Address Prediction and Recovery in EECS 470 Lecture Winter 2024
Explore the concepts of address prediction, recovery, and interrupt recovery in EECS 470 lecture featuring slides developed by prominent professors. Topics include branch predictors, limitations of Tomasulo's Algorithm, various prediction schemes, branch history tables, and more. Dive into bimodal,
0 views • 42 slides
Understanding Flag Registers in Microprocessor 8086
This content discusses the flag registers in the Microprocessor 8086, covering conditional flags such as Carry Flag (CF), Auxiliary Flag (AF), Parity Flag (PF), Zero Flag (ZF), Sign Flag (SF), and Overflow Flag (OF), as well as control flags including Trap Flag (TP), Interrupt Flag (IF), and Directi
1 views • 23 slides
Understanding System Management Mode (SMM) in x86 Processors
System Management Mode (SMM) is a highly privileged mode in x86 processors that provides an isolated environment for critical system operations like power management and hardware control. When the processor enters SMM, it suspends all other tasks and runs proprietary OEM code. Protecting SMM is cruc
1 views • 26 slides
Understanding Processor Interrupts and Exception Handling in Zynq Systems
Learn about interrupts, exceptions, and their handling in Zynq Systems. Explore concepts like interrupt sources, Cortex-A9 processor interrupts, interrupt terminology, and the difference between pooling and hardware interrupts. Gain insights into interrupt service routines, interrupt pins, interrupt
0 views • 60 slides
Exploring Words: The Meaning of ".rupt.
Delve into the world of ".rupt." with this collection of words and their meanings. From financial terms like "bankrupt" to sudden changes described as "abrupt," this list covers various aspects of breaking, disrupting, and changing. Explore how interruptions, disruptions, and dishonesty are captured
0 views • 22 slides
Exploring Words Related to Breaking and Disruption
Delve into a collection of words centered around the concept of breaking, from financial ruin to unexpected interruptions and dishonest actions. Explore terms like bankrupt, abrupt, interrupt, disrupt, and more, each capturing a facet of disruption and breaking away from norms.
0 views • 22 slides
Explore Syria: Cities in Conflict
Delve into the realities of Syria through descriptions of its cities at war, where bombings interrupt daily life and affect the economy. The impact of the conflict is evident in the shifting population and heightened security measures. Discover how the war has shaped the landscapes and livelihoods o
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Interrupts in Computer Systems
Interrupts in computer systems play a crucial role in handling various events and managing the flow of instructions. This content discusses the types of interrupts, causes, handling procedures, and the role of supervisory modes in modern computers. It covers topics such as internal and external inte
0 views • 29 slides
Understanding Descriptor Tables and Registers in Computer Systems
Descriptor tables in computer systems group segment descriptors together for efficient memory management. They consist of Global Descriptor Table (GDT), Local Descriptor Table (LDT), and Interrupt Descriptor Table (IDT). The Global Descriptor Table (GDT) is a crucial table that is shared by all prog
0 views • 18 slides
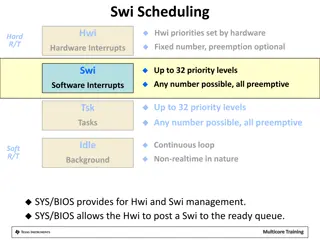
Real-Time Interrupt Handling and Scheduling in SYS/BIOS
This content covers the management of hardware and software interrupts, interrupt priorities, scheduling rules, and execution flow for real-time systems using SYS/BIOS. It discusses the handling of interrupts by the Hardware Interrupt (Hwi) and Software Interrupt (Swi) components, priority levels, p
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Interrupt Processing in Operating Systems
An interrupt in an operating system disrupts the normal sequence of instructions executed by the processor. When an interrupt occurs, the OS takes control, saves the state of the interrupted process, analyzes the interrupt, and passes control to the appropriate routine. There are six classes of inte
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding MIPS I/O and Interrupt Handling
Delve into the world of MIPS architecture, exploring how I/O operations and interrupts are managed. Learn about memory organization, system functions, I/O registers, and kernel data. Discover how SPIM facilitates input and output handling, including reading from the keyboard and managing output. Div
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Computer Organization: Instruction Set Architecture and Interrupts
Explore the critical concepts of Computer Organization focusing on Instruction Set Architecture (ISA) and Interrupts. ISA serves as the interface between hardware and software, enabling programmers to write machine language programs effectively. Learn about Application Binary Interface (ABI), interr
0 views • 26 slides
Understanding I/O Systems and Devices
I/O systems and devices play a crucial role in computer operations. They can be categorized into block devices and character devices based on their functionalities. Block devices store information in fixed-size blocks with addresses, while character devices handle character streams. Some devices, li
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Interrupts in PIC16F Microcontrollers
Explore the key sources of interrupts in PIC16F627A/628A/648A, accessing registers, enabling interrupts, and managing local interrupts such as Timer 0 alarms and B0 pin changes. Learn how to set interrupts on desired events and understand the corresponding flag bits for interrupt occurrence.
