Fire extinguisher ball
SpecialityGeochem introduces a revolutionary solution for fire safety with its Fire Extinguisher Ball, a compact yet powerful device designed to combat sudden fires effectively. Engineered with cutting-edge technology, this ball offers an innovative approach to fire suppression, making it an indispe
6 views • 2 slides
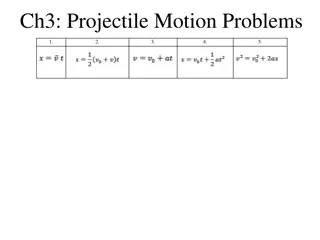
Understanding Projectile Motion: Characteristics, Examples, and Formulas
Projectile motion involves the motion of objects under the influence of gravity, with both vertical and horizontal components. This type of motion is seen in activities such as throwing a ball, kicking a football, or dropping objects. The motion is described by specific formulas, including calculati
1 views • 19 slides
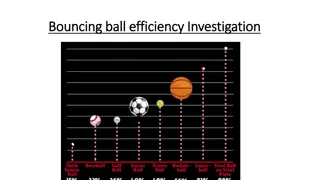
Efficiency Investigation Through Bouncing Ball Experiment
Explore the efficiency of different types of balls by conducting a bouncing ball experiment. Measure bounce heights, calculate efficiency percentages, create a bar graph, and draw conclusions based on the results obtained. Understand the energy transformations involved in the bouncing process and co
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Inertia
Newton's first law of inertia states that objects remain at rest or in uniform motion unless acted upon by an external force. This law, also known as the law of inertia, explains how objects tend to maintain their current state of motion unless influenced by an external force. Objects at rest stay a
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Frames of Reference and Relative Motion
Motion is defined as a change in position over time. To describe motion accurately, one needs to understand frames of reference and relative motion. Frames of reference are systems of objects used to determine if something is in motion, while relative motion involves movement in relation to a refere
3 views • 14 slides
Understanding Motion: Concepts and Definitions in Physics
Motion in physics is defined as the change in position of an object over time. It involves concepts like rest, motion, distance, displacement, rate of motion, and types of motion. Rest and motion are relative to a reference point, while distance and displacement differ in their scalar and vector nat
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Ball Pythons: Fascinating Facts and Behaviors
Ball pythons, known for their heat pits and night vision, have fascinating adaptations for hunting and survival in the wild. They use camouflage to hide from predators, roll into a ball when scared, and have unique eye placement for 360-degree vision. These snakes thrive in savannah and thorn scrub
2 views • 8 slides
Understanding Linear and Rotational Motion in Physics
Explore the concepts of linear momentum, center of mass, rotational motion, and angular displacement in physics. Learn how to determine the center of mass of objects, analyze motion of particle groups, and understand the conservation of momentum in systems under external forces. Delve into the funda
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Circular Motion in Physics
Circular motion involves objects moving in a circular path at a constant speed, experiencing acceleration and centripetal force. This motion is characterized by angular speed, centripetal acceleration, and the necessary centripetal force. The concept of uniform circular motion and angular displaceme
3 views • 38 slides
2021 University of La Verne College of Law Barrister's Ball Awards Ceremony
Explore the highlights of the 2021 University of La Verne College of Law Barrister's Ball Awards Ceremony, honoring outstanding professors and adjunct professors for their dedication to students. Professor Michele Assael-Shafia and Professor Dean McVay received the Professor of the Year and Adjunct
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Newton's First Law of Motion
Exploring the foundational concepts of motion and forces, this content delves into Isaac Newton's First Law of Motion. Describing how objects behave when the net force acting on them is zero, the law highlights the significance of inertia and balanced forces in determining an object's state of rest
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Forces in Motion: A Comprehensive Overview
Forces play a crucial role in our daily activities, influencing motion and direction. This chapter delves into the concept of forces as pushes or pulls, exploring balanced and unbalanced forces and their impact on velocity. By examining real-life scenarios like kicking a soccer ball or opening a doo
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's laws of motion, including the principles of inertia and dynamics, explain how objects move and interact with forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while the second law explains how a net force is required to change an object's vel
0 views • 21 slides
Investigation of Falling Ball Motion Using Electronic Balance
