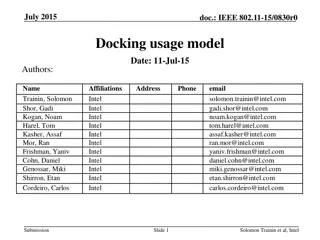
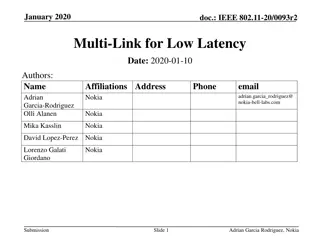
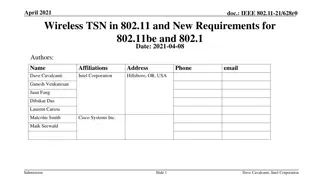
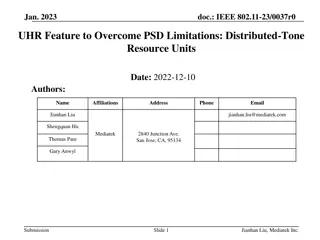
End-to-End Delay Control of Multimedia Applications over Multihop Wireless Links
Pervasive multimedia communications face challenges like channel fading and interference, making end-to-end delay control crucial in multi-hop wireless networks. This study discusses QoS requirements, upper-layer adaptation, and frameworks for ensuring optimal multimedia packet delivery. Techniques such as WTP Scheduler and Delay Monitor play key roles in managing end-to-end delay efficiently.
- Multimedia Communications
- Wireless Networks
- End-to-End Delay Control
- QoS Requirements
- Packet Prioritization
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
End-to-End Delay Control of Multimedia Applications over Multihop Wireless Links Wenbo He, Klara Nahrstedt University of Illinois at Urbana Champaign Xue Liu McGill University
Introduction Pervasive and ubiquitous multimedia communications are in great demand recently channel fading, multipath fading, and interference from background noise and neighbors end-to-end delay control in multi-hop wireless network is important for multimedia applications Upper-layer adaptation Prior studies 2
Design QoS requirements on two quantifiable metrics End-to-end latency Variance (jitter) Application layer adaptation: select an acceptable end-to-end delay requirement according to network condition feedback control in middleware: with the selected end-to-end delay requirement, prioritize multimedia packets dynamically according to observed delay 3
Differentiation WTP Scheduler (network layer) Service differentiation The actual quality level of each class will vary with traffic loads, the quality ratio between classes will remain constant in various-sized timescales selects the packet with the maximum normalized waiting time can control the average end-to-end delay by adjusting the priority of the multimedia flow 5
Delay Monitor (middleware) Measures the average round trip delay incurred to deliver multimedia packets for each application sender attaches time stamps when sending the packets receiver acquires the attached time stamp, and sends a middleware ACK back to the sender with the acquired time stamp sender retrieves the sending time stamp, and compares it with the current time stamp 6
Classifier (middleware) determines the service classes for packets according to their priorities Each service class is represented by the class parameter, which is a number obtained by rounding up the priority in a certain range 7
Requirement Adaptor (application layer) End-to-end latency, variance (jitter) D = {d1< d2< ... < dm} denotes the set of the multiple delay levels jreqdenotes required jitter selecting a delay expectation dreqfrom the set D according to network load condition Different delay expectations in set D result in different audio or video qualities 8
Priority Adaptor (middleware) Proportional (P) controller, Intergraded (I) controller dynamically adjust the priority of a multimedia application multimedia application to meet the end-to-end delay requirement priority adaptor delay requirement e(k) = d(k) refdelay wireless multihop system If e(k) can be kept around zero, the end-to-end delay of the system will be stabilized around the desired level Delay Monitor Whenever the delay monitor gets an estimated delay, the controller updates the priority 9
Experiments setup IEEE 802.11b environment two scenarios to evaluate the impact of feedback control framework on end-to-end delay provision in wireless ad hoc networks adopt javax.sound.sampled.AudioFormat to specify data format in audio streams 13
Scenario 1 14
Scenario 2 15
Efficiency of Priority Adaptation - scenario 1 End-to-end delay Without priority update Variable background traffic 16
Efficiency of Priority Adaptation - scenario 2 End-to-end delay Without priority update 17
End-to-End Delay Control for Multiple Multimedia Flows 18
Conclusion presents a feedback control framework for end-to- end delay management embedded in upper layers of the protocol stack The upper-layer adaptation is independent of PHY/MAC layer protocols can be widely used on different PHY/MAC hardware and protocols 21
Progress Available bandwidth estimation testbed Iperf or WBest? Ubuntu with Atheros chip as an access point hostapd with wmm settings 22