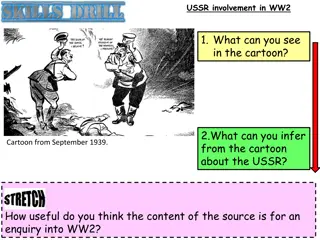
The Nazi Rise to Power and Seizure of Control
The ascent of the Nazi party in Germany was fueled by key factors such as high unemployment, effective propaganda, use of terror tactics, fear of communism, and the inadequacy of the existing democratic leadership. Through a series of events and political maneuvers, Hitler was eventually appointed Chancellor and granted sweeping powers, leading to the establishment of a totalitarian regime marked by oppression and violence.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
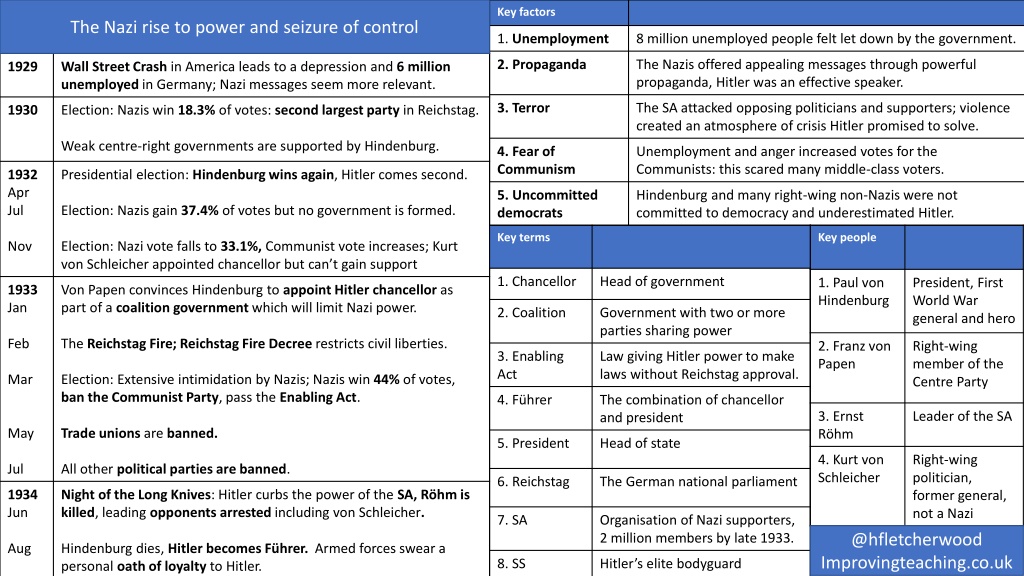
Key factors The Nazi rise to power and seizure of control 1. Unemployment 8 million unemployed people felt let down by the government. 2. Propaganda The Nazis offered appealing messages through powerful propaganda, Hitler was an effective speaker. 1929 Wall Street Crash in America leads to a depression and 6 million unemployedin Germany; Nazi messages seem more relevant. 3. Terror The SA attacked opposing politicians and supporters; violence created an atmosphere of crisis Hitler promised to solve. 1930 Election: Nazis win 18.3% of votes: second largest party in Reichstag. Weak centre-right governments are supported by Hindenburg. 4. Fear of Communism Unemployment and anger increased votes for the Communists: this scared many middle-class voters. 1932 Apr Jul Presidential election: Hindenburg wins again, Hitler comes second. 5. Uncommitted democrats Hindenburg and many right-wing non-Nazis were not committed to democracy and underestimated Hitler. Election: Nazis gain 37.4% of votes but no government is formed. Key terms Key people Nov Election: Nazi vote falls to 33.1%, Communist vote increases; Kurt von Schleicher appointed chancellor but can t gain support 1. Chancellor Head of government 1. Paul von Hindenburg President, First World War general and hero 1933 Jan Von Papen convinces Hindenburg to appoint Hitler chancellor as part of a coalition government which will limit Nazi power. 2. Coalition Government with two or more parties sharing power Feb The Reichstag Fire; Reichstag Fire Decree restricts civil liberties. 2. Franz von Papen Right-wing member of the Centre Party 3. Enabling Act Law giving Hitler power to make laws without Reichstag approval. Mar Election: Extensive intimidation by Nazis; Nazis win 44% of votes, ban the Communist Party, pass the Enabling Act. 4. F hrer The combination of chancellor and president 3. Ernst R hm Leader of the SA May Trade unions are banned. 5. President Head of state 4. Kurt von Schleicher Right-wing politician, former general, not a Nazi Jul All other political parties are banned. 6. Reichstag The German national parliament 1934 Jun Night of the Long Knives: Hitler curbs the power of the SA, R hm is killed, leading opponents arrested including von Schleicher. 7. SA Organisation of Nazi supporters, 2 million members by late 1933. @hfletcherwood Improvingteaching.co.uk Aug Hindenburg dies, Hitler becomes F hrer. Armed forces swear a personal oath of loyalty to Hitler. 8. SS Hitler s elite bodyguard
Idea/concept/knowledge Representation: image, model, metaphor Wall Street Crash 2008 financial crisis Vote increase Vote chart Nazi/Communist rivalry Nazi propaganda poster showing the hammer and sickle being crushed Fear of Communism Reminder of basic Communist beliefs: why might middle class people be opposed to these? President/Chancellor role Analogy of the role of the Queen vs Prime Minister, but where the Queen uses her ceremonial powers Show picture of Hindenburg meeting Hitler emphasise body language, decorations Enabling Act A law giving Hitler the power to make his own laws what s the consequence of this for a legislature? SA intimidation Imagine if you were trying to give a talk in class, and every time you spoke, someone shouted rude things at you and they jostled you as they left: would you come back for a second talk? Night of the Long Knives Quotations from Rohm emphasising his arrogance and hunger for power, left-wing ideas
Misconception Possible response Confuses SA/SS Pictures of uniforms, emphasising the SS as an elite force, SA as a mass movement Emphasise the length of time between the two late 1920s visit Germany poster Show voting figures for the Communists Confuse hyperinflation with the Great Depression The unemployed all turned to the Nazis Hitler s rise was inexorable Emphasise the contingency, fall in votes in November 1932 election Emphasise the ups and downs of the voting figures Show anti-Hitler propaganda Emphasise greater support among middle classes: link back to the Spartacists & the general strike against the Kapp Putsch Propaganda brainwashed the Germans Working classes were driven to vote for the Nazis
Horizon knowledge Value/application Prussia Authoritarian rule by Bismarck (but see also Prussian Landtag opposed to the Nazis) Italy Mussolini as model dictator for Hitler Communists Reminder of what the Communist party stands for, link with Animal Farm Show quotations for/against Hitler from the British press Unanimity for/against Hitler
Main content Wall Street Crash German economy Increasing popular support for the Nazis Terror, intimidation, repeated elections Foreshadow Revisit Horizon knowledge US in the 1920s Misconcept ions German money in the USA Increasing popular support for the Nazis Terror Hyperinflation and 1923 Weakness of democracy in the early 1920s Kapp Putsch and right-wing attempts at power All/none in favour of Hitler Seizure of control after becoming chancellor Mussolini s seizure of power, Communist dictatorship of the proletariat SA/SS, only SA violence Propaganda = brainwashing Seizure of control Further repression More free elections, role of the SA