Approaches in Studying Human-Environment Relationship
Explore different approaches to understanding the dynamic relationship between humans and their environment, including deterministic, teleological, possibilistic, and economic deterministic perspectives. These approaches shed light on how human actions and interactions with the environment have evol
3 views • 9 slides
Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in Regular Language Theory
An exploration of Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in the context of Regular Languages, covering their definition, functioning, application in recognizing input strings, and building a DFA for a specific language. The Chomsky Hierarchy and the significance of Regular Languages are also briefly di
2 views • 41 slides
Pushdown Automata and Language Acceptance
Pushdown Automata (PDA) provide a theoretical framework for recognizing context-free languages. In PDA, the acceptance of a language depends on reaching a final state or having an empty stack. This concept is illustrated through examples and the distinction between deterministic and non-deterministi
2 views • 10 slides
Deterministic Turing Machines
Detailed explanation of Deterministic Turing Machines, their constituents, formal definition, determinism, and special statuses such as Start, Accept, Reject, and Loop. Includes visual representations and key concepts of deterministic Turing machines.
1 views • 14 slides
Concurrent Revisions: A Deterministic Concurrency Model
Exploring a deterministic concurrency model proposed by Daan Leijen and Sebastian Burckhardt, focusing on concurrent programming, threads, locks, futures, promises, transactions, and the resolution of conflicts in parallel performance.
0 views • 36 slides
Overview of Computational Complexity Theory: Savitch's Theorem, PSPACE, and NL-Completeness
This lecture delves into Savitch's theorem, the complexity classes PSPACE and NL, and their completeness. It explores the relationship between time and space complexity, configuration graphs of Turing machines, and how non-deterministic space relates to deterministic time. The concept of configurati
0 views • 67 slides
Issues in Context-Free Grammar: Ambiguity, Precedence, Associativity, and More
Delve into the complexities of context-free grammar, exploring concepts such as ambiguity, precedence, associativity, left recursion, and left factoring. Learn about the challenges posed by left recursion and the differences between ambiguous and unambiguous, as well as deterministic and non-determi
0 views • 7 slides
Enhancing Replay Interface Efficiency in System Debugging
Efforts by researchers at Microsoft Research Asia and MIT focus on enhancing replay interface efficiency for system debugging. The motivation stems from the non-determinism challenges caused by time, user input, network I/O, and thread interleaving. The study observes that only certain parts of a pr
0 views • 26 slides
Compiler Data Structures and NFA to DFA Conversion
Compiler data structures play a crucial role in the compilation process, handling lexical analysis to code generation. Understanding the conversion from non-deterministic finite automata (NFA) to deterministic finite automata (DFA) is essential for efficient language processing and optimization.
0 views • 10 slides
P vs. NP: A Comprehensive Overview
Delve into the complexities of computational problem-solving with insights on P, NP, NP-complete, determinism, and non-determinism. Explore the distinctions between deterministic and non-deterministic algorithms and the implications they have on problem-solving capabilities. Gain a deeper understand
2 views • 22 slides
Systematic Testing of Reactive Software - A Case Study on LG Electric Oven
Overview of a case study conducted on LG Electric Oven using systematic testing of reactive software with non-deterministic events. The study focused on detecting concurrency bugs in the software controller of the oven through an automated testing framework that generates event timing sequences. It
0 views • 32 slides
Cross-Device Tracking for Better Engagement
Delve into the world of cross-device tracking with insights on probabilistic vs. deterministic matching models, limitations of third-party cookies, reasons to engage in cross-device tracking, and the distinctions between probabilistic and deterministic matching methods. Explore how tracking across m
0 views • 41 slides
Time Distribution System R&D Update for Hyper-Kamiokande Experiment
In the February 2020 update, Stefano Russo from LPNHE Paris presented the progress on the time distribution system R&D for the Hyper-Kamiokande experiment. The focus is on implementing a bidirectional data exchange link with a large bandwidth capacity for synchronous, phase-deterministic protocol. T
0 views • 17 slides
Concurrent Revisions: A Model for Deterministic Concurrency
This content discusses a deterministic concurrency model called Concurrent Revisions, focusing on interactive applications with large shared data structures. It covers the challenges of conflicting tasks, conventional concurrency control methods, and proposes a programming model based on revisions a
1 views • 41 slides
Overview of Nested Data Parallelism in Haskell
