Advancements in Simple Multigraph Convolution Networks by Xinjie Shen
Explore the latest innovations in simple multigraph convolution networks presented by Xinjie Shen from South China University of Technology. The research evaluates existing methods, such as PGCN, MGCN, and MIMO-GCN, and introduces novel techniques for building credible graphs through subgraph-level
5 views • 6 slides
Apache Spark: Fast, Interactive, Cluster Computing
Apache Spark, developed by Matei Zaharia and team at UC Berkeley, aims to enhance cluster computing by supporting iterative algorithms, interactive data mining, and programmability through integration with Scala. The motivation behind Spark's Resilient Distributed Datasets (RDDs) is to efficiently r
0 views • 41 slides
Bellman-Ford and Dynamic Programming on Graphs
Exploring Bellman-Ford and Floyd-Warshall algorithms, Dijkstra's Algorithm, shortest path problems, dynamic programming on graphs, and solving distances in a directed acyclic graph. Learn about recurrences, evaluation orders, topological sort, and handling cycles in graphs.
3 views • 39 slides
Privacy-Preserving Analysis of Graph Structures
Explore the world of graph structures and differential privacy in data publishing networks, focusing on preserving privacy while releasing structural information about graphs. Differential privacy techniques such as edge privacy and subgraph counts are discussed in detail, highlighting the challenge
0 views • 20 slides
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) for Causal Inference
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) play a crucial role in documenting causal assumptions and guiding variable selection in epidemiological models. They inform us about causal relationships between variables and help answer complex questions related to causality. DAGs must meet specific requirements like
1 views • 63 slides
Recent Applications of Quasi-Poly Time Hardness in Densest k-Subgraph
Recent applications of the Birthday Repetition technique have demonstrated the quasi-polynomial time hardness in various computational problems, including AM with k provers, Dense CSPs, Free games, and Nash equilibria. These applications also explore the potential implications in signaling theory an
0 views • 18 slides
Challenges and Innovations in Relational Engine Algorithms
Exploring the complexity of processing graph data in relational query engines, this content delves into the challenges faced, practices adopted in academia, and innovative solutions like LMS-NPRR, trie join, and specialized data structures. It discusses the difficulties in handling acyclic vs. cycli
1 views • 27 slides
Dynamic Programming in Algorithms
Dynamic programming and linear programming are powerful techniques that come into play when specialized methods fall short. Dynamic programming involves solving a problem by breaking it down into smaller subproblems and solving them incrementally. In this approach, the nodes represent subproblems, a
0 views • 40 slides
Finding Reductions in NP-Hardness Proofs
To find a polynomial-time many-one reduction from a known NP-hard decision problem A to a target problem B, ensure that the reduction maps inputs correctly such that the output for A is 'yes' if and only if the output for B is 'yes.' An example is demonstrated using Subgraph Isomorphism and Hamilton
0 views • 32 slides
Introduction to Technology Mapping Using Linear Delay Model
Explore the process of technology mapping on a Directed Acyclic Graph (DAG) using a linear delay model. Learn about transforming circuits into subject graphs, utilizing sample cell libraries, and implementing circuits to meet user requirements. The challenges of technology mapping, circuit recovery,
0 views • 23 slides
Bayesian Networks: A Comprehensive Overview
Bayesian networks, also known as Bayes nets, provide a powerful tool for modeling uncertainty in complex domains by representing conditional independence relationships among variables. This outline covers the semantics, construction, and application of Bayesian networks, illustrating how they offer
0 views • 17 slides
Efficient and Effective Duplicate Detection in Hierarchical Data
This study explores the efficient and effective detection of duplicates in hierarchical data, focusing on fuzzy duplicates and hierarchical relationships in XML. It discusses the current and proposed systems, including the use of Bayesian networks for similarity computations. The methods involve vec
0 views • 25 slides
CILK: An Efficient Multithreaded Runtime System
CILK is a multithreaded runtime system designed to develop dynamic, asynchronous, and concurrent programs efficiently. It utilizes a work-stealing thread scheduler and relies on a directed acyclic graph (DAG) model for computations. With a focus on optimizing critical paths and total work, CILK enab
0 views • 44 slides
TopK Interesting Subgraph Discovery in Information Networks
