Evaluating Cell Fate Determinants: Regulation of Notch by Prospero Transcription Factor
This study delves into the intricate interactions of cell fate determinants, focusing on the potential regulatory role of the Prospero transcription factor on the Notch signaling pathway. Through an evaluation of Prospero and Notch signaling, the research examines the impact of their collaboration in cell fate determination, particularly in the Drosophila eye. The background, methods, results, implications, and areas for further study are outlined, shedding light on the complex mechanisms underlying cell fate regulation.
- Cell Fate Determinants
- Prospero Transcription Factor
- Notch Signaling
- Regulation
- Cell Fate Determination
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
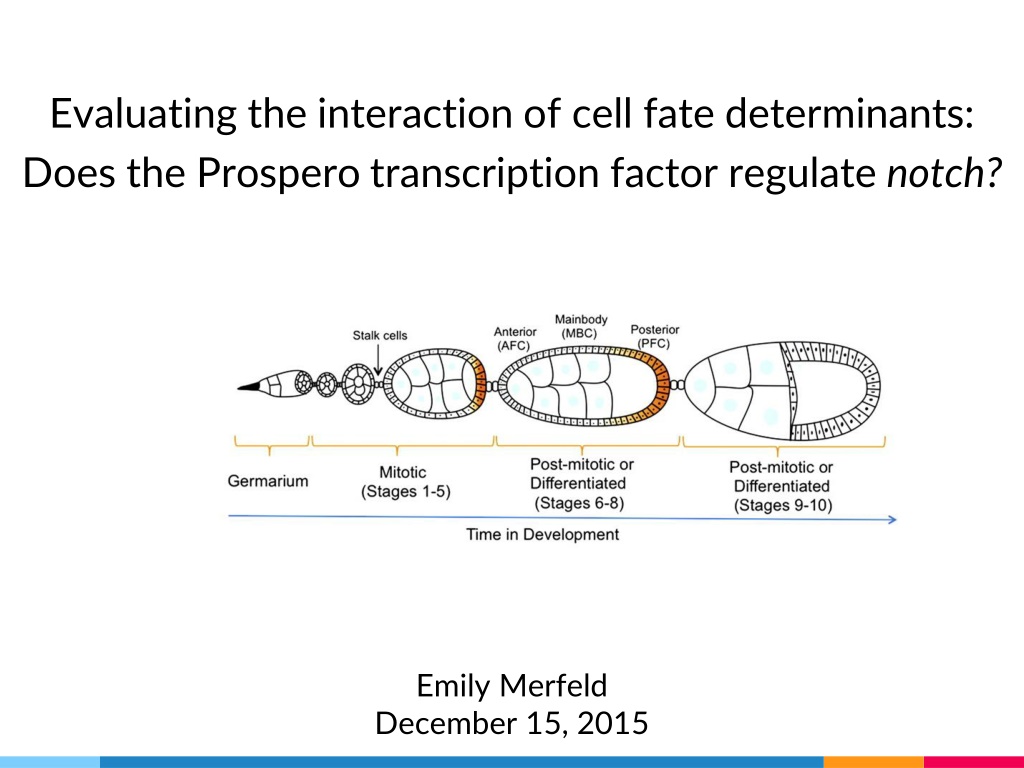
Evaluating the interaction of cell fate determinants: Does the Prospero transcription factor regulate notch? Emily Merfeld December 15, 2015
Outline 1. Background: Prospero and Notch signaling 1. Methods: Data and High-Level Coding Steps 1. Results 1. Implications & Areas for Further Study
Outline 1. Background: Prospero and Notch signaling 1. Methods: Data and High-Level Coding Steps 1. Results 1. Implications & Areas for Further Study
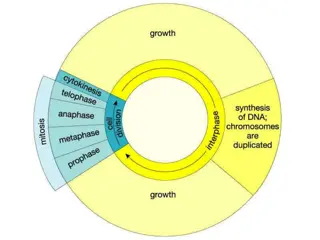
Background I: Cell fate Homem and Knoblich, 2012
Background II: Prospero Mutation of prospero altered gene expression in specific cell types, altered cell type ratio1 Prospero regulation of cell fate through several mechanisms: asymmetric localization of Prospero during division of neural stem cells2 regulation of stem cell self-renewal vs. cell proliferation3 1Doe et al., 1991 2Spana and Doe, 1995; 3Choksi et al., 2006
Background III: Notch Mutation of notch altered cell type ratio, altered growth & morphology Specific Notch pathway receptor and ligand expression cell fate determination1,2 Haines and Irvine, 2003 1Artavanis-Tsakonas et al.,, 1995; 2Haines and Irvine, 2003
Background IV: Prospero / Notch Interaction Prospero and Notch act together in cell fate determination in the Drosophila eye (1 photoreceptor neuron : 4 epithelial cells)1 Prospero is regulated by Notch in cell fate determination in sensory organs2 Notch signaling, and cell fate determination in general, rely on feedback regulation3 Does the Pros transcription factor bind to the notch promoter region as one form of such regulation? 1Charlton-Perkins et al., 2011; 2Reddy and Rodrigues, 1999; 3Artavanis-Tsakonas et al., 1999
Outline 1. Background: Prospero and Notch signaling 1. Methods: Data and High-Level Coding Steps 1. Results 1. Implications & Areas for Further Study
