Core Area of Statutory Bank Branch Audit and Review of Advances by Hitesh Pomal
Explore the core areas of statutory bank branch audit, advances, NPAs, types of advances, review of advances, and considerations during the review. Learn about sanctioned terms, parameters, consortium advances, and frequent MOCs reported by auditors. Understand IRAC norms regarding income recognition and asset classification.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Core Area of Statutory Bank Branch Audit ADVANCES & NPA CA Hitesh Pomal
Presentation Walkthrough..
Types of Advances 1. Funded Loans Term Loans Cash Credit Overdraft Funded Interest Term Loans Demand Loans
2. Non-Funded Loans Letter of Credit (LC) Bank Guarantee (BG) Bills Discounting
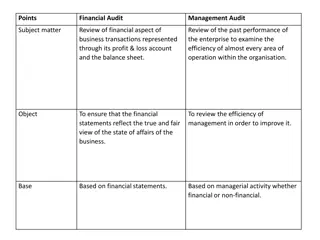
Review of Advances
Sanction