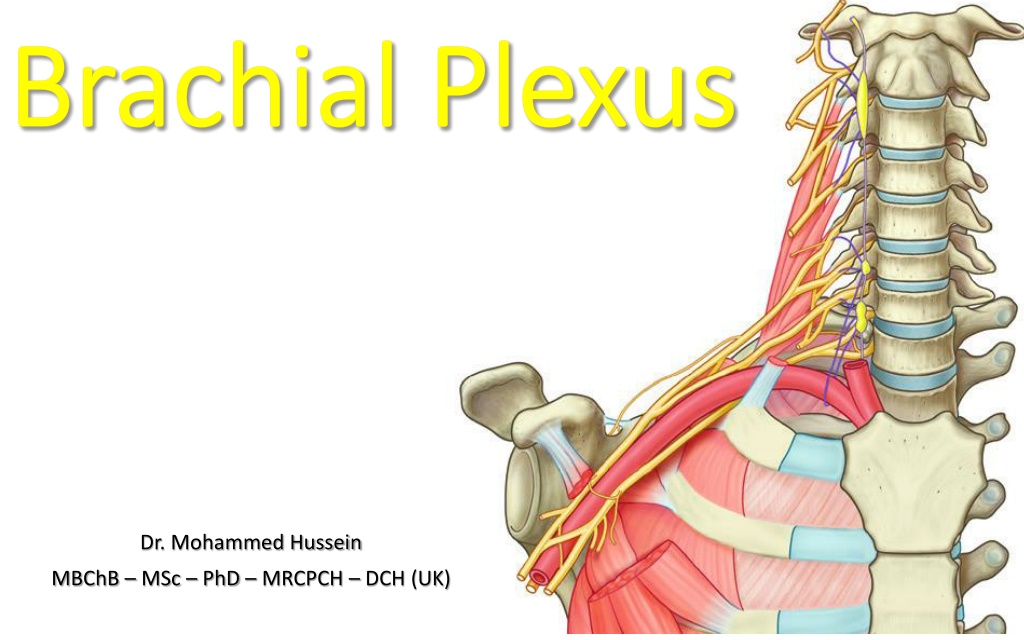
Understanding the Brachial Plexus Anatomy and Function
The brachial plexus is a crucial network of nerves in the upper limb, formed by nerve fibers originating from C5 to T1 spinal levels. It plays a significant role in innervating the upper extremity muscles and providing sensory feedback. The plexus is categorized into roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and branches, with each part serving specific functions in nerve transmission. Knowledge of the brachial plexus structure is essential for understanding upper limb pathology, diagnosing nerve injuries, and performing surgical interventions.
Uploaded on Jul 19, 2024 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Brachial Plexus Brachial Plexus Dr. Mohammed Hussein MBChB MSc PhD MRCPCH DCH (UK)
Nerve Nerve plexuses plexuses Nerve plexuses are combined nerve fibers from different sources or levels to form new nerves with specific targets or destinations. Nerve plexuses are either somatic or visceral.
Brachial Plexus Brachial Plexus The brachial plexus is a somatic nerve plexus formed by: 1. The anterior rami of C5 to C8 2. Most of the anterior ramus of T1
Brachial Plexus Brachial Plexus The plexus originates in the neck, passes laterally and inferiorly over rib I, and enters the axilla
Brachial Plexus Brachial Plexus Proximal parts of the brachial plexus are posterior to the subclavian artery in the neck. While more distal regions of the plexus surround the axillary artery. Subclavian artery Axillary artery
The parts of the brachial plexus, from medial to lateral, are: Roots + Trunks Divisions + Cords Branches
CI CII Roots CIII Trunks CIV C5 Anterior rami of spinal nerves C5-T1 CV C6 CVI Divisions C7 CVII C8 Cords T1 TI Terminal branches
Cords Roots Terminal Branches Divisions Trunk C5 Anterior Lateral Superior C6 C7 Posterior Posterior Middle C8 Medial Anterior Inferior T1
Roots Roots C5 C6 C7 Subclavian A. C8 T1
Trunks Trunks The three trunks of the brachial plexus originate from the roots, pass laterally over rib I, and enter the axilla. The Superior (Upper) Trunk Union of C5 and C6 roots C5 is formed by C6 C7 The Middle Trunk Continuation of the C7 root is a C8 T1 The Inferior (Lower) Trunk Union of the C8 and T1 roots is formed by
Divisions Divisions Each of the three trunks of the brachial plexus divides into an anterior and a posterior division: The three posterior divisions combine to form parts of the brachial plexus that give rise to nerves associated with the posterior compartments of the arm and forearm. The three anterior divisions form parts of the brachial plexus that ultimately give rise to peripheral nerves associated with the anterior compartments of the arm and forearm. No peripheral nerves originate directly from the divisions of the brachial plexus.
The Trunks The Divisions
Cords Cords The three cords of the brachial plexus originate from the divisions The posterior cord is formed by the union of all posterior divisions The lateral cord is the union of the anterior divisions of superior and middle trunks The medial cord is the direct continuation of the anterior division of inferior trunk
The Divisions The cords are related to the 2nd part of the axillary artery. The lateral cord is lateral to the artery. The medial cord is medial to the artery. The posterior cord is posterior to the artery.
Generally: Nerves associated with the anterior compartments of the upper limb arise from the medial and lateral cords Nerves associated with the posterior compartments of the upper limb arise from the posterior cord
Branches Branches Generally there are 16 branches 2 from the Roots 2 from the Superior Trunk 0from the Divisions 12 from the Cords o 3 form the lateral cord o 5 from the medial cord o 5 from the posterior cord
12 0 2 2 3 5 5
Branches of Roots Branches of Roots 2 2 Branches Branches 1. Dorsal scapular N. 1. Dorsal scapular N. 2. Long thoracic N. 2. Long thoracic N.