Methods I: Data notch promoter region: 1000 nucleotides upstream of the promoter, found through the UCSC Drosophila genome browser
Methods I: Data notch promoter region: attcctttgagccatagtccacccgaggctttgagttctcagcaatcaggcgaatgtttcgacgcttttcgatgagaacg tttcttcgttcgcctatcgataaccagttatcgatgatggtgagtcatgactcatgactggccacgagccaagtggggga ggagagaccgaaatagtcgcccacgccgaagtatctgaagtagctgccacaaggggcaaactcgtttgtcagctaag aaaaacccctttgccgactcgaccggcccagcatcattcatcagtttttgactgcaacttttacatcgcagcccattccc agtgcatttcattccattccaacgttccgggcgctttacaaatttaaagatcgtggccccatcaccgccgcctttcttctg tttcttctgcagcttccactcttcttcggcttccttggccgcttgtgttgcatgacctccttagggcgtaactgtgcttaagc atccaatccgccccgcagatcattggttaaagaattggtcggtgatgcgagtggatggaccaagaagacggggaaat gatagcctctggaattggcgcaattttcgccgagatttgctcacttgaataagcttttctgatgtttaaccgcctgggcat gaaactgttcaaaaatgaatggatgaagaatgctgggtaccaaaaaaaaaaaagcagaggaattcccctatataatcg tataatcgaagttacgataggttacccacggaatttcgagatgattcatttagttctgtttcgtttttttattttatttttttta ttttttttttttgagctagtctaattgtttatgcttacattttattgggttttaatttttcttcaaagggccgcttcaatctttttc ctctttgtgtttgtcttagattatttttaacgttttccttgttactttttcggtgccctcaacttgttttcccagcgaacaatttt agtgagttgccgcccgctgctgtgc
Methods I: Data Pros transcription factor binding site: C-A/t-c/t-N-N-C-T/c Table 1, Hassan et al., 1997
Methods II: High-level steps 1. Enumerate all possible binding sites from the consensus 1. Determine if any of these binding sites appear in the region upstream of notch
Methods II: Trickiest Problem Problem: enumerate all binding motifs from C-A/T-C/T-N-N-C-T/C Toy example: enumerate all binding motifs from A/T-C/T Input: bindingSite = A/TC/T Output: bindingSiteList = [ AC , AT , TC , TT ]
Methods II: Trickiest Problem Pseudocode generate blank bindingSiteList to hold all permutations of bindingSite for each element of bindingSite: if the element is a slash: add the letter before the slash to a permutation in bindingSiteList then add the letter after the slash to the next permutation otherwise add the element itself to BSL This method fills by column. Thus we have Repeats! A C T T A C T T bindingSiteList = [ AC , TT , AC , TT ] BSL=
Methods II: Trickiest Problem New approach: build a tree bindingSiteList = [ AC , AT , TC , TT ]
Methods II: Trickiest Problem Tree Method for C-A/T-N bindingSiteList = [ CAA , CAC , CAT, CAG , CTA, CTC, CTT, CTG]
bindingSiteList = ['cacaact', 'cacaacc', 'cacatct', 'cacatcc', 'cacacct', 'cacagcc', 'cactact', 'cactacc', 'cacttct', 'cacttcc', 'cactcct', 'cactccc', 'cactgct', 'cactgcc', 'caccact', 'caccacc', 'cacctct', 'caccccc', 'caccgct', 'cacgacc', 'cacgtct', 'cacgccc', 'cacggct', 'cataacc', 'catatct', 'catatcc', 'catacct', 'cataccc', 'catagct', 'catagcc', 'cattact', 'cattacc', 'catttct', 'catttcc', 'cattcct', 'cattccc', 'cattgct', 'cattgcc', 