Understanding Rocks and the Rock Cycle
Explore the world of rocks through this educational content on Earth's surface, rock cycle, rock types (igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic), and the formation of igneous rocks from magma and lava. Learn how rocks are made of minerals, the continuous process of the rock cycle, and the classification of igneous rocks based on mineral composition and crystal size. Understand the origins of intrusive and extrusive igneous rocks in this comprehensive guide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Rocks Chapter 3 Earth s Surface
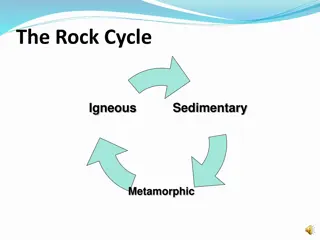
Rock Cycle 3.1
Rocks are made of minerals Rock a naturally formed solid that is usually made up of one or more types of minerals. Rocks and minerals are different! Minerals are always made of the same elements in the same proportions. Rocks do not have to have the same elements and proportions.
Rocks are all around Earth is built almost entirely of rock. Below the crust, Earth is made of solid and molten rock. Rocks can change, but this is a long slow process.
Rock Cycle Rock Cycle the natural process that form, change, break down and re-form rocks. There is no beginning and end to the cycle. There is no particular order, rocks can go back and forth between processes.
Rock Types Igneous Rock forms when molten rock cools and becomes solid. Sedimentary Rock forms when pieces of older rocks, plants and other material get pressed or cemented together. Metamorphic Rock forms when heat or pressure causes older rocks to change into new types of rocks.
Rock Cycle Fill in the blanks on the rock cycle handout. Check that you filled it out correctly! Paste the completed rock cycle into your science notebook.
Magma and Lava form different igneous rocks Igneous rocks form when molten rock cools and becomes solid. Magma is molten rock inside Earth. Lava is molten rock at Earth s surface. Igneous rocks are classified based on their mineral composition and crystal size.
Origin of Igneous Rocks: (where they form) Intrusive igneous rock forms when magma cools inside the Earth Extrusive igneous rock forms when lava cools on Earth s surface
Textures of Igneous Rocks The texture of an igneous rock depends on how quickly the magma or lava cools. Texture is the size of the mineral crystals. Slow cooling allows time for crystals to form. Intrusive Fast cooling leaves no time for crystals to form. Extrusive
Composition of Igneous Rocks Most igneous rocks are made up of silicate minerals. Remember silicate minerals are the most common group in Earth s crust. Igneous rocks high in silica are light in color. Igneous rocks low in silica are dark in color.
Intrusive Formed inside crust Large crystals due to slow cooling Extrusive Formed at surface Small crystals due to fast cooling Review and compare
High Silica Light in color Granite and ryholite Low Silica Dark in color Basalt and gabbro Review and compare
Igneous rocks last a long time Intrusive Rock formations As magma pushes up toward Earth's surface, it makes channels and other formations underground. Igneous rock can be left at the surface as other, weaker types of rock have been worn away.
Igneous rocks last a long time Extrusive Rock Formations Lava that is low in silica, such as basalt lava, flows easily and spreads out in thin sheets over great distances. Lava with more amounts of silica does not flow easily and tends to volcanoes with steep sides.
Hypothesis writing If 20 mL of water are put in 4 different containers Then the water from the ________________ will evaporate the fastest Because ________________________
Sedimentary Rocks 3.3 Materials that make up sediments 3 Groups of Sedimentary Rocks The processes that form Sedimentary Rocks Sedimentary Rocks record the past This is the outline for the notes Do not write it yet
Materials that makeup Sediments Sediments materials that settle out of water or air 1. Pieces of rocks 2. Pieces of minerals 3. Plant remains 4. Animal remains
Sediments Sediments are the small particles that form together to make sedimentary rocks Are the result of weathering and erosion Can be transported by wind and water
Groups of Sedimentary Rocks A. Rock Particles Pressure layers of sediment get pressed together to form rock Older layers are at the bottom Crystalized minerals cement particles together 1. 2.
Groups of Sedimentary Rocks B. Plants or shells get pressed together Coal made of plant remains Limestone made of shells of ocean organisms 1. 2.
Groups of Sedimentary Rocks C. Minerals re-form from water When water evaporates minerals are left behind Rock salt and gypsum are examples
Recording the past Fossils Evidence of wind and water in the past