Critique of Causal Metaphysics and Empiricism
In this content, the author critiques the metaphysics of causation from an empiricist perspective, exploring the limitations of empiricism in understanding the contingent truths of the world. It discusses causal antifundamentalism, various forms of skepticism, including Humean skepticism, and challe
4 views • 55 slides
Understanding Bayesian Model Comparison in Neuroimaging Research
Exploring the process of testing hypotheses using Statistical Parametric Mapping (SPM) and Dynamic Causal Modeling (DCM) in neuroimaging research. The journey from hypothesis formulation to Bayesian model comparison, emphasizing the importance of structured steps and empirical science for successful
4 views • 36 slides
Optimizing Homework Effect on Student Achievement Through Causal Machine Learning
Using TIMSS 2019 data from Ireland, a study conducted at Maynooth University explores the impact of homework frequency, duration, and question types on student achievement in math and science. By leveraging causal machine learning techniques, researchers aim to provide insights for educators on effe
0 views • 31 slides
Understanding Association and Causation in Epidemiological Studies
Exploring the concepts of association and causation in epidemiological studies, this content delves into the complexities of determining if exposure leads to disease risk. It discusses different types of associations, such as spurious, indirect, and direct causal associations, illustrating the chall
5 views • 43 slides
Understanding Disease Causation and Frequency Measures
The concept of disease causation delves into the factors that play a role in the development of diseases, emphasizing the importance of studying causation for prevention, control, and treatment. To infer causation, certain conditions must be met, and a causal relationship is characterized by associa
0 views • 47 slides
Understanding Fixed Effects Regression for Causal Inference in Social Research
Explore the concept of fixed effects regression for obtaining causal estimates with observational data, focusing on the association between social participation and depressive symptoms. Discover how this method controls for time-invariant factors and eliminates confounding variables, providing a clo
0 views • 49 slides
Introduction to Econometrics and Machine Learning
Econometrics and machine learning intersect in decision-making scenarios where causal and counterfactual questions arise. This talk explores the relationship between the two fields, highlighting the identification of causal quantities and the flexible estimation techniques employed. Examples demonst
2 views • 53 slides
Targeted Learning Framework for Causal Effect Estimation Using Real World Data
Hana Lee, Ph.D., presents a webinar on the Targeted Learning Framework for Causal Effect Estimation using Real World Data (TMLE). The project aims to help the FDA develop a structured approach to incorporating real-world data into regulatory decision-making. TMLE offers a systematic roadmap aligned
0 views • 27 slides
Understanding the Process and Types of Research Design
The process of research design involves interactive stages occurring simultaneously, leading to the creation of a structured study. There are three main types of research design: exploratory, descriptive, and experimental (or causal). Each type has its own objectives and methods. Exploratory researc
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Research Methods: Quantitative, Qualitative, and Mixed Approaches
This introduction provides an overview of qualitative, quantitative, and mixed methods research, highlighting key differences and various types of research approaches. It delves into exploratory, descriptive, and causal research methodologies, offering insights into problem discovery, data collectio
0 views • 50 slides
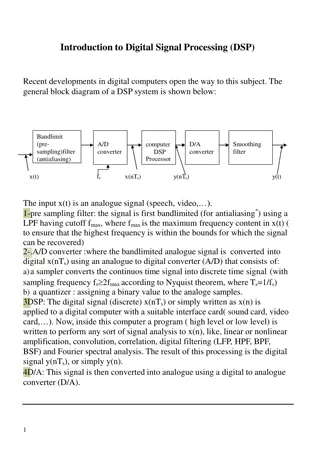
Overview of Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Systems and Implementations
Recent advancements in digital computers have paved the way for Digital Signal Processing (DSP). The DSP system involves bandlimiting, A/D conversion, DSP processing, D/A conversion, and smoothing filtering. This system enables the conversion of analog signals to digital, processing using digital co
1 views • 24 slides
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) for Causal Inference
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) play a crucial role in documenting causal assumptions and guiding variable selection in epidemiological models. They inform us about causal relationships between variables and help answer complex questions related to causality. DAGs must meet specific requirements like
1 views • 63 slides
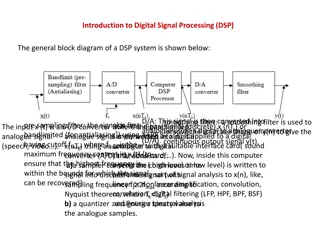
Understanding Digital Signal Processing (DSP) Systems: Linearity, Causality, and Stability
Digital Signal Processing (DSP) involves converting signals between digital and analog forms for processing. The general block diagram of a DSP system includes components like D/A converters, smoothing filters, analog-to-digital converters, and quantizers. DSP systems can be classified based on line
1 views • 12 slides