This study explores the motion phases of a falling ball by analyzing the readings of an electronic balance connected to a PC. The experiment involves a light frame releasing a ball into water in a beaker placed on the balance, with results indicating different motion states. Through detailed phases
2 views • 22 slides
Study on the Relationship Between Release Distance and Bounce Distance of Golf Ball
Experiment investigating how the release distance affects the bounce distance of a golf ball from bounce one to bounce two. The hypothesis suggests that a greater release distance will result in the ball traveling farther. Controlled variables include the angle of the ramp, ball, height, and surface
0 views • 13 slides
Experiment on Golf Ball Bounce Distances
This experiment explores how the release distance affects the bounce distance of a golf ball, showing that a higher release distance leads to a greater distance between bounces. By conducting controlled drops and measurements, the hypothesis regarding the impact of momentum on the ball's travel dist
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Fear of Falling: Causes, Consequences, and Assessment
Fear of falling is a prevalent concern among older adults and individuals with certain health conditions. It can lead to negative outcomes such as increased risk of falls, activity avoidance, and decreased mental well-being. Factors contributing to fear of falling include perceived threat to balance
1 views • 39 slides
Understanding Vertical Motion and Gravity in Kinematics
Explore the principles of vertical motion and gravity in kinematics through scenarios involving throwing objects, free-fall motion, and calculating heights. Learn how to model vertical motion with acceleration due to gravity, find maximum heights of thrown objects, solve extended problems, and under
2 views • 12 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Explore the fundamental concepts of Newton's Laws of Motion, including net forces, combining forces, balanced versus unbalanced forces, and the concept of inertia. Learn how these principles explain the behavior of objects in motion and at rest, and discover the impact of mass on an object's resista
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Simultaneous Fouls in Sports Officiating
Explore the concept of simultaneous fouls in sports officiating, including their definition, rule application, and impacts on gameplay. Learn how to determine when fouls occur, differentiate live ball and dead ball fouls, and identify the first offender in simultaneous live ball fouls. Gain insights
1 views • 30 slides
Football Fundamentals Explained: Possession, Downs, Dead Ball, Kicks
Understanding the key concepts of football fundamentals including possession, downs, dead ball, and kicks. Learn about live ball possession, changes in possession, downs determination, defensive fouls, dead ball situations, and handling kicks during gameplay.
0 views • 15 slides
Baseball Umpire Training Presentation Highlights 2013
This presentation covers various aspects of baseball umpiring rules and scenarios, focusing on dead ball situations. Created by John Hickey, the slides detail instances where the ball becomes dead immediately, such as when a pitch touches a batter's clothes, or when the batter swings and misses as t
0 views • 60 slides
Understanding Joint Motion: Osteokinematic and Arthrokinematic Movements
Joint motion involves osteokinematic movements, which are under voluntary control and include flexion, extension, and more. End-feel sensations like bony, capsular, and springy block indicate different joint conditions. Arthrokinematic motion refers to how joint surfaces move during osteokinematic m
0 views • 17 slides
Comparison of New and Old Cave Configurations in Neutron Ball Testing
This content discusses the comparison between the new and old cave configurations in the Neutron Ball testing part II. It showcases images and descriptions of the different cave configurations, highlighting the progress in research at the Cyclotron Institute. The Neutron Ball's functionality and tes
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Rule 4: Ball In Play, Dead Ball, Out of Bounds
Exploring Rule 4 of the game rules, this article delves into Ball In Play, Dead Ball, and Out of Bounds situations, discussing key scenarios like legal snaps, live ball becoming dead, and the impact of inadvertent whistles. It covers rules regarding ball positioning, player actions, and referee sign
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion explain the relationship between forces and motion. The first law states that an object in motion stays in motion unless acted upon by a net force, while the second law describes how force is related to an object's mass and acceleration. The third law states that for every ac
0 views • 21 slides
Exploring Free Fall Motion of a Bouncing Ping-Pong Ball
Delve into the fascinating world of free fall motion by observing and analyzing the behavior of a bouncing ping-pong ball. The objective is to calculate free fall acceleration and showcase Newton's 2nd Law in action. Through engaging activities and theoretical discussions, students will gain insight
