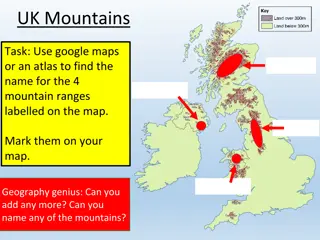
Understanding Rock Formation and the Rock Cycle
Explore how the Earth's surface is formed through the classification of rocks based on their processes of formation. Learn about different rock types such as igneous, sedimentary, and metamorphic rocks, and understand concepts like the rock cycle and the effects of pressure on sedimentary rocks.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Standards Review Rocks Rocks - -S6E5 how the earth s surface is formed. how the earth s surface is formed. c. Classify rocks by their process of formation. S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of . Students will investigate the scientific view of
2. . A student examining a rock notices that it 2. . A student examining a rock notices that it has large crystals and shades of colors such has large crystals and shades of colors such as gray and pink. as gray and pink. A. A. igneous rock igneous rock B. B. stratified rock stratified rock C. C. sedimentary rock sedimentary rock D. D. metamorphic rock metamorphic rock 1. 1. A scientist categorized a rock as an A scientist categorized a rock as an extrusive igneous rock. Another scientist extrusive igneous rock. Another scientist could accurately categorize the same rock could accurately categorize the same rock as as A. A. intrusive igneous. intrusive igneous. B. B. clastic sedimentary. clastic sedimentary. C. C. metamorphic. metamorphic. D. D. volcanic volcanic 4. Which of these BEST 4. Which of these BEST describes the concept of the rock cycle? rock cycle? A. A. sedimentary rocks may be re sedimentary rocks may be re- -melted several times times B. B. rocks move in circles on the earth as the earth rocks move in circles on the earth as the earth rotates rotates C. C. rocks can be moved from place to place on the rocks can be moved from place to place on the earth without changing earth without changing D. D. rocks are continually changing, and any type of rocks are continually changing, and any type of rock may be rock may be transformed into another type by appropriate transformed into another type by appropriate processes processes the concept of the 3. When buried sediments are subjected to 3. When buried sediments are subjected to pressure, the mineral grains are squeezed pressure, the mineral grains are squeezed together. What is the result of this action? together. What is the result of this action? melted several A. A. Volcanoes Volcanoes B. B. Earthquakes Earthquakes C. C. new rock is formed new rock is formed D. D. layers rise to the surface layers rise to the surface
2. . A student examining a rock notices that it 2. . A student examining a rock notices that it has large crystals and shades of colors such has large crystals and shades of colors such as gray and pink. as gray and pink. A. A. igneous rock igneous rock B. B. stratified rock stratified rock C. C. sedimentary rock sedimentary rock D. D. metamorphic rock metamorphic rock 1. 1. A scientist categorized a rock as an A scientist categorized a rock as an extrusive igneous rock. Another scientist extrusive igneous rock. Another scientist could accurately categorize the same rock could accurately categorize the same rock as as A. A. intrusive igneous. intrusive igneous. B. B. clastic sedimentary. clastic sedimentary. C. C. metamorphic. metamorphic. D. D. volcanic volcanic 3. When buried sediments are subjected to 3. When buried sediments are subjected to pressure, the mineral grains are squeezed pressure, the mineral grains are squeezed together. What is the result of this action? together. What is the result of this action? 4. With of these BEST describes the concept of the 4. With of these BEST describes the concept of the rock cycle? rock cycle? A. A. sedimentary rocks may be re sedimentary rocks may be re- -melted several times times B. B. rocks move in circles on the earth as the earth rocks move in circles on the earth as the earth rotates rotates C. C. rocks can be moved from place to place on rocks can be moved from place to place on the earth without changing the earth without changing D. D. rocks are continually changing, and any type rocks are continually changing, and any type of rock may be transformed into another type of rock may be transformed into another type by appropriate processes by appropriate processes melted several A. A. Volcanoes Volcanoes B. B. Earthquakes Earthquakes C. C. new rock is formed new rock is formed D. D. layers rise to the surface layers rise to the surface
