleration, consent, and constitutionalism. The evolution of liberalism emphasized
1 views • 18 slides
Critical Perspectives on Postcolonialism and Structuralism in Spivak's Work
Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak is known for her critical engagement with postcolonial theory and deconstruction, challenging traditional Western perspectives. By drawing on thinkers like Derrida and Foucault, Spivak offers a unique lens to interrogate power dynamics, hegemony, and resistance. Her work r
0 views • 31 slides
Examining State-Level and Dyadic Explanations for War in Global Politics
Understanding the reasons why certain states are more war-prone than others involves exploring factors such as economy, internal opposition, and political systems. Marxist explanations argue that capitalist economies are more prone to war due to issues like overproduction, wealth inequality, and imp
0 views • 17 slides
Social Work Ideology for the 21st Century: Educational Imperative
Social work education must adapt to current global challenges by reexamining ethical principles in light of perpetual warfare, fake news, and economic globalization. This paper discusses the relevance of social values in a changing world and proposes pedagogies for promoting a modern social work ide
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Ideology and Society: Perspectives and Beliefs
Explore the significance of ideology in shaping societal perspectives, beliefs, and values. Understand the impact of ideologies on laws, societal structures, and individual behavior. Delve into concepts such as liberalism, individualism, and collectivism to gain insights into human societies through
4 views • 26 slides
Perspectives on Youth Culture Through Functionalist and Neo-Marxist Views
Functionalist and Neo-Marxist perspectives on youth culture offer contrasting views on its purpose in society. Functionalist theorists emphasize the role of youth culture in providing a transitional phase for young people, aiding in their social integration and development of independence. On the ot
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Critical Theory in International Relations: A Deep Dive
Critical theory in IR since the mid-1980s challenges traditional views by emphasizing culture, ideology, and societal structures over objective truths. This approach questions the relationship between theory and practice, highlighting issues of inequality beyond just class, including race, ethnicity
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Popular Culture and Ideology
Popular culture encompasses the lived practices and artistic products of society, contrasting with high culture. Various definitions highlight its appeal to a wide audience and its distinction from high culture. The relationship between popular culture and ideology is explored through practices that
0 views • 15 slides
Exploring Critical Theory Through Literary Criticism and Analogy
Delve into the realm of critical theory through literary criticism, using the analogy of different perspectives on seeing an orange to understand the various facets of analysis like reader response, Marxist/social power, feminist/gender, and psychoanalytic criticism. Discover how critical theory hel
0 views • 9 slides
Analysis of Ideology in Thomas Pynchon's "The Crying of Lot 49
This analysis delves into the story and ideology in Thomas Pynchon's novel "The Crying of Lot 49". The plot follows Oedipa Maas as she investigates the mystery of Tristero, a secret postal service. Set in California during the 1960s, the novel reflects the societal context of America during the Cold
0 views • 15 slides
Labor Super-Exploitation and Value Transfer in Global Economy
Original research explores how labor super-exploitation and transformation drive international value transfer in the capitalist system. The study bridges orthodox Marxist and Ricardian perspectives, offering new insights into unequal exchange and imperialism.
1 views • 21 slides
Changing Trends in Cuban-American Voter Ideology
Explore the evolving political ideology of Cuban-American voters from 1991 to 2011 through data on migration, residency, naturalization, and political exceptionalism. Uncover how these trends have influenced Miami's Latino demographics and the Cuban perspective on US/Cuba relations.
0 views • 24 slides
An Unequal Contest: Geertz vs. Roseberry on the Balinese Cockfight
This analysis compares Geertz's famous essay on the Balinese cockfight with Roseberry's critique, arguing that Roseberry's focus on economic factors, inequality, conflict, and dynamic social processes provides a more comprehensive analysis compared to Geertz's entertaining yet partial interpretation
0 views • 20 slides
Understanding Marxist Theory: Key Concepts and Implications
The Marxist theory, rooted in Karl Marx's philosophy, emphasizes the control of means of production as a determinant of societal power dynamics. This ideology examines economic power, materialism versus spirituality, class conflict, and the role of art, literature, and ideologies in shaping culture
0 views • 17 slides
Marxist Perspectives on Crime and Law Enforcement
Traditional Marxism views crime as a product of poverty and capitalism, emphasizing the manipulation of values by the powerful to maintain control. Marxism challenges the idea that law reflects the will of the people, arguing that it serves the interests of the ruling class by passing and enforcing
0 views • 19 slides
Economic Nationalism and Development Pattern in India
Economic nationalism in India was characterized by the elements of economic planning, autarchy, and socialism. The development pattern focused on capital goods industries, inward orientation, and state ownership. Two interpretations of this pattern were influenced by economic theory and Marxist pers
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Classical Marxism: Key Concepts and Critiques
Marxism, rooted in the ideas of Karl Marx, emphasizes the significance of economic relations in shaping social and political structures. Classical Marxism focuses on economism, determinism, materialism, and structuralism, viewing history through a lens of class struggle and offering an emancipatory
0 views • 21 slides
Exploring Critical Theory Strategies in Literary Analysis
Delve into the diverse approaches of Critical Theory to interpret and analyze literary works with new lenses. From Formalist and Biographical Criticism to Historical and Marxist perspectives, uncover hidden layers and meanings in texts through multiple viewpoints. Explore the role of psychoanalytic
0 views • 24 slides
Explaining Crime: Sociological Perspectives and Methods
Sociologists explain crime through various theories such as Marxist, New Right, and subcultural explanations, as well as through the lens of labeling theory. They explore factors like social order, control, formal and informal rules, and the impact of societal structures on criminal behavior. Method
0 views • 10 slides
Comprehensive Education Revision Overview for Exam Preparation
Delve into a detailed overview of education topics including exam structures, theories, relationships, gender, ethnicity, and social policy. Explore sample questions for both 10-mark and 30-mark scenarios, with guidance on applying material and evaluating perspectives. Additionally, familiarize your
0 views • 24 slides
The Frankfurt School and Cultural Critique
The Frankfurt School, a group of critical theorists, challenged traditional Marxist views on culture and ideology. They examined how mass media and consumer culture influenced society, highlighting the role of ideas in reflecting economic positions. Despite capitalism's stability, they explored the
0 views • 25 slides
Reimagining Theoretical Boundaries: Spivak's Critical Perspectives
Gayatri Chakravorty Spivak challenges traditional categories by constantly revising her critical theories in response to societal changes. She explores the silencing of subaltern women, drawing on post-structuralist and Marxist ideas to question Western imperialism. Spivak's work reflects a dynamic
0 views • 26 slides
The Rise of Cultural History II: History and Anthropology Historiography
This content explores the concepts of cultural history, Marxist thought, cultural hegemony, and the works of Antonio Gramsci. It delves into the history of anthropology, discussing key figures such as Franz Boas and Malinowski, and highlights the intersection of anthropology and history in understan
0 views • 9 slides
Approaches to Study of Indian Politics: Liberal, Marxist, and Gandhian Perspectives
Political Science encompasses various approaches such as Liberal, Marxist, and Gandhian for studying Indian politics. Scholars have explored the nature of the Indian state post-independence, focusing on democratization, social heterogeneity, and class dynamics. The Marxist approach views the state a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding the State and Law: Key Concepts and Perspectives
The discussion delves into the essence of the state and law, exploring various theoretical approaches such as social, Marxist, and political-legal perspectives. It defines the state as the main institution of the political system integrating social classes, powers, and politics, with persistent feat
1 views • 30 slides