0 views • 25 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion: Inertia, Forces, and Acceleration
Delve into the fundamentals of Newton's first and second laws of motion, exploring concepts such as inertia, the relationship between forces and acceleration, and the procedure for solving force problems. Discover how objects behave when left to themselves, and grasp the significance of forces in ch
0 views • 21 slides
Animating a Wrecking Ball in PowerPoint for Dynamic Presentations
Explore the exciting process of animating a wrecking ball in PowerPoint to enhance your presentations. This engaging tutorial provides step-by-step instructions on creating impactful visual effects using stunning images of wrecking ball construction and stone wall construction. Learn how to bring yo
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Newton's Laws of Motion
Newton's Laws of Motion describe how objects behave in response to external forces. The first law states that objects in motion remain in motion unless acted upon by a force, while objects at rest stay at rest. The second law relates force, mass, and acceleration, showing how they are interconnected
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Corner Kicks in Soccer
A corner kick is a method of restarting play awarded to the attacking team when the ball exits the field over the goal line without a goal being scored. Direct goals are possible, and players can't be offside receiving the ball. The kick is taken from the corner arc, and opposing players must mainta
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Dynamic Systems in Simulink: A Cannon Ball Example
Explore the vertical motion of a cannon ball under gravity in Simulink, starting with basic equations and progressing to modeling air resistance. Learn how to analyze two-dimensional motion using vectors and avoid hidden errors related to vectors in your simulations.
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Explore the concepts of motion, distance, speed, and velocity as they relate to Newton's Laws of Motion. Learn about measuring motion, calculating speed, graphing motion on distance-time graphs, and understanding velocity. Discover how motion is constant and how relative motion is used. Practice cal
0 views • 36 slides
Understanding Motion and Newton's Laws
Motion is the constant change in position of objects, measured by distance and displacement. Speed is the rate of motion, while velocity includes direction. Graphing motion helps visualize speed changes over time. Newton's Laws explain the behavior of objects in motion.
0 views • 38 slides
Understanding Dependent and Relative Motion in Dynamics
Dependent Motion and Relative Motion are fundamental concepts in Dynamics, providing the foundation for future analysis. Dependent Motion involves constraints like ropes or cables, while Relative Motion considers observers in motion. Dynamics involves applying a limited set of equations in diverse w
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Motion: Types and Physics
Motion refers to a body changing position with respect to its surroundings. Different types of motion include linear, rotatory, and oscillatory motion. The physics relating to motion is called Mechanics, which comprises Dynamics and Kinematics. Scalars and vectors play a crucial role in describing t
0 views • 8 slides
Projectile Motion Practice Problems and Solutions
Explore a series of projectile motion problems and solutions involving scenarios such as a ball being kicked, a football being kicked by a place-kicker, an airplane dropping a care package, and a player throwing a ball horizontally. Learn to calculate speed, time in the air, maximum height, hang tim
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Motion Perception in Computational Vision
In computational vision, the concept of motion opponency plays a crucial role in how the brain processes left and right motion inputs. By examining psychophysical results and the construction of motion opponent energy filters, we explore how the brain handles motion information. Additionally, the Ve
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Motion in Physics: Definitions and Examples
An object is said to be in motion if it changes position with time, while rest implies no change. Learn about types of motion such as linear and circular, as well as vibratory motion and reference points. Explore how objects can be in motion relative to one reference point while at rest relative to
0 views • 4 slides
Evolution of Motion Theories: Aristotle to Einstein
Explore the progression of motion theories from Aristotle's belief in a force for motion to Galileo's discoveries on gravity, Newton's laws of motion, and Einstein's theories of relativity and quantum mechanics. Discover how our understanding of motion has evolved over the centuries, shaping the way
0 views • 20 slides