'catcact', 'catcacc', 'catctct', 'catctcc', 'catccct', 'catcccc', 'catcgct', 'catcgcc', 'catgact', 'catgacc', 'catgtct', 'catgtcc', 'catgcct', 'catgccc', 'catggct', 'catggcc', 'ctcaact', 'ctcaacc', 'ctcatct', 'ctcatcc', 'ctcacct', 'ctcaccc', 'ctcagct', 'ctcagcc', 'ctctact', 'ctctacc', 'ctcttct', 'ctcttcc', 'ctctcct', 'ctctccc', 'ctctgct', 'ctctgcc', 'ctccact', 'ctccacc', 'ctcctct', 'ctcctcc', 'ctcccct', 'ctccccc', 'ctccgct', 'ctccgcc', 'ctcgact', 'ctcgacc', 'ctcgtct', 'ctcgtcc', 'ctcgcct', 'ctcgccc', 'ctcggct', 'ctcggcc', 'cttaact', 'cttaacc', 'cttatct', 'cttatcc', 'cttacct', 'cttaccc', 'cttagct', 'cttagcc', 'ctttact', 'ctttacc', 'cttttct', 'cttttcc', 'ctttcct', 'ctttccc', 'ctttgct', 'ctttgcc', 'cttcact', 'cttcacc', 'cttctct', 'cttctcc', 'cttccct', 'cttcccc', 'cttcgct', 'cttcgcc', 'cttgact', 'cttgacc', 'cttgtct', 'cttgtcc', 'cttgcct', 'cttgccc', 'cttggct', 'cttggcc'] 'cacaccc', 'cacagct', 'cacctcc', 'caccgcc', 'cacgtcc', 'cacggcc', 'cacccct', 'cacgact', 'cacgcct', 'cataact',
promoterRegion = attcctttgagccatagtccacccgaggctttgagttctcagcaat caggcgaatgtttcgacgcttttcgatgagaacgtttcttcgttcg cctatcgataaccagttatcgatgatggtgagtcatgactcatga ctggccacgagccaagtgggggaggagagaccgaaatagtcgc ccacgccgaagtatctgaagtagctgccacaaggggcaaactcg tttgtcagctaagaaaaacccctttgccgactcgaccggcccagc atcattcatcagtttttgactgcaacttttacatcgcagcccattcc cagtgcatttcattccattccaacgttccgggcgctttacaaattta aagatcgtggccccatcaccgccgcctttcttctgtttcttctgca gcttccactcttcttcggcttccttggccgcttgtgttgcatgacct ccttagggcgtaactgtgcttaagcatccaatccgccccgcagat cattggttaaagaattggtcggtgatgcgagtggatggaccaag aagacggggaaatgatagcctctggaattggcgcaattttcgcc gagatttgctcacttgaataagcttttctgatgtttaaccgcctggg catgaaactgttcaaaaatgaatggatgaagaatgctgggtacc aaaaaaaaaaaagcagaggaattcccctatataatcgtataatc gaagttacgataggttacccacggaatttcgagatgattcatttag ttctgtttcgtttttttattttattttttttattttttttttttgagctagtc taattgtttatgcttacattttattgggttttaatttttcttcaaaggg ccgcttcaatctttttcctctttgtgtttgtcttagattatttttaacgt tttccttgttactttttcggtgccctcaacttgttttcccagcgaaca attttagtgagttgccgcccgctgctgtgc bindingSiteList = ['cacaact', 'cacaacc', 'cacatct', 'cacatcc', 'cacacct', 'cacagcc', 'cactact', 'cactacc', 'cacttct', 'cacttcc', 'cactcct', 'cactccc', 'cactgct', 'cactgcc', 'caccact', 'caccacc', 'cacctct', 'caccccc', 'caccgct', 'cacgacc', 'cacgtct', 'cacgccc', 'cacggct', 'cataacc', 'catatct', 'catatcc', 'catacct', 'cataccc', 'catagct', 'catagcc', 'cattact', 'cattacc', 'catttct', 'catttcc', 'cattcct', 'cattccc', 'cattgct', 'cattgcc', 'catcact', 'catcacc', 'catctct', 'catctcc', 'catccct', 'catcccc', 'catcgct', 'catcgcc', 'catgact', 'catgacc', 'catgtct', 'catgtcc', 'catgcct', 'catgccc', 'catggct', 'catggcc', 'ctcaact', 'ctcaacc', 'ctcatct', 'ctcatcc', 'ctcacct', 'ctcaccc', 'ctcagct', 