Discovering top-K interesting subgraphs in information networks is crucial for various applications like network bottlenecks, team selection, resource allocation, and more. This research focuses on developing low-cost indexes and novel algorithms to efficiently detect these subgraphs. The contributi
0 views • 26 slides
Graph Summarization on Hierarchical DAGs
Explore top-k graph summarization techniques on Hierarchical Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) like Disease Ontology, ImageNet, and Wikipedia Categories. Understand motivations for summarization, related works, and the kDAG-Problem. Discover algorithms, experiments, and conclusions for efficient graph
0 views • 38 slides
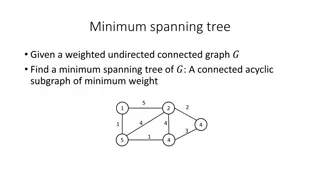
Greedy Algorithms: Minimum Spanning Tree Analysis
Explore the concept of Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) in the context of greedy algorithms, focusing on Kruskal's Algorithm. Understand the methodology behind selecting the minimum weighted subgraph that connects all vertices in a weighted graph efficiently. Delve into problem-solving strategies and app
2 views • 39 slides
Epidemiology Concepts in Research and Analysis
Exploring important epidemiology concepts such as exposure, outcome, risk, confounders, effect measures, and more, this content delves into variable selection using Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) for causal inference in research and analysis. Understanding these concepts is crucial for conducting ro
0 views • 37 slides
Minimum Spanning Trees in Graph Theory
Exploring the concept of minimum spanning trees in undirected, weighted graphs. A spanning tree is a connected acyclic subgraph that includes all vertices of the original graph. The Minimum Spanning Tree (MST) problem involves finding the tree with the smallest total edge weight. The cycle property
0 views • 42 slides
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs)
Explore the significance of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in comprehending data structures, addressing issues like bias, loss to follow up, and missing data impacts in studies. Gain insights into key concepts, nodes, arrows, causality, associations, causal structures, and the role of confounders. E
0 views • 26 slides
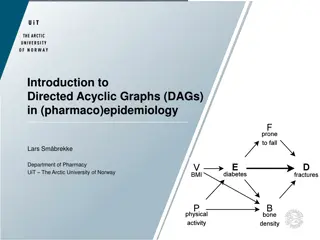
Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in Epidemiology
Exploring the significance of Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in pharmacoepidemiology, this content delves into the challenges faced in analyzing observational data and the benefits of DAGs in identifying confounders, mediators, and colliders. The conclusion emphasizes the importance of transparent r
0 views • 58 slides
Subgraph Matching for Cloud Service Placement in Datacenters
This research explores the efficient placement of cloud services in datacenters through subgraph matching, focusing on compatibility and resource optimization between customers and providers in cloud computing environments. The study highlights challenges in dynamic subgraph matching and the limitat
1 views • 29 slides
Interactive Protocols in Arthur-Merlin Games for Graph Nonisomorphism
Explore the concept of interactive protocols in Arthur-Merlin games for determining graph nonisomorphism. Arthur, a powerless knight, seeks to trust Merlin's advice but Merlin, all-powerful yet untrustworthy, must find ways to convince Arthur. Utilizing randomness, the games delve into graph isomorp
0 views • 13 slides
Overview of DAGs in Causal Inference
Understanding Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs) in causal inference is crucial for guiding research questions and analyzing causal relationships. This overview covers the basics of DAGs, their requirements, and applications in analyzing causal assumptions. Dive into the world of DAGs to enhance your re
0 views • 28 slides
Efficient Bitruss Decomposition for Large-scale Bipartite Graphs
Bitruss decomposition is a powerful concept in graph theory to identify cohesive subgraphs in bipartite graphs. This paper by Kai Wang, Xuemin Lin, Lu Qin, Wenjie Zhang, and Ying Zhang presents an efficient approach for computing bitruss numbers of edges in large-scale bipartite graphs. The study ex
0 views • 25 slides
Games on Graphs
This presentation discusses the concept of Acyclic Unique Sink Orientations (AUSOs) on graphs, exploring their motivations, definitions, and algorithms for finding the sink. It also covers Linear Programming, focusing on maximizing linear objective functions subject to linear inequalities, exemplifi
0 views • 36 slides
Applications of Depth-First Search in Graph Topology
Discover the significance of graph topology and the applications of Depth-First Search (DFS) in laying out data for interpretation. Learn about topological sorting, Directed Acyclic Graphs (DAGs), and the correctness of topological sort.
