Overview of Army Modeling and Simulation Office
The U.S. Army Modeling and Simulation Office (AMSO) serves as the lead activity in developing strategy and policy for the Army Modeling and Simulation Enterprise. It focuses on effective governance, resource management, coordination across various community areas, and training the Army Analysis, Mod
1 views • 8 slides
Understanding Atmosphere Composition and Structure in Climatology
The study of climatology, focusing on the atmosphere, is presented by Dr. Banashree Saikia, covering topics such as atmospheric composition, insolation, temperature variations, atmospheric pressure, wind systems, atmospheric moisture, climatic classification, cyclones, and monsoons. The atmosphere,
1 views • 9 slides
Historic Precipitation Hydrologic Modeling with HEC-HMS Slides by Greg Karlovits, Emily Moe, Daniel Black
Delve into the world of hydrologic modeling with HEC-HMS through a detailed presentation by experts Greg Karlovits, Emily Moe, and Daniel Black. Explore meteorologic models, atmospheric boundary conditions, basin modeling, and simulation runs in this informative slide series.
0 views • 12 slides
Capacity Zone Modeling for Forward Capacity Auction 17 Results
This presentation unveils the Capacity Zone modeling calculations for Forward Capacity Auction 17 associated with the 2026-2027 Capacity Commitment Period by ISO-NE PUBLIC. It delves into boundary definitions, import-constrained zone modeling, and market rules guiding the assessments and modeling pr
0 views • 16 slides
Understanding Geopotential and Geopotential Height in Atmospheric Thermodynamics
Explore the concept of geopotential and geopotential height in atmospheric sciences, focusing on their significance in understanding gravitational and centrifugal forces on Earth. Learn about the definition, calculation, and applications of geopotential height in relation to atmospheric properties a
1 views • 14 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Moisture in Physical Geography
Atmospheric moisture, in the form of water vapor, liquid water, and ice, plays a crucial role in shaping weather and climate. This course delves into the dynamics of atmospheric moisture, including its distribution, effects on weather patterns, and impact on various climatic factors such as precipit
0 views • 7 slides
Distribution Feeder Modeling and Analysis Overview
This document delves into the modeling, optimization, and simulation of power distribution systems, specifically focusing on Distribution Feeder Modeling and Analysis. It covers the components of a typical distribution feeder, series components, Wye-Connected Voltage Regulator modeling, and equation
0 views • 14 slides
Understanding Data Modeling vs Object Modeling
Data modeling involves exploring data-oriented structures, identifying entity types, and assigning attributes similar to class modeling in object-oriented development. Object models should not be solely based on existing data schemas due to impedance mismatches between object and relational paradigm
0 views • 17 slides
Evolution of Modeling Methodologies in Telecommunication Standards
Workshop on joint efforts between IEEE 802 and ITU-T Study Group 15 focused on information modeling, data modeling, and system control in the realm of transport systems and equipment. The mandate covers technology architecture, function management, and modeling methodologies like UML to YANG generat
1 views • 16 slides
Understanding Geometric Modeling in CAD
Geometric modeling in computer-aided design (CAD) is crucially done in three key ways: wireframe modeling, surface modeling, and solid modeling. Wireframe modeling represents objects by their edges, whereas surface modeling uses surfaces, vertices, and edges to construct components like a box. Each
1 views • 37 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Thickness and Its Applications
Atmospheric thickness refers to the difference in geopotential height between two pressure surfaces, which is dependent on the mean virtual temperature of the layer in between. This concept plays a key role in determining temperature gradients, identifying fronts, and aiding in weather forecasting,
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Synoptic Meteorology: A Comprehensive Overview
Synoptic meteorology delves into various aspects of atmospheric sciences, encompassing scales of atmospheric motion, weather maps, air masses, fronts, jet streams, and more. Through the study of synoptic meteorology, meteorologists gain insights into interpreting the state of the troposphere and for
1 views • 17 slides
Introduction to Dynamic Structural Equation Modeling for Intensive Longitudinal Data
Dynamic Structural Equation Modeling (DSEM) is a powerful analytical tool used to analyze intensive longitudinal data, combining multilevel modeling, time series modeling, structural equation modeling, and time-varying effects modeling. By modeling correlations and changes over time at both individu
0 views • 22 slides
System Modeling and Simulation Overview
This content provides insights into CPSC 531: System Modeling and Simulation course, covering topics such as performance evaluation, simulation modeling, and terminology in system modeling. It emphasizes the importance of developing simulation programs, advantages of simulation, and key concepts lik