The paper by Simon Peyton Jones, Manuel Chakravarty, Gabriele Keller, and Roman Leshchinskiy explores nested data parallelism in Haskell, focusing on harnessing multicore processors. It discusses the challenges of parallel programming, comparing sequential and parallel computational fabrics. The evo
0 views • 55 slides
Ensuring Orthogonal Security in Data Encryption Processes
Addressing the challenge of data confidentiality in untrusted server environments through the use of encryption techniques such as deterministic and non-deterministic encryption. The goal is to achieve full functionality independently of data encryption, allowing for secure processing of data querie
0 views • 21 slides
Shadow: Scalable and Deterministic Network Experimentation in Cybersecurity
The presentation discusses the concept of deterministic experimentation in cybersecurity, emphasizing the importance of experimental control and scalability in large distributed systems like Tor. It introduces Shadow, a network simulator designed to achieve repeatable and realistic experiments for r
0 views • 15 slides
Achieving Deterministic Latency in JESD204B Links
JESD204B links utilize high-speed serdes technology to provide benefits like improved densities and simplified layouts. This presentation discusses understanding and designing link latency, offering insights into achieving deterministic latency and managing link delay variations.
1 views • 49 slides
Midterm I review
Dive into the key concepts of Finite Automata including Deterministic and Non-deterministic Finite Automata, their definitions, differences, construction checklists, NFA to DFA conversion techniques, and more. Explore syllabus topics on formal proofs, regular expressions, and the pumping lemma for r
0 views • 15 slides
Computer Simulation Models Classification
Computer simulation models are classified based on various characteristics such as static or dynamic, deterministic or stochastic, and discrete or continuous. Static models represent systems at a specific point in time, while dynamic models depict changes over time. Deterministic models involve no r
0 views • 8 slides
Deterministic Safety Assessment: Selecting Postulated Initiating Events
In this training course on nuclear safety, the exercise focuses on selecting Postulated Initiating Events of LB LOCA type. Participants learn the methodology and significance of selecting these events and the arguments supporting their choices. Through case studies and analysis, safety analysts and
0 views • 10 slides
IEEE 802.11-17/1428r1 Deterministic Backoff Rules
This document dated September 2017 discusses deterministic backoff rules for IEEE 802.11-17/1428r1, outlining specific algorithms for managing backoff periods in wireless communication systems. It delves into scenarios of collisions, interruptions, and access delays, providing insights into how to o
1 views • 15 slides
IEEE 802.11-17/1428r1 Deterministic Backoff Rules
This document discusses the deterministic backoff rules for IEEE 802.11-17/1428r1 protocol. It covers scenarios where fewer than three consecutive collisions occur and outlines the specific backoff algorithm to be followed. The document includes simulations and analysis pertaining to deterministic b
1 views • 19 slides
Theoretical Computer Science: Deterministic Finite Automata
In the beginning of the course, we delve into computational models starting with deterministic finite automata (DFA). Explore the history of automata theory and the significance of DFAs in computing. Witness the foundation of automata theory laid by pioneers such as Kleene, McCulloch, and Pitts.
0 views • 15 slides
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and Deterministic Networking
Time-Sensitive Networking (TSN) and Deterministic Networking (DetNet) technologies enable low-latency, guaranteed packet propagation, time-aware scheduling, high reliability, and seamless redundancy for critical applications in various sectors such as industrial automation, communication systems, an
0 views • 41 slides
Formal Verification in Systems Software: Understanding State Machine Behavior
This material delves into the formal verification of systems software, focusing on state machine definitions and behaviors. It covers topics such as state space, state assignment, and predicates for state transitions like CheckOut and CheckIn. The content emphasizes the importance of deterministic a
0 views • 12 slides
Understanding Deterministic and Non-Deterministic Data in Mechanical Engineering
Explore the concepts of deterministic and non-deterministic data in the field of mechanical engineering. Learn how to classify data, differentiate between types of physical variables, and understand the implications for experimental methods. Get insights into the application of random signals in mec
1 views • 13 slides
Low Latency Deterministic Networks in IEEE 802.15.4: Overview and Use Cases
Explore the motivation behind Low Latency Deterministic Networks (LLDN) in IEEE 802.15.4, addressing latency issues and proposing solutions. Discover the applications in industrial settings like factory automation, automotive production, and logistics. Delve into network topology designs, with a foc
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Deterministic Context-Free Languages
Discover the concept of Deterministic Context-Free Languages (DCFL) - a subset of context-free languages accepted by Deterministic Push-Down Automata. Learn about their properties, importance, and examples.
