Understanding Air Pressure, Air Masses, and Fronts in Earth Science
Explore the concepts of air pressure, air masses, and fronts in Earth Science. Learn about the influence of high and low-pressure systems, isotherms, pressure centers, global winds, the Coriolis Effect, and how air masses like continental and maritime affect weather patterns. Discover the impact of different air masses such as continental polar, maritime polar, continental tropical, and maritime tropical on North America's climate.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
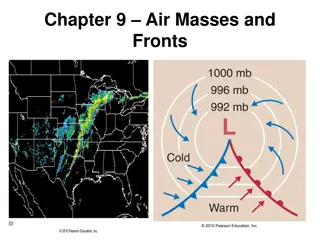
AIR PRESSURE, AIR MASSES AND FRONTS Earth Science
Air Pressure Air Pressure: The weight of the air pushing down on the surface of earth. Barometer: The tool that measures air pressure.
High and Low Pressure Systems High pressure is caused by Cool, Dry air SINKING. Low pressure is caused by Warm, Moist air RISING. Cool, Dry Air = High Pressure = Clear Skies Warm, Moist Air = Low Pressure = Cloudy Skies
ISOTHERMS Isotherms: Lines connecting place of equal temperature
Pressure Centers Isobars: Lines on a map connecting places with equal pressure. This shows you the area of High and Low Pressure. Arrows show direction of wind.
DRAWING ISOBARS 000
Global Winds Global Winds: the global circulation of air from HIGH pressure to LOW pressure. THE WINDS WILL BLOW FROM HIGH TO LOW The winds would go either North or South except for the Coriolis Effect causes the wind to curve to the RIGHT What Global Winds affect North America? Prevailing Westerlies
Coriolis Effect The apparent curve of the wind to the right in the Northern Hemisphere. Caused by Earth s Rotation http://www.wiley.com/college/strahler/0471480533/animations/ch07_a nimations/animation2.html
Pressure Systems Surface winds: High = Move OUT of the center Low = Move IN toward the center Add the Coriolis effect (curve to the right) Motion around a High = Clockwise Motion around a Low = Counter Clockwise AntiCyclone Cyclone
AIR MASSES Air Mass: A large volume of air defined by its TEMPERATURE and WATER VAPOR. c = Continental = Dry m = Maritime = Moist P = Polar = Cold T = Tropical = Warm cP = Continental Polar air = mP = Maritime Polar air = cT = Continental Tropical = mT = Maritime Tropical = Cold, Dry air from Canada Cold, Moist air from N. Atlantic Warm, Dry air from Mexico Warm, Moist air from Gulf of Mexico
Frontal Boundaries Frontal Boundary = Where two different air masses collide. Cool, Dry air collides with Warm, Moist air.
Cold Front Cold Front = Where a cP air mass collides with a mT air mass. cP air is doing the pushing. mT air is rising UP creating vertical clouds. Cumulonimbus clouds Thunderstorm What is the weather at A? What is the weather at B? What is the weather at C? C B A
Warm Front Warm Front = When a mT air mass collides with a cP air mass. mT air mass is doing the pushing. As mT air pushes, it rises over the cP air creating low horizontal clouds. Stratus, nimbostratus, cirrus What is the weather at A? What is the weather at B? What is the weather at C? A C B
Weather Map Symbols Identify the weather map symbols to determine weather in your area. Cold Front = Warm Front = cP mT
Weather Forecasting cP NW mT SW
Current U.S. Weather Map May 24, 2011
Fridays Weather Map mP mT
Hurricanes 3 things needed to form a hurricane Low Pressure Warm ocean temperatures High humidity
Hurricane Where are hurricanes located when at their strongest? Winds over 76 mph
Hurricanes What happens when the hurricane hits land?
Weather Station Model Used to deliver a lot of information in a small space