0 views • 28 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure Variations at Different Altitudes
Atmospheric pressure varies with altitude due to the weight of the air column above. This activity explores how Otto von Guericke's experiments with vacuum systems demonstrate the power of air pressure. Theoretical concepts of atmospheric pressure are discussed, highlighting its relation to gravity
0 views • 28 slides
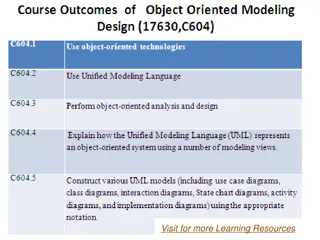
Understanding Object Modeling in Software Development
Object modeling is a crucial concept in software development, capturing the static structure of a system by depicting objects, their relationships, attributes, and operations. This modeling method aids in demonstrating systems to stakeholders and promotes a deeper understanding of real-world entitie
1 views • 65 slides
Coupled Ocean-Atmosphere Modeling on Icosahedral Grids
Coupled ocean-atmosphere modeling on horizontally icosahedral and vertically hybrid-isentropic/isopycnic grids is a cutting-edge approach to modeling climate variability. The design goals aim to achieve a global domain with no grid mismatch at the ocean-atmosphere interface, with key indicators such
1 views • 21 slides
Cutting-Edge Atmospheric Chemistry Modeling Research at Barcelona Supercomputing Center
Conducted by the Atmospheric Composition Group at Barcelona Supercomputing Center, this cutting-edge research focuses on atmospheric chemistry modeling using advanced tools and frameworks like HERMESv3 and MONARCH. The team's approach integrates various modules to study complex processes influencing
0 views • 16 slides
Exploring Aerosol Microphysics and Aqueous Phase Chemistry in Atmospheric Research
This material delves into the study of aerosol microphysics and aqueous phase chemistry in the context of atmospheric research. It discusses topics such as scale-dependencies, obstacles in development, working groups for MUSICA, and the importance of various processes in aerosol modeling. The conten
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Fluid Statics and Atmospheric Pressure Measurements
Exploring the concept of fluid statics, this content delves into topics such as how atmospheric pressure is measured, buoyancy, and why a steel boat can float. It covers the measurement of pressure, the relationship between pressure and depth in fluids, and demonstrations showcasing these principles
0 views • 24 slides
Understanding Spatial Extremes: Complex Time Methods in Hydro-Atmospheric Dynamics
This study explores the use of complex time methods and chameleon scalar fields in understanding and modeling spatial extremes in hydrological and atmospheric systems. By transforming Lagrangian processes and introducing chameleon scalar fields, the research unveils new insights into the mechanism g
0 views • 9 slides
Overview of Low-Cost Sensors for Atmospheric Composition Measurement
This publication provides an insightful overview of low-cost sensors for measuring atmospheric composition, covering topics like sensor technologies, applications in atmospheric sciences and air quality management, and evaluation methods. It emphasizes the importance of not only the technical perfor
0 views • 17 slides
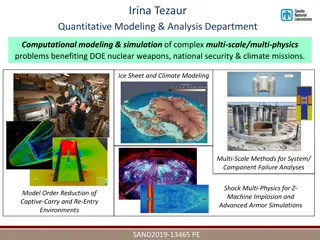
Advancing Computational Modeling for National Security and Climate Missions
Irina Tezaur leads the Quantitative Modeling & Analysis Department, focusing on computational modeling and simulation of complex multi-scale, multi-physics problems. Her work benefits DOE nuclear weapons, national security, and climate missions. By employing innovative techniques like model order re
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Circulation on Earth
An atmospheric circulation driven by temperature differences between the equator and poles influences global weather patterns. The sun's changing angle throughout the year results in various pressure areas and the formation of large circulation cells. The main effects include the transport of humidi
0 views • 11 slides
Understanding Cumulus Parameterization and Mass-Flux Schemes in Atmospheric Science
Explore the significance of mass-flux schemes in cumulus parameterization, their interaction with grid-scale microphysics, and the key elements and assumptions involved. Learn about the objectives, components, and limitations of classical cumulus schemes for atmospheric modeling. Gain insights into
0 views • 23 slides
Understanding Cloud and Precipitation Processes in Atmospheric Science
This week's module focuses on measuring, predicting, and modeling single-column processes related to clouds and precipitation. Topics covered include ODE and PDE models, advection equations, orographic clouds, warm and cold cloud processes, condensation, warm-rain processes, and more. The importance
0 views • 17 slides
Understanding the Planetary Boundary Layer in Atmospheric Science
The Planetary Boundary Layer (PBL) plays a crucial role in atmospheric dynamics, divided into surface, mixed, stable, and residual layers. During the day, the mixed layer experiences convective motions due to surface heating, while the stable layer dominates during the night. Understanding these lay