1 views • 13 slides
Deterministic Random Walks for Network Exploration and Cover Time Analysis
Explore the concept of deterministic random walks in network exploration. Understand the cover time and its significance in traversing graphs efficiently. Discover the simplicity and robustness of random walks in navigating through connected graphs.
0 views • 58 slides
Exploring Quantum Logic and Robotics: Examples and Insights
Delve into the fascinating realm of quantum logic and robotics with examples of deterministic and non-deterministic matrices in quantum robots. Understand the concepts of superposition, entanglement, and transformation through permutative and non-permutative matrices, shedding light on the futuristi
0 views • 23 slides
Theory of Computation: Context-Free Languages and Turing Machines
Explore the world of context-free languages, formal grammars, Pushdown Automata, and Turing machines within the realm of theoretical computer science. Understand the closure properties of regular and context-free languages and delve into the computational power of Turing machines. Learn about langua
0 views • 24 slides
Virtual Machine Logging and Replay for Intrusion Analysis
Explore the innovative approach of ReVirt for intrusion analysis using virtual machine logging and replay techniques. Learn about attacks, current systems, UMLinux, Trusted Computing Base, deterministic vs. non-deterministic events, and cooperative logging in this comprehensive study." (Approximatel
0 views • 16 slides
Compiler Design Overview and Phases
Learn about the introduction to compilers, their functions, compiler phases, finite state machines, deterministic finite automata (DFA), and non-deterministic finite automata (NDFA), essential concepts in compiler design.
0 views • 8 slides
NFA and DFA in Compiler Design - Explained with Examples
Learn about Non-Deterministic Finite Automata (NFA) and Deterministic Finite Automata (DFA) in compiler design. Understand their definitions, differences, and conversion process with detailed examples.
1 views • 8 slides
Deterministic and Combinatorial Algorithms for Submodular Maximization
Explore deterministic and combinatorial algorithms for submodular maximization with examples like Max DiCut and Max k-Cover. Learn about submodular optimization and continuous relaxations in various applications such as combinatorics, machine learning, and image processing.
0 views • 25 slides
Automated Unit Test Generation Using Mocking for Environment Dependencies
The study discusses how automated test generation tools can face challenges with low coverage and non-deterministic results in classes with environment dependencies. By utilizing a mock library to interact with the virtual environment, test coverage is increased, and deterministic test results are p
0 views • 36 slides
Detecting Assumptions on Deterministic Implementations of Non-deterministic Specifications
Explore the challenges of code assumptions in deterministic implementations of non-deterministic specifications. Learn about the potential risks of assuming deterministic behavior and how tools like NonDex can help in detecting and addressing such issues to improve code reliability.
0 views • 23 slides
Deterministic Algorithms for Submodular Maximization Problems
Explore deterministic algorithms for submodular maximization problems, with examples in cut functions and coverage functions. Learn about submodular functions, maximization problems, and the necessity of randomization. Discover a history of algorithms and approximation techniques." (Characters: 298)
0 views • 17 slides
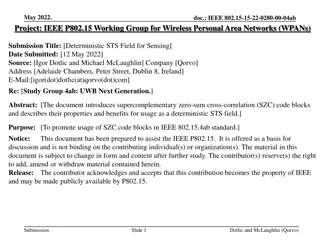
Deterministic STS Field for Sensing in Wireless Personal Area Networks
This document introduces supercomplementary zero-sum cross-correlation code blocks for usage as a deterministic STS field in IEEE 802.15.4ab standard, aiming to promote the adoption of SZC code blocks. The submission emphasizes the properties and benefits of SZC code blocks and highlights their pote
0 views • 11 slides