'ctcagcc', 'ctctact', 'ctctacc', 'ctcttct', 'ctcttcc', 'ctctcct', 'ctctccc', 'ctctgct', 'ctctgcc', 'ctccact', 'ctccacc', 'ctcctct', 'ctcctcc', 'ctcccct', 'ctccccc', 'ctccgct', 'ctccgcc', 'ctcgact', 'ctcgacc', 'ctcgtct', 'ctcgtcc', 'ctcgcct', 'ctcgccc', 'ctcggct', 'ctcggcc', 'cttaact', 'cttaacc', 'cttatct', 'cttatcc', 'cttacct', 'cttaccc', 'cttagct', 'cttagcc', 'ctttact', 'ctttacc', 'cttttct', 'cttttcc', 'ctttcct', 'ctttccc', 'ctttgct', 'ctttgcc', 'cttcact', 'cttcacc', 'cttctct', 'cttctcc', 'cttccct', 'cttcccc', 'cttcgct', 'cttcgcc', 'cttgact', 'cttgacc', 'cttgtct', 'cttgtcc', 'cttgcct', 'cttgccc', 'cttggct', 'cttggcc'] 'cacaccc', 'cacagct', 'cacctcc', 'caccgcc', 'cacgtcc', 'cacggcc', 'cacccct', 'cacgact', 'cacgcct', 'cataact',
promoterRegion = attcctttgagccatagtccacccgaggctttgagttctcagcaat caggcgaatgtttcgacgcttttcgatgagaacgtttcttcgttcg cctatcgataaccagttatcgatgatggtgagtcatgactcatga ctggccacgagccaagtgggggaggagagaccgaaatagtcgc ccacgccgaagtatctgaagtagctgccacaaggggcaaactcg tttgtcagctaagaaaaacccctttgccgactcgaccggcccagc atcattcatcagtttttgactgcaacttttacatcgcagcccattcc cagtgcatttcattccattccaacgttccgggcgctttacaaattta aagatcgtggccccatcaccgccgcctttcttctgtttcttctgca gcttccactcttcttcggcttccttggccgcttgtgttgcatgacct ccttagggcgtaactgtgcttaagcatccaatccgccccgcagat cattggttaaagaattggtcggtgatgcgagtggatggaccaag aagacggggaaatgatagcctctggaattggcgcaattttcgcc gagatttgctcacttgaataagcttttctgatgtttaaccgcctggg catgaaactgttcaaaaatgaatggatgaagaatgctgggtacc aaaaaaaaaaaagcagaggaattcccctatataatcgtataatc gaagttacgataggttacccacggaatttcgagatgattcatttag ttctgtttcgtttttttattttattttttttattttttttttttgagctagtc taattgtttatgcttacattttattgggttttaatttttcttcaaaggg ccgcttcaatctttttcctctttgtgtttgtcttagattatttttaacgt tttccttgttactttttcggtgccctcaacttgttttcccagcgaaca attttagtgagttgccgcccgctgctgtgc bindingSiteList = ['cacaact', 'cacaacc', 'cacatct', 'cacatcc', 'cacacct', 'cacagcc', 'cactact', 'cactacc', 'cacttct', 'cacttcc', 'cactcct', 'cactccc', 'cactgct', 'cactgcc', 'caccact', 'caccacc', 'cacctct', 'caccccc', 'caccgct', 'cacgacc', 'cacgtct', 'cacgccc', 'cacggct', 'cataacc', 'catatct', 'catatcc', 'catacct', 'cataccc', 'catagct', 'catagcc', 'cattact', 'cattacc', 'catttct', 'catttcc', 'cattcct', 'cattccc', 'cattgct', 'cattgcc', 'catcact', 'catcacc', 'catctct', 'catctcc', 'catccct', 'catcccc', 'catcgct', 'catcgcc', 'catgact', 'catgacc', 'catgtct', 'catgtcc', 'catgcct', 'catgccc', 'catggct', 'catggcc', 'ctcaact', 'ctcaacc', 'ctcatct', 'ctcatcc', 'ctcacct', 'ctcaccc', 'ctcagct', 'ctcagcc', 'ctctact', 'ctctacc', 'ctcttct', 'ctcttcc', 'ctctcct', 'ctctccc', 'ctctgct', 'ctctgcc', 'ctccact', 'ctccacc', 'ctcctct', 'ctcctcc', 'ctcccct', 'ctccccc', 'ctccgct', 'ctccgcc', 'ctcgact', 'ctcgacc', 'ctcgtct', 'ctcgtcc', 'ctcgcct', 'ctcgccc', 'ctcggct', 