2. The part of the rock cycle that transforms 2. The part of the rock cycle that transforms compressed rock formed from sea organism compressed rock formed from sea organism shells into a harder, denser rock is shells into a harder, denser rock is 1. 1. How are sedimentary rocks made? How are sedimentary rocks made? A. A. Magma or lava is cooled. Magma or lava is cooled. B. B. Materials are pressed together. Materials are pressed together. C. C. Chemical reactions change minerals. Chemical reactions change minerals. D. D. Earthquakes cause small pieces to Earthquakes cause small pieces to fall. fall. A. A. igneous rock becoming sedimentary igneous rock becoming sedimentary rock rock B. B. igneous rock becoming metamorphic igneous rock becoming metamorphic rock. rock. C. C. metamorphic rock becoming igneous metamorphic rock becoming igneous rock rock D. D. sedimentary rock becoming sedimentary rock becoming metamorphic rock. metamorphic rock. 3. Which of these are parts of the geologic 3. Which of these are parts of the geologic process that changes metamorphic rock into process that changes metamorphic rock into sedimentary rock? sedimentary rock? A. A. volcanic eruption and lava flow volcanic eruption and lava flow B. B. igneous intrusion and solidification igneous intrusion and solidification C. C. faulting and displacement faulting and displacement D. D. erosion and deposition erosion and deposition 4. Identify the next step in this sequence of events 4. Identify the next step in this sequence of events that occurs in the formation of rock. that occurs in the formation of rock. buried, compacted, heated, and ________ buried, compacted, heated, and ________ A. A. Buried Buried B. B. Eroded Eroded C. C. Deposited Deposited D. D. Recrystallized Recrystallized
2. . The part of the rock cycle that transforms 2. . The part of the rock cycle that transforms compressed rock formed from sea organism compressed rock formed from sea organism shells into a harder, denser rock is shells into a harder, denser rock is 1. 1. How are sedimentary rocks made? How are sedimentary rocks made? A. A. Magma or lava is cooled. Magma or lava is cooled. B. B. Materials are pressed together. Materials are pressed together. C. C. Chemical reactions change minerals. Chemical reactions change minerals. D. D. Earthquakes cause small pieces to Earthquakes cause small pieces to fall. fall. A. A. igneous rock becoming sedimentary rock igneous rock becoming sedimentary rock B. B. igneous rock becoming metamorphic igneous rock becoming metamorphic rock. rock. C. C. metamorphic rock becoming igneous metamorphic rock becoming igneous rock rock D. D. sedimentary rock becoming metamorphic sedimentary rock becoming metamorphic rock. rock. 3. Which of these are parts of the geologic 3. Which of these are parts of the geologic process that changes metamorphic rock into process that changes metamorphic rock into sedimentary rock? sedimentary rock? 4. . Identify the next step in this sequence of 4. . Identify the next step in this sequence of events that occurs in the formation of rock. events that occurs in the formation of rock. buried, compacted, heated, and ________ buried, compacted, heated, and ________ A. A. Buried Buried B. B. Eroded Eroded C. C. Deposited Deposited D. D. Recrystallized Recrystallized A. A. volcanic eruption and lava flow volcanic eruption and lava flow B. B. igneous intrusion and solidification igneous intrusion and solidification C. C. faulting and displacement faulting and displacement D. D. erosion and deposition erosion and deposition
Standards Review Rocks Rocks - -S6E5 how the earth s surface is formed. how the earth s surface is formed. d. Processes That Change Rocks S6E5. Students will investigate the scientific view of . Students will investigate the scientific view of
1. When a layer of sediment is deposited on 1. When a layer of sediment is deposited on the ocean floor, what is the next step in the the ocean floor, what is the next step in the formation of sedimentary rocks? formation of sedimentary rocks? 2. A huge, jagged rock sits atop a windy cliffside. Over 2. A huge, jagged rock sits atop a windy cliffside. Over a period of many years, how will the rock MOST LIKELY a period of many years, how will the rock MOST LIKELY change? change? A. A. Heating Heating B. B. Burying Burying C. C. Eroding Eroding D. D. weathering weathering A. A. It will become larger and smoother. It will become larger and smoother. B. B. It will become smaller and smoother. It will become smaller and smoother. C. C. It will become bigger and less smooth. It will become bigger and less smooth. D. D. It will become smaller and less smooth. It will become smaller and less smooth. 4. Small islands can form during the constructive 4. Small islands can form during the constructive process called process called A. A. erosion. erosion. B. B. Deposition. Deposition. C. C. Earthquakes. Earthquakes. D. D. Weathering. Weathering. 3. Which process accounts for the formation of 3. Which process accounts for the formation of horizontally layered rocks? horizontally layered rocks? A. A. Compaction and Cementation Compaction and Cementation B. B. Weathering and Erosion Weathering and Erosion C. C. Melting Melting D. D. Cooling Cooling