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Interrupts and Timers in Microcontrollers
Microprocessors function as finite state machines, with instructions loaded from memory and executed in sequence. However, interrupts allow for urgent out-of-turn servicing of signals, providing a way to handle asynchronous events. Learn how to utilize interrupts efficiently with examples on Arduino
0 views • 9 slides
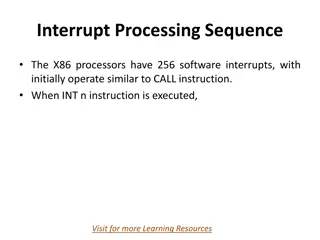
Understanding Interrupt Processing Sequence in X86 Processors
X86 processors have 256 software interrupts, functioning similarly to a CALL instruction. When an INT n instruction is executed, the processor follows a sequence involving pushing the flag register, clearing flags, finding the correct ISR address, and transferring CPU control. Special interrupts lik
0 views • 10 slides
Embedded Systems Lab 10: Timer and Interrupt
This lab focuses on learning about timers and interrupts in embedded systems using MQX at National Tsing Hua University. It covers creating timer components, starting timers, and provides examples on simulating the control of an LED using timers. The content includes code snippets and explanations r
0 views • 15 slides
ARM Cortex-M Interrupt and Exception Programming Overview
Explore the fundamentals of interrupts and exceptions programming in ARM Cortex-M microcontrollers. Topics include interrupt handling mechanisms, interrupt vector table, interrupt priorities, control registers, and transitioning from reset to boot programs. Gain insights into the privileged executio
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Interrupts in 8051 Microcontroller
Interrupts in 8051 microcontrollers allow the system to respond to asynchronous events while multitasking on a single CPU, giving the illusion of handling many things simultaneously. They introduce the concept of priority, enabling preference over simultaneous interrupts. The interrupt vectors deter
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs) in PLC Programming
Interrupt Service Routines (ISRs) are crucial in handling interrupting events in programmable logic controller (PLC) systems that require immediate attention. They can be triggered by events, timers, and register matches, executing outside the normal ladder scan. ISRs have priority order for handlin
0 views • 5 slides
Understanding Fundamental Concepts of Interrupts in Embedded Systems
Explore the fundamental concepts of interrupts in embedded systems, including interrupt handling, maskability, priority, service routines, and interrupt vectors. Learn how interrupts allow the CPU to handle special events efficiently, coordinate I/O activities, and prevent CPU tie-up, enhancing syst
0 views • 57 slides
Understanding Microcontroller Interrupts and Applications
Explore the fundamental concepts of interrupts, PWM, timer/counters, and ADC in microcontrollers. Learn how to use interrupts for tasks like LED blinking, control LED brightness with PWM, and read voltage using ADC. Get insights on interrupt routines, enabling interrupts through registers, and tips
0 views • 32 slides
Understanding Interrupt Handling with LPC2148 in Electronics & Telecommunication
Introduction to interrupt handling with LPC2148 focusing on ARM processors, IRQ, FIQ, associated registers, interrupt enabling, types of interrupts (FIQ, Vectored IRQ, Non-Vectored IRQ), and differences between Vectored and Non-Vectored interrupts in the context of LPC2148. Discusses interrupt sourc
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Interrupt Handling in MSP430 Embedded Systems
This lab explores the intricacies of handling interrupts in MSP430, covering types of interrupts, enabling interrupts, and the execution flow when an interrupt is requested and serviced. Topics include interrupt service routines, clearing interrupt flags, and enabling/disabling maskable interrupts.