Understanding Causal Consistency in Distributed Systems
This content covers the concept of causal consistency in computing systems, exploring consistency models such as Causal Linearizability and Eventual Sequential. It explains the importance of logical clocks like Lamport and vector clocks, and how they ensure order in distributed systems. The concept
0 views • 35 slides
Scalable Causal Consistency for Wide-Area Storage with COPS
This paper delves into the importance of scalable causal consistency for wide-area storage with the COPS system. It explores desired properties such as availability, low latency, partition tolerance, and scalability within data centers. The document discusses the challenges of achieving consistency
0 views • 41 slides
Understanding Causal Inference and Scientific Goals
Explore the significance of causal inference in science, the goals of scientific research, and the importance of developing an understanding of causal associations. Delve into topics like causal pattern recognition, mechanistic understanding, and potential outcomes frameworks to enhance your underst
0 views • 76 slides
Understanding the Scientific Method: Observations, Questions, and Hypotheses
Explore the scientific method concept of making observations, asking questions, and forming hypotheses. Learn the difference between causal and descriptive questions and practice applying them. Understand how to approach a situation like a non-starting washing machine through causal and descriptive
0 views • 28 slides
Estimation of Causal Effects using Propensity Score Weighting
Understanding causal effects through methods like propensity score weighting is crucial in institutional research. This approach helps in estimating the impact of various interventions, such as a writing program, by distinguishing causation from correlation. The use of propensity score matching aids
0 views • 22 slides
MFMSA_BIH Model Build Process Overview
This detailed process outlines the steps involved in preparing, building, and debugging a back-end programming model known as MFMSA_BIH. It covers activities such as data preparation, model building, equation estimation, assumption making, model compilation, and front-end adjustment. The iterative p
0 views • 10 slides
Understanding Causal Inference and Causal Graphs in Drug Efficacy Studies
This content delves into the concept of causal inference using causal graphs, specifically focusing on the relationship between a drug (D) and its effectiveness in curing a condition (C). It discusses the importance of distinguishing correlation from causation and explores scenarios where confoundin
0 views • 66 slides
Understanding Spatial Extremes: Complex Time Methods in Hydro-Atmospheric Dynamics
This study explores the use of complex time methods and chameleon scalar fields in understanding and modeling spatial extremes in hydrological and atmospheric systems. By transforming Lagrangian processes and introducing chameleon scalar fields, the research unveils new insights into the mechanism g
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Causal Factors in Illness: Toxins, Smoking, and Contributing Causes
Causal standards for illness attribution, toxins' role in disease onset and expression, and the impact of factors like smoking and contributing causes on health outcomes are explored. The distinction between certain and contributing causes, as well as the level of certainty in carcinogen classificat
1 views • 19 slides
Enhancements in Causal Forecasting: SPM 11.0.1/11.1 Overview
Key enhancements in SPM 11.0.1/11.1 focus on improving forecast accuracy through variable history slices, causal forecasting for multiple streams, multi-threading capabilities, easy access to product rollout and causal value pages, and more. The Next Gen Causal Forecasting introduces additional feat
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Dispositions: The Conditional Analysis Approach
Explore the concept of dispositions, also known as capacities or causal powers, and the traditional Conditional Analysis (CA) approach as a dominant account of dispositions. Learn about the features and examples of dispositions such as fragility, solubility, mass, and charge, and how objects exhibit
0 views • 25 slides
MBA Program Assessment and Causal Model Analysis: Insights and Integration
Delve into the assessment value chain of the 2021-2022 MBA Report, exploring inputs, outcomes, impacts, and outputs to measure student learning outcomes and satisfaction. Analyze the causal model relationships affecting student satisfaction with learning, aiming to enhance outcomes and impacts for i
0 views • 13 slides
Statistical Issues in Clinical Trials: Insights from 13th Annual Conference
The 13th annual conference on Statistical Issues in Clinical Trials covered topics such as penalties for extra variation and limited degrees of freedom, the Diet-Heart Hypothesis, controlled trials, unit of randomization, and causal inference. Speakers highlighted the importance of addressing cluste
0 views • 10 slides
Exploring Causal Inference Models and Data-Driven Methods
Delve into various examples of causal inference models and data analysis methods, from traditional statistical models to cutting-edge data-driven approaches like AI/ML. Understand the challenges of causality interpretation and explore the trade-offs between data size, prediction, and causality in di
0 views • 9 slides
Understanding Causality in Social Policy: A Comprehensive Overview
This content delves into the concept of causality in social policy, focusing on different types of causal relationships and frameworks for causal analysis. It explores the importance of understanding causality for evidence-based policy making and evaluation, touching on key questions and relevant ba
0 views • 55 slides
Principles of Econometrics: Multiple Regression Model Overview
Explore the key concepts of the Multiple Regression Model, including model specification, parameter estimation, hypothesis testing, and goodness-of-fit measurements. Assumptions and properties of the model are discussed, highlighting the relationship between variables and the econometric model. Vari
1 views • 31 slides
Making a Convincing Causal Argument on Teen Smoking Effects
In collaboration with classmates, brainstorm about addressing various audiences regarding the detrimental health effects of teen smoking. Explore potential causes, gather supporting evidence, and consider audience engagement to craft a persuasive argument. Analyze existing causal arguments presented
0 views • 52 slides
Causal Relationships in Replication Systems
In this piece, we explore various aspects of causal relationships within replication systems such as the significance of logical and vector clocks, updates propagation in systems like Bayou, and commitment to learning order in asynchronous replication systems. Through analyzing scenarios and stateme
0 views • 8 slides
Understanding Causal Consistency in Computing Systems
Explore the concept of Causal Consistency in Computing Systems, covering topics such as consistency hierarchy, Causal+ Consistency, relationships in causal consistency, practical examples, and its implementation within replication systems. Learn how it ensures partial ordering of operations and conv
0 views • 31 slides
Scalable Causal Consistency for Wide-Area Storage with COPS
This paper discusses the implementation of scalable causal consistency in wide-area storage systems using COPS. It delves into the key-value abstraction, wide-area storage capabilities, desired properties such as ALPS, scalability improvements, and the importance of consistency in operations. Variou
0 views • 42 slides
Forecasting Short-Term Urban Rail Passenger Flows Using Dynamic Bayesian Networks
A study presented a dynamic Bayesian network approach to forecast short-term urban rail passenger flows in the Paris region. The research addresses the challenges of incomplete data, unexpected events, and the need for real-time forecasting in public transport networks. By leveraging Bayesian networ
0 views • 19 slides
Understanding Experimental and Quasi-Experimental Designs
Explore the foundations of experimental and quasi-experimental designs, delving into causal relationships, counterfactual reasoning, and the importance of validating statistical and internal conclusions. Learn about causes, effects, and the complexity of determining causation in research. Discover R
0 views • 46 slides
Cost Analysis for Evaluation: Strategies and Methods
This document delves into the realm of cost-effectiveness analysis for evaluation purposes, emphasizing the significance of defining measures of effectiveness, distinguishing intermediate versus final outcomes, establishing effectiveness through causal analysis, and exploring different types of rese
0 views • 21 slides
Understanding Experimental Design and Validity Trade-offs in Research
Explore the concepts of experimental design, trade-offs in research validity, causal relationships, evidence, and controls in experiments. Delve into lab and field experiments, manipulation of variables, controls, and the importance of causal evidence in research. Consider the impact of extraneous f
0 views • 42 slides
Methods for Quantifying Efficacy-Effectiveness Gap in Randomized Controlled Trials
This research discusses the quantification of the efficacy-effectiveness gap in randomized controlled trials (RCTs), particularly focusing on examples in Acute Respiratory Distress Syndrome (ARDS). It explores the challenges of RCTs, ethical considerations, and the use of observational data for caus
0 views • 8 slides
Overview of DAGs in Causal Inference
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in causal inference is crucial for guiding research questions and analyzing causal relationships. This overview covers the basics of DAGs, their requirements, and applications in analyzing causal assumptions. Dive into the world of DAGs to enhance your re
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Latent Variable Modeling in Statistical Analysis
Latent Variable Modeling, including Factor Analysis and Path Analysis, plays a crucial role in statistical analysis to uncover hidden relationships and causal effects among observed variables. This method involves exploring covariances, partitioning variances, and estimating causal versus non-causal
0 views • 59 slides