1 views • 17 slides
Efficient Cut Algorithms in Graph Structures
This content covers efficient cut algorithms in graph structures, focusing on partitioning graph vertices, computing minimum-cut values, and a short history of min-cut algorithms. It explains the contraction algorithm, cut sparsifier subgraph computation, and the general contraction algorithm. The m
0 views • 25 slides
Bell & Coins Example
Bayesian networks provide a powerful tool for modeling diseases, symptoms, and risk factors. These directed acyclic graphs help in understanding the relationships between variables and making probabilistic inferences. By utilizing Bayesian networks, it becomes feasible to represent complex scenarios
0 views • 31 slides
Frequent subgraph mining
In this overview, we delve into various aspects of frequent subgraph mining, discussing types of graphs, analyzing graphs for data mining tasks, input-output processes, and the goal of discovering repeated subgraphs in graph databases.
1 views • 13 slides
Classes of networks
This content delves into various classes of networks including acyclic directed networks, algorithms to check for acyclicity, vertex layouts, and hypergraphs. It also explores bipartite networks and their transformation from hypergraphs, offering insights into different network structures and proper
0 views • 32 slides
CS 1501 RECITATION 6
The Minimum Spanning Tree Problem involves finding the connected subgraph with the smallest weight in a weighted graph, important for real-world applications like network design. Prim's Algorithm is a well-known method for constructing a minimum spanning tree efficiently. This algorithm selects edge
0 views • 45 slides
Minimum spanning tree
In the realm of graph theory, the quest for the minimum spanning tree in weighted undirected connected graphs is a crucial pursuit. This involves finding a connected acyclic subgraph with the least total weight, paving the way for efficient network optimization and resource allocation.
0 views • 26 slides
Minimum Spanning Trees: Graph Optimization Problem
A graph optimization problem focusing on finding an acyclic subset in an undirected graph that connects all vertices with minimal total weight. This involves exploring Kruskal's and Prim's algorithms for solving the minimum spanning tree problem by leveraging safe edges and cuts. The concept of grow
0 views • 20 slides
Parallel Programming Graph Algorithms: Fundamentals and Representations
Delve into the core concepts of parallel programming graph algorithms, covering topics such as undirected vs. directed graphs, adjacency, paths, cyclic vs. acyclic structures, and efficient graph representations on computers. Gain insights into key graph theory principles essential for algorithm des
0 views • 18 slides
Colorful Connected Graph Problem Overview
The Colorful Connected Graph Problem involves finding a connected subgraph with a minimum number of vertices containing at least one vertex of each color. Considered an NP-complete decision problem, it has various real-world applications in fields such as Protein-Protein Interaction Networks, Sensor
0 views • 46 slides
Modeling Mass Protest Adoption in Social Networks Using Geometric Brownian Motion
This study explores the adoption of mass protests in social network communities through the application of Geometric Brownian Motion. The research delves into the dynamics of protest participant growth, the underlying social network structures, and the trust functions modeled as a GBM process. Addit
0 views • 11 slides
Network Design with Degree Constraints: Problems and Results
Delve into the complexities of network design with degree constraints as outlined in the joint work by Guy Kortsarz, Rohit Khandekar, and Zeev Nutov. Explore various minimum-cost spanning subgraph scenarios, arborescence/tree spanning challenges, and prize-collecting Steiner network designs with deg
0 views • 17 slides
Embedding-Based Subgraph Isomorphism for Bug Detection
Explore how SICode utilizes embedding-based subgraph isomorphism identification to detect bugs in code efficiently. Learn about the challenges in subgraph matching algorithms and the solution offered by graph neural networks. Dive into the approach of SICode in training embedding models and detectin
0 views • 20 slides
Dynamic Graph Neural Networks for Anomaly Detection in Time Series
Explore how DGNN utilizes dynamic graph neural networks to detect anomalies in multivariate time series data efficiently. The approach includes Dynamic Subgraph Generation and Adaptive Graph Attention Network for precise learning of temporal relationships, outperforming traditional methods like PCA
1 views • 16 slides
Diversified Top-k Subgraph Querying in Large Graphs - Problem Definition and Solutions
Explore the problem of top-k subgraph querying in large graphs, aiming to provide diversified results with reduced overlap. Learn about the challenges, naive solutions, and proposed algorithms, including Ullmann framework and diversified top-k maximal clique approach.
0 views • 19 slides