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Interrupts and MicroBlaze in Advanced Embedded Systems
Dive into the world of interrupts in embedded systems with a focus on MicroBlaze architecture. Learn how interrupts enable multitasking, the process of handling interrupts, and generating interrupts in MicroBlaze. Explore custom IP integration and gain insights into interrupt-driven programming. Dis
0 views • 32 slides
Project 2: Preemption in CS 4411 - Spring 2017
Project 2 focuses on addressing issues of selfish threads, starvation, and interruption handling within multi-level feedback queue scheduling. The project introduces clock interrupts, alarms, interrupt handlers, and addresses the importance of performance optimization for handling shared data struct
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Computer Architecture Interrupts and Exceptions
Computer architecture interrupts and exceptions are essential for handling external events and unexpected conditions during program execution. Interrupts are caused by external events such as I/O requests, timers, or hardware failures, while exceptions occur due to specific instruction executions. W
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Interrupts in Embedded Systems using MicroBlaze
Dive into the world of interrupts in embedded systems with a focus on using the MicroBlaze soft core processor and custom IP to handle interrupts efficiently. Learn about the significance of interrupt service routines, interrupt handling process, and how to generate interrupts in MicroBlaze for seam
0 views • 30 slides
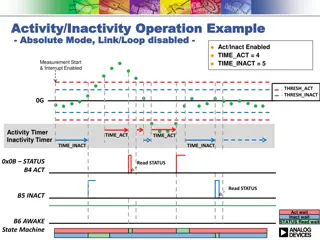
Activity/Inactivity Operation Example in Various Modes
Explore different modes of activity and inactivity operations with examples and configurations. Learn about absolute mode, referenced mode, enabled and disabled states, time settings, timers, measurement starting, interrupt enabling, and status monitoring in a comprehensive guide. Gain insights into
0 views • 7 slides
MSP430 and MSP432 MCU Porting Guide: Code Compatibility and DriverLib Usage
Learn how to port code between MSP430 and MSP432 microcontrollers, ensuring register access compatibility using DriverLib, and adapting interrupt handling. Explore recommendations for developing new code, utilizing system features, and handling data types. Discover portability considerations for var
0 views • 10 slides
8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous Operation
The 8-bit Timer/Counter2 with PWM and Asynchronous Operation features single compare unit, glitch-free operation, phase-correct PWM, frequency generator, clock prescaler, interrupt sources, and external clocking options. It includes registers for control, counter, output compare, asynchronous status
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding X86 ISA Flags in System Security
This article delves into the details of various flags in the X86 ISA architecture, such as CF (Carry Flag), PF (Parity Flag), AF (Auxiliary Flag), ZF (Zero Flag), SF (Sign Flag), TF (Trace Flag), IF (Interrupt Flag), DF (Direction Flag), OF (Overflow Flag), and IOPL (Input Output Privilege Level). T
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Exceptional Control Flow in Computer Systems
Control flow mechanisms in computer systems have evolved to handle exceptional events triggered by external system states. This includes exceptions, interrupts, and context switches that enable the CPU to respond to events like data arrival, user inputs, and system timeouts. Exception handling invol
0 views • 66 slides
Vocabulary Week 6: Root "RUPT" Meaning Break or Burst
Explore words like disruption, abrupt, bankrupt, promote, interrupt, corrupt, initiate, erupt, rupture, and disrupt that are derived from the root "RUPT," meaning to break or burst. Understand their meanings through example sentences and images, enhancing your vocabulary with academic words for ever
0 views • 15 slides
Overview of Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller's Computer Systems & Telematics
This content discusses various aspects of computer systems and telematics as taught by Prof. Dr.-Ing. Jochen Schiller at Freie Universität Berlin, Germany. It covers topics such as operating systems, computer networks, network security, and examples illustrating key concepts. The content explains p
0 views • 31 slides
Real-Time Analysis and Architectures for Automotive Systems
Delve into the realm of real-time analysis and architectures for automotive systems through a comprehensive exploration of scheduling models, schedulability conditions, critical instances, utilization analysis, response time analysis, practical factors, and more. Understand how context switches and
0 views • 40 slides
Overview of 8085 Microprocessor Architecture
Intel 8085 microprocessor, introduced in 1977 as an 8-bit MP with 40-pin dual-in-line chip, operates on a single +5V supply at a clock speed of about 3MHz. It features 16-bit address bus capable of addressing up to 64KB memory, N-MOS technology, multiplexed data and address buses, interrupt support,
0 views • 52 slides