'ctcggcc', 'cttaact', 'cttaacc', 'cttatct', 'cttatcc', 'cttacct', 'cttaccc', 'cttagct', 'cttagcc', 'ctttact', 'ctttacc', 'cttttct', 'cttttcc', 'ctttcct', 'ctttccc', 'ctttgct', 'ctttgcc', 'cttcact', 'cttcacc', 'cttctct', 'cttctcc', 'cttccct', 'cttcccc', 'cttcgct', 'cttcgcc', 'cttgact', 'cttgacc', 'cttgtct', 'cttgtcc', 'cttgcct', 'cttgccc', 'cttggct', 'cttggcc'] 'cacaccc', 'cacagct', 'cacctcc', 'caccgcc', 'cacgtcc', 'cacggcc', 'cacccct', 'cacgact', 'cacgcct', 'cataact',
Outline 1. Background: Prospero and Notch signaling 1. Methods: Data and High-Level Coding Steps 1. Results 1. Implications & Areas for Further Study
Results: Pros binding sites in notch promoter region attcctttgagccatagtccacccgaggctttgagttctcagcaatcaggcgaatgtttcgacgcttttcgatga gaacgtttcttcgttcgcctatcgataaccagttatcgatgatggtgagtcatgactcatgactggccacgagc caagtgggggaggagagaccgaaatagtcgcccacgccgaagtatctgaagtagctgccacaaggggcaa actcgtttgtcagctaagaaaaacccctttgccgactcgaccggcccagcatcattcatcagtttttgactgca acttttacatcgcagcccattcccagtgcatttcattccattccaacgttccgggcgctttacaaatttaaagat cgtggccccatcaccgccgcctttcttctgtttcttctgcagcttccactcttcttcggcttccttggccgcttgt gttgcatgacctccttagggcgtaactgtgcttaagcatccaatccgccccgcagatcattggttaaagaattg gtcggtgatgcgagtggatggaccaagaagacggggaaatgatagcctctggaattggcgcaattttcgccg agatttgctcacttgaataagcttttctgatgtttaaccgcctgggcatgaaactgttcaaaaatgaatggatga agaatgctgggtaccaaaaaaaaaaaagcagaggaattcccctatataatcgtataatcgaagttacgatag gttacccacggaatttcgagatgattcatttagttctgtttcgtttttttattttattttttttattttttttttttgagct agtctaattgtttatgcttacattttattgggttttaatttttcttcaaagggccgcttcaatctttttcctctttgtg tttgtcttagattatttttaacgttttccttgttactttttcggtgccctcaacttgttttcccagcgaacaattttag tgagttgccgcccgctgctgtgc bindingSites = ['catgact', 'ctttgcc', 'ctcgacc', 'cattccc', 'catcacc', 'caccgcc', 'ctcttct', 'cttggcc', 'catgacc', 'cttttct', 'ctcaact']
Outline 1. Background: Prospero and Notch signaling 1. Methods: Data and High-Level Coding Steps 1. Results 1. Implications & Areas for Further Study
Implications Pros transcription factor may regulate Notch expression in cells novel mechanism of cell differentiation regulation Relevance to cancer: Misregulation of cell differentiation has been linked to cancer development and tumorous growth1 Preestablished role of Notch2and Prospero3 signaling in cancer interactive role in cancer? 1Al-Hajj et al., 2003; 2Arnold et al., 2015; 3Lu et al., 2012
Areas for Further Study Computational problems Is this statistically significant? Does the Pros transcription factor regulate other elements of the Notch signaling pathway? Artavania-Taakonas et al., 1999 Empirical problems in vitro: are these sequences sufficient for Pros binding? in vivo: do prospero-KDs show altered notch RNA expression?
