Understanding Floating Point Representation of Numbers
Floating point representation is crucial in computer arithmetic operations. It involves expressing real numbers as a mantissa and an exponent to preserve significant digits and increase the range of values stored. This normalized floating point mode allows for efficient storage and manipulation of r
0 views • 12 slides
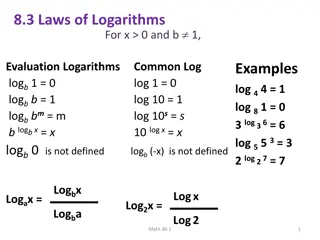
Understanding Laws of Logarithms: Exponents vs. Logarithms
Laws of Logarithms explain the properties and rules governing logarithmic functions, involving evaluations, conversions, additions, subtractions, and comparisons with exponent laws. Through examples, the laws of logarithms are applied to simplify expressions and evaluate logarithmic equations. The r
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding Polynomial Degrees and Special Names
The degree of a polynomial is determined by its highest exponent, with specific names for each degree level. From the basic constant to the nth degree polynomial, this guide showcases the different degrees and their characteristics, helping you grasp the concept of polynomial functions easily.
0 views • 18 slides
Understanding Python Operators: Arithmetic, Comparison, and Assignment
Python language supports various types of operators such as arithmetic operators for addition, subtraction, multiplication, division, modulus, exponent, and floor division. It also includes comparison operators to check equality, inequality, greater than, less than, greater than or equal to, and les
1 views • 11 slides
Understanding Algebraic Expressions and Exponents
Master the basics of algebraic expressions, simplification, and exponent rules in this lesson. Learn to interpret word problems into algebraic expressions, apply properties of real numbers, and solve algebraic problems step by step. Practice evaluating expressions, simplifying equations, and underst
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Floating Point Representation in Binary Systems
In computer systems, decimal numbers are represented in memory using scientific notation. This involves moving the decimal point and using mantissa and exponent to maintain precision and range. The transition to representing numbers in binary involves multiplying by 2 to the power instead of 10. Uti
2 views • 22 slides
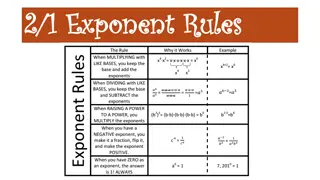
Exponent Rules and Practice for Math Class
Explore the concept of dividing powers with the same base and raising a quotient to a power in this math lesson. The materials include warm-up exercises, practice sheets, objectives, examples, and a new seating chart. Dive into the world of exponent rules with engaging visuals and clear explanations
0 views • 35 slides
Understanding Data Storage and Compression Techniques
Explore various concepts related to data storage and compression, including higher revision techniques, watch points for debugging, RAID disk mirroring, media compression methods, mantissa and exponent representation, and the impact of precision/range adjustments in numerical calculations. Learn abo
0 views • 13 slides
Turning Negative Exponents into Positive Exponents Explained
Learn how to convert negative exponents into positive exponents by identifying the placement of negatives in the numerator or denominator, and moving the exponent accordingly. Follow these simple steps to master this fundamental math concept easily.
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Exponents and Powers in Chapter 12
This chapter delves into the fundamental concepts of exponents and powers, including their properties and applications. Explore various slides covering topics such as basic operations with exponents, laws of exponents, scientific notation, and solving exponent equations.
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding the Process of Reversing Differentiation
Reversing the differentiation process involves finding the function knowing its derivative. By increasing the exponent by 1, dividing by the new exponent, and adding a constant term, the antiderivative of a function can be determined. The general form of an antiderivative involves adding a constant,
0 views • 13 slides
Understanding Floating Point Formats and Arithmetic in Digital Design
Today's lecture covers the concepts of floating-point formats and arithmetic in digital design, focusing on special cases, normalized and denormalized numbers, as well as IEEE 754 format representation. Through examples and explanations, learn how to convert decimal numbers to single-precision binar
0 views • 19 slides
Evaluation of Coordinated Spatial Reuse in Multi-AP Scenarios for IEEE 802.11-23/1972r1
Evaluation of Coordinated Spatial Reuse (SR) in a 4AP scenario for IEEE 802.11-23/1972r1 in November 2023. The study focuses on improving throughput in multiple BSS environments through coordinated SR. The simulation parameters include AWGN channel, pathloss exponent, noise figure, and other key fac
0 views • 15 slides
Understanding Floating-Point Numbers in C++: IEEE Standard 754
Floating-point numbers are approximate representations of real numbers used in programming. IEEE Standard 754 defines how floating-point data is stored, including single and double precision formats. Learn about the sign, mantissa, exponent, biases, precision, overflow, and underflow in floating-poi
0 views • 25 slides
Communication Steps for Parallel Query Processing: Insights from MPC Model
Revealing the intricacies of parallel query processing on big data, this content explores various computation models such as MapReduce, MUD, and MRC. It delves into the MPC model in detail, showcasing the tradeoffs between space exponent and computation rounds. The study uncovers lower bounds on spa
0 views • 25 slides
Solving Equations with Exponents and Radicals
Explore the concepts of radicals and nth roots in solving equations involving exponents and radicals. Understand how to find the domain and range of functions graphically. Practice changing between radical and exponent notation, evaluating nth roots of real numbers, and solving real-life problems us
0 views • 33 slides
Understanding Constants and Literals in C++ Programming
Constants and literals in C++ are fixed values that the program cannot alter. They come in various types such as integer numerals, floating-point numerals, characters, strings, and boolean values. Integer literals can be decimal, octal, or hexadecimal constants, while floating-point literals have in
0 views • 7 slides
Comments on Draft Risk Evaluation for Asbestos by Gabor Mezei, M.D., Ph.D.
Gabor Mezei, M.D., Ph.D., a Principal Scientist at Exponent, Inc., provides insightful comments on the Draft Risk Evaluation (DRE) for asbestos. He highlights the occurrence of mesothelioma in the absence of asbestos and challenges the assumption of increased risk in users of AABL. Mezei references
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Properties of Exponents in Algebra
Explore the properties of exponents in algebra to simplify expressions and work with scientific notation efficiently. Learn about the zero exponent property, negative exponent property, product property, power of a product property, power of a power property, quotient property, and how to use these
0 views • 66 slides