Understanding Cage Culture in Aquaculture
Cage culture involves cultivating fish in meshed boxes submerged in water bodies like rivers, lakes, estuaries, and seas. Originating about 200 years ago, it has evolved into an intensive aquaculture method. Components like cage frame, floats, sinkers, and nets play crucial roles in this farming technique. Various types of cages, such as fixed, floating, submerged, and movable, cater to different environments for fish farming. Adequate feeding, including natural nutrients and artificial feed, ensures optimal fish production in cages, ranging from 3000 to 25,000 kg/ha/year in large-scale operations.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
CAGE CULTURE Mr. Bhartendu Vimal Guest Faculty-Asst. Professor CoF, Kishanganj, BASU, Patna
INTRODUCTION Culture of fishes in meshed boxes placed in water is called cage culture. It is an intensive method of aquaculture. Cage culture is practiced in areas where there is sufficient water movement. It is done in river, lakes, estuaries & seas.
HISTORY Cage culture originated in kampuchia about 200 years ago. Originally cages were used to transport fishes alive from the capture area to the market area.
COMPONENTS OF A CAGE FRAME- It can be made up of wood, plastic or steel. Generally plastic is used. FLOATS- They are made up of empty barrels or polythene balls. SINKERS- They are made up of stone concrete or metal.
NET -Three types of nets are present inner net, outer net & cover net. It is made up nylon, weld mesh or wooven split bamboo.
STRUCTURE OF CAGE The cage may be square, rectangular, circular six sided or eight sided. Generally, square and rectangular cages are prefered for culture. Normal size of the cage is 20 to 60 metre cube.
TYPES OFCAGES Based on installation cages are categorised into following types- FIXED CAGES- Installed in running water FLOATINGCAGES- Lakes,rivers & offshore water. SUBMERGED & MOVABLE CAGES- Areas affected by cyclone.
FEEDING The water movement bring in nutrients & natural feed. In addition artificial feed is also given. Example- Ricebran Fish meal Soyabean cake
FISH PRODUCTION The fish production ranges from 3000 to 25,000 kg/ha/year in large cages.
STOCKING DENSITY There is no standard stocking density for cages. The probable stocking density is given below- Carp fry- 210/metre cube Carp fingerlings 40/metre cube Tilapia 150/metre cube Murrel 40/metre cube
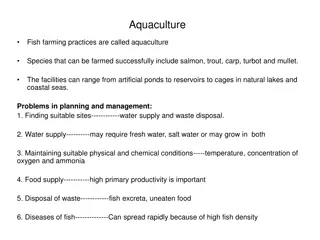
MANAGEMENT OF CAGES LOCATION PLANNING CAGE PREPRATION WATER QUALITY CONTROL SEED QUALITY ASSURANCE DISEASE ISSUE & MANAGEMENT HARVESTING
Advantages & limitations of cage culture Advantages Relatively low investment High production, faster growth Easy observation & management Treatment of disease Limitations Risk of theft Risk of fish lost Disease outbreak & control Low tolerance to poor water quality Movement and relocation of cages Difficult to operate in rough weather Water exchange is essential Rapid fouling Feed lost Environmental impacts (feed lost, fish waste Use available water resources Easy harvest Optimum use of feed High stocking density culture Reduce pressure on land Control reproduction Control predators and competitors