2. A huge, jagged rock sits atop a windy cliffside. 2. A huge, jagged rock sits atop a windy cliffside. Over a period of many years, how will the rock MOST Over a period of many years, how will the rock MOST LIKELY change? LIKELY change? When a layer of sediment is deposited on the When a layer of sediment is deposited on the ocean floor, what is the next step in the ocean floor, what is the next step in the formation of sedimentary rocks? formation of sedimentary rocks? A. A. It will become larger and smoother. It will become larger and smoother. B. B. It will become smaller and smoother. It will become smaller and smoother. C. C. It will become bigger and less smooth. It will become bigger and less smooth. D. D. It will become smaller and less smooth. It will become smaller and less smooth. A. A. Heating Heating B. B. Burying Burying C. C. Eroding Eroding D. D. weathering weathering 3. Which process accounts for the formation of 3. Which process accounts for the formation of horizontally layered rocks? horizontally layered rocks? 4. Small islands can form during the 4. Small islands can form during the constructive process called constructive process called A. A. Compaction and Cementation Compaction and Cementation B. B. Weathering and Erosion Weathering and Erosion C. C. Melting Melting D. D. Cooling Cooling A. A. erosion. erosion. B. B. Deposition. Deposition. C. C. Earthquakes. Earthquakes. D. D. Weathering. Weathering.
Standards Review Ocean Characteristics Ocean Characteristics S6E3. Students will recognize the S6E3. Students will recognize the significant role of water in earth processes. significant role of water in earth processes. c. Describe the composition, location, and subsurface topography of the world s oceans.
The continents do not end at the shoreline. Land The continents do not end at the shoreline. Land forms continue under the sea extending from the forms continue under the sea extending from the continental shelf to the deep ocean floor with a vast continental shelf to the deep ocean floor with a vast variety of life. variety of life. 2. The Hawaiian Islands were formed by 2. The Hawaiian Islands were formed by seamounts that rose above the ocean seamounts that rose above the ocean surface. What was the original source of the surface. What was the original source of the seamounts? seamounts? A. underwater volcanoes A. underwater volcanoes B. earthquakes B. earthquakes C. Landslides C. Landslides D. faulting D. faulting 1. 1. Choose a list of terms describing land forms Choose a list of terms describing land forms found on the ocean floor. found on the ocean floor. A. A. continental shelf and slope, mid continental shelf and slope, mid- -ocean ridge, rift zone, trench, and the ocean basin rift zone, trench, and the ocean basin B. B. continental rise and shelf, continent, ridge, continental rise and shelf, continent, ridge, canyon, trench, and typhoon canyon, trench, and typhoon C. C. tectonic plates, continental slope, island, tectonic plates, continental slope, island, mountain, reef, and the ocean barrier mountain, reef, and the ocean barrier D. D. continental shelf, ocean basin, mountain continental shelf, ocean basin, mountain ridge, rise, and tidal wave ridge, rise, and tidal wave ocean ridge, 4. How can you BEST describe the 4. How can you BEST describe the continental shelf? continental shelf? A. A. The continental shelf is very deep. The continental shelf is very deep. B. B. The continental shelf is the same The continental shelf is the same width around the edges of the width around the edges of the continents. continents. C. C. The continental shelf is the part of the The continental shelf is the part of the continent located above the water. continent located above the water. D. D. The continental shelf is an extension The continental shelf is an extension of the continent under the ocean of the continent under the ocean water. water. 3. There are three major oceans on Earth. They are 3. There are three major oceans on Earth. They are the the erosion erosion A. A. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. B. B. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. C. C. Atlantic, Arctic, and Antarctic Oceans. Atlantic, Arctic, and Antarctic Oceans. D. D. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indonesian Oceans Atlantic, Pacific, and Indonesian Oceans.