References Al-Hajj, M., Wicha, M. S., Benito-Hernandez, A., Morrison, S. J., & Clarke, M. F. (2003). Prospective identification of tumorigenic breast cancer cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 100(7), 3983 8. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0530291100 Arnold, K. M., Opdenaker, L. M., Flynn, D., & Sims-mourtada, J. (2015). Cancer Growth and Metastasis of Treatment Resistance in Breast Cancer. Cancer Growht and Metastasis, 1 13. http://doi.org/10.4137/CGM.S11286.RECEIVED Artavanis-tsakonas, S., Rand, M. D., & Lake, R. J. (1999). Notch Signaling : Cell Fate Control and Signal Integration in Development. Signal Transduction, 284(April), 770 776. http://doi.org/10.1126/science.284.5415.770 Charlton-Perkins, M., Whitaker, S. L., Fei, Y., Xie, B., Li-Kroeger, D., Gebelein, B., & Cook, T. (2011). Prospero and Pax2 combinatorially control neural cell fate decisions by modulating Ras- and Notch-dependent signaling. Neural Development, 6(1), 20. http://doi.org/10.1186/1749-8104-6-20 Choksi, S. P., Southall, T. D., Bossing, T., Edoff, K., de Wit, E., Fischer, B. E., Brand, A. H. (2006). Prospero acts as a binary switch between self-renewal and differentiation in Drosophila neural stem cells. Developmental Cell, 11(6), 775 89. http://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2006.09.015 Doe, C., Chu-LaGraff, Q., Wright, D., & Scott, M. (1991). The prospero gene specifies cell fates in the Drosophila central nervous system. Cell. Retrieved from http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/0092867491904639 Haines, N., & Irvine, K. D. (2003). Glycosylation regulates Notch signalling. Nature Reviews. Molecular Cell Biology, 4(10), 786 797. http://doi.org/10.1038/nrm1228 Hassan, B., Li, L., Bremer, K. a., Chang, W., Pinsonneault, J., & Vaessin, H. (1997). Prospero is a panneural transcription factor that modulates homeodomain protein activity. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 94(20), 10991 10996. http://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.94.20.10991 Lu, M.-H., Huang, C.-C., Pan, M.-R., Chen, H.-H., & Hung, W.-C. (2012). Prospero Homeobox 1 Promotes Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Colon Cancer Cells by Inhibiting E-cadherin via miR-9. Clinical Cancer Research, 18(23), 6416 6425. http://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0832 Reddy, G. V, & Rodrigues, V. (1999). Sibling cell fate in the Drosophila adult external sense organ lineage is specified by prospero function, which is regulated by Numb and Notch. Development, 126(10), 2083 92. Retrieved from http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/10207134 Spana, E. P., & Doe, C. Q. (1995). The prospero transcription factor is asymmetrically localized to the cell cortex during neuroblast mitosis in Drosophila. Development (Cambridge, England), 121, 3187 3195. http://doi.org/10.1016/0168-9525(96)81394-1