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 Dorsal scapular nerve C6 C7 T1 T2
C1 C2 C3 C4 C5 C6 Long thoracic nerve C7 T1 T2
2 2 Branches of Branches of Superior Superior Trunk Trunk Branches Branches 1. 1. Supra Suprascapular N. scapular N. 2. Nerve to 2. Nerve to Sub Subclavius clavius
Superior trunk Suprascapular nerve
Suprascapular nerve Suprascapular foramen Supraspinatus and infraspinatus muscles
Superior trunk Nerve to subclavius
3 3 Branches of Branches of Lateral Lateral Cord Cord Branches Branches 1. 1. Lateral Lateral pectoral N. pectoral N. 2. Musculocutaneous N. 2. Musculocutaneous N. 3. The 3. The lateral lateral root of median N. root of median N.
Lateral pectoral nerve Musculocutaneous nerve Lateral root of median nerve Median nerve Branches of lateral cord 1. Lateral pectoral nerve 2. Musculocutaneous nerve 3. Lateral root of median nerve
5 5 Branches of Branches of Medial Medial Cord Cord Branches Branches 1. 1. Medial Medial pectoral N. pectoral N. 2. 2. Medial Medial Cut. N. of arm Cut. N. of arm 3. 3. Medial Medial Cut. N. of forearm Cut. N. of forearm 4. The 4. The medial medial root of median N. root of median N. 5. Ulnar N. 5. Ulnar N.
Medial pectoral nerve Medial cutaneous nerve of arm Median nerve Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm Ulnar nerve Branches of medial cord 1. Medial pectoral nerve 2. Medial cutaneous nerve of arm 3. Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm 4. Medial root of median nerve 5. Ulnar nerve
5 5 Branches of Posterior Cord Branches of Posterior Cord Branches Branches STARS STARS 1. Superior 1. Superior S Subscapular N. ubscapular N. 2. 2. T Thoracodorsal N. horacodorsal N. 3. 3. A Axillary N. xillary N. 4. 4. R Radial N. adial N. 5. Inferior 5. Inferior S Subscapular N. ubscapular N.
Branches of posterior cord 1. Superior Subscapular nerve 2. Thoracodorsal nerve 3. Axillary nerve 4. Radial nerve 5. Inferior Subscapular nerve
Superior subscapular nerve Thoracodorsal nerve Inferior subscapular nerve Posterior cutaneous nerve of arm Branches of posterior cord 1. Superior Subscapular nerve 2. Thoracodorsal nerve 3. Axillary nerve 4. Radial nerve 5. Inferior Subscapular nerve
Branches of the roots Branches of the roots Branch name Dorsal scapular Origin C5 root Root value (Spinal segment) C5 Function Motor: Rhomboid major, Rhomboid minor, Levator scapulae
Branches of the roots Branches of the roots Branch name Long thoracic Origin C5 to C7 roots Root value (Spinal segment) C5 to C7 Function Motor: Serratus anterior
Branches of the superior trunk Branches of the superior trunk Branch name Suprascapular Origin Superior trunk Root value (Spinal segment) C5, C6 Function Motor: Supraspinatus, infraspinatus
Branches of the superior trunk Branches of the superior trunk Branch name Nerve to subclavius Origin Superior trunk Root value (Spinal segment) C5, C6 Function Motor: Subclavius
Branches of the lateral cord Branches of the lateral cord Branch name Lateral pectoral Origin Lateral cord Root value (Spinal segment) C5 to C7 Function Motor: Pectoralis major
Branches of the lateral cord Branches of the lateral cord Branch name Musculocutaneous Origin Lateral cord Root value (Spinal segment) C5 to C7 Motor: All muscles in the anterior compartment of the arm Sensory: Skin on lateral side of forearm Function
Branches of the medial cord Branches of the medial cord Branch name Medial pectoral Origin Medial cord Root value (Spinal segment) C8, T1 Function Motor: Pectoralis major, pectoralis minor
Branches of the medial cord Branches of the medial cord Branch name Medial cutaneous nerve of arm Origin Medial cord Root value (Spinal segment) C8, T1 Function Sensory: Skin on medial side of distal one-third of arm
Branches of the medial cord Branches of the medial cord Branch name Medial cutaneous nerve of forearm Origin Medial cord Root value (Spinal segment) C8, T1 Function Sensory: Skin on medial side of side of forearm
Branches of the medial cord Branches of the medial cord Branch name Ulnar Origin Medial cord Root value (Spinal segment) C8, T1 Motor: All intrinsic muscles of the hand (except three thenar muscles and two lateral lumbricals) and FCU and medial of FDP Sensory: medial 1 fingers Function
The median nerve The median nerve Branch name Median nerve Origin Medial and lateral cords Root value (Spinal segment) (C5), C6 to T1 Motor: All muscles in the anterior compartment of the forearm (except 1 & 1/2 muscles) and thenar and lateral 2 lumbricals Sensory: lateral 3 fingers Function
Branches of the posterior cord Branches of the posterior cord Branch name Superior subscapular Origin Posterior cord Root value (Spinal segment) C5, C6 Function Motor: Subscapularis
Branches of the posterior cord Branches of the posterior cord Branch name Inferior subscapular Origin Posterior cord Root value (Spinal segment) C5, C6 Function Motor: Subscapularis, teres major