The continents do not end at the shoreline. Land The continents do not end at the shoreline. Land forms continue under the sea extending from the forms continue under the sea extending from the continental shelf to the deep ocean floor with a continental shelf to the deep ocean floor with a vast variety of life. vast variety of life. 2. The Hawaiian Islands were formed by 2. The Hawaiian Islands were formed by seamounts that rose above the ocean seamounts that rose above the ocean surface. What was the original source of the surface. What was the original source of the seamounts? seamounts? 1. 1. Choose a list of terms describing land forms Choose a list of terms describing land forms found on the ocean floor. found on the ocean floor. A. underwater volcanoes A. underwater volcanoes B. earthquakes B. earthquakes C. Landslides C. Landslides D. faulting D. faulting A. A. continental shelf and slope, mid continental shelf and slope, mid- -ocean ridge, rift zone, trench, and the ocean ridge, rift zone, trench, and the ocean basin basin B. B. continental rise and shelf, continent, ridge, continental rise and shelf, continent, ridge, canyon, trench, and typhoon canyon, trench, and typhoon C. C. tectonic plates, continental slope, island, tectonic plates, continental slope, island, mountain, reef, and the ocean barrier mountain, reef, and the ocean barrier D. D. continental shelf, ocean basin, mountain continental shelf, ocean basin, mountain ridge, rise, and tidal wave ridge, rise, and tidal wave ocean 4. How can you BEST describe the continental 4. How can you BEST describe the continental shelf? shelf? A. A. The continental shelf is very deep. The continental shelf is very deep. B. B. The continental shelf is the same width The continental shelf is the same width around the edges of the continents. around the edges of the continents. C. C. The continental shelf is the part of the The continental shelf is the part of the continent located above the water. continent located above the water. D. D. The continental shelf is an extension of The continental shelf is an extension of the continent under the ocean water. the continent under the ocean water. 3. There are three major oceans on Earth. They 3. There are three major oceans on Earth. They are the are the erosion erosion A. A. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. B. B. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indian Oceans. C. C. Atlantic, Arctic, and Antarctic Oceans. Atlantic, Arctic, and Antarctic Oceans. D. D. Atlantic, Pacific, and Indonesian Oceans Atlantic, Pacific, and Indonesian Oceans.
1. 1. Compare and contrast continental shelves Compare and contrast continental shelves and continental slopes. and continental slopes. 2. A part of an ocean basin area where new 2. A part of an ocean basin area where new ocean floor is formed is ______________. ocean floor is formed is ______________. A. abyssal plain. A. abyssal plain. B. mid B. mid- -ocean ridge. ocean ridge. C. continental shelf. C. continental shelf. D. trench. D. trench. 4. How does new ocean floor form? 4. How does new ocean floor form? 3. Submerged, inactive volcanic peaks located 3. Submerged, inactive volcanic peaks located on the ocean basins are known as ___________. on the ocean basins are known as ___________. A. trenches. A. trenches. B. continental slopes. B. continental slopes. C. seamounts. C. seamounts. D. continental shelves. D. continental shelves.
2. A part of an ocean basin area where new 2. A part of an ocean basin area where new ocean floor is formed is ______________. ocean floor is formed is ______________. 1. 1. Compare and contrast continental shelves Compare and contrast continental shelves and continental slopes. and continental slopes. A. abyssal plain. A. abyssal plain. B. B. mid mid- -ocean ridge. ocean ridge. C. continental shelf. C. continental shelf. D. trench. D. trench. They are adjacent to each other. They are adjacent to each other. Shelves are relatively flat; slopes Shelves are relatively flat; slopes steeper steeper 4. How does new ocean floor form? 4. How does new ocean floor form? 3. Submerged, inactive volcanic peaks located 3. Submerged, inactive volcanic peaks located on the ocean basins are known as ___________. on the ocean basins are known as ___________. Lava erupting from mid Lava erupting from mid- -ocean ridges forms new ocean floor. new ocean floor. ocean ridges forms A. trenches. A. trenches. B. continental slopes. B. continental slopes. C. C. seamounts. seamounts. D. continental shelves. D. continental shelves.