0 views • 18 slides
NSF Atmospheric Chemistry Program Overview
The NSF Atmospheric Chemistry Program aims to characterize the chemical composition of the atmosphere, understand chemical processes, quantify fluxes of chemical substances, study natural and anthropogenic causes of variability, and assess impacts on climate. The program supports research through pe
0 views • 6 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Chemistry Measurements and Methods
Explore the various types of atmospheric chemistry measurements, including research vs. monitoring, gas phase species, satellite vs. in situ observations, and spectroscopy and chromatography methods. Discover how researchers and regulatory bodies use different techniques to study and monitor air qua
0 views • 34 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Composition and Structure
The presentation covers fundamental concepts related to the Earth's atmosphere, including its composition, origin of oxygen, dry and moist layers, standard atmosphere layers, and temperature variations. Key topics discussed include the primordial atmosphere, atmospheric constituents, water vapor dis
0 views • 58 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Thermodynamics and Environmental Lapse Rate
Explore the concepts of atmospheric thermodynamics including the Parcel Method, Environmental Lapse Rate, and Conditionally Unstable Atmosphere. Dive into the details of how air parcels behave in different atmospheric conditions and understand the significance of temperature changes in the atmospher
0 views • 27 slides
GEOS-Chem Atmospheric Chemistry Model Overview
GEOS-Chem, developed by Daniel J. Jacob at Harvard University, is a global model of atmospheric composition used to understand human and natural influences on the environment. The model addresses various atmospheric chemistry issues on different scales, from local to global, and is regularly updated
0 views • 19 slides
NetLogo - Programmable Modeling Environment for Simulating Natural and Social Phenomena
NetLogo is a powerful and versatile programmable modeling environment created by Uri Wilensky in 1999. It allows users to simulate natural and social phenomena by giving instructions to multiple agents operating independently, making it ideal for modeling complex systems evolving over time. NetLogo
0 views • 7 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Stability and Adiabatic Processes
Atmospheric stability is crucial in determining weather conditions. Different processes such as adiabatic cooling play a significant role in the vertical movement of air masses. Understanding the environmental lapse rate, moist and dry adiabatic rates, and the concept of conditional instability help
0 views • 4 slides
Understanding Atmospheric Pressure, Wind Variations, and Humidity in Weather Systems
The atmosphere is composed of various elements like gaseous molecules, water vapor, and dust particles. Key weather variables include atmospheric pressure, temperature, humidity, wind, cloud cover, and precipitation. Atmospheric pressure is influenced by the weight of air above a point, with average
0 views • 17 slides
Prediction of Metallicity and C/O Ratios for Hot Jupiter Exoplanets
Dr. Graeme Melville from the University of NSW explores the modeling of atmospheres for hot Jupiter exoplanets, emphasizing the importance of temperature, PT profiles, metallicity, and the C/O ratio. Utilizing the Versatile Software for Transfer of Atmospheric Radiation (VSTAR), the research aims to
0 views • 27 slides
The DC and AC global atmospheric electric circuits as central tenets in Earth system science today
The presentation at the EGU General Assembly highlighted the significance of DC and AC global atmospheric electric circuits in Earth system science. Key references from 2007 to 2018 underscore the evolving research in this field, exploring the interconnectedness between the space environment and the
0 views • 23 slides
Addressing the Gap Between Graduates' Skills and Employers' Expectations in Atmospheric Geosciences
The article discusses the skills gap in the atmospheric geosciences field, highlighting key technical and communication skills needed by graduates and postgrads. It explores strategies to bridge this gap through surveys, creative solutions, and innovative approaches like updating degree requirements
0 views • 5 slides
Analysis of Atmospheric Parameters and Transmission at OHP in 2018
This analysis focuses on the atmospheric parameters and transmission at the Observatoire de Haute-Provence (OHP) during 2018, with a specific emphasis on distinguishing between typical winter and summer conditions. The study utilizes MERRA2 data from January to August to examine pressure, precipitab
0 views • 16 slides
Atmospheric Correction Techniques for Satellite Image Enhancement
Atmospheric correction is essential for improving the quality of Remote Sensing images captured by satellites. This process involves correcting for the effects of atmospheric gases such as scattering and absorption on the measured Top-of-Atmosphere (TOA) reflectance. Techniques like molecular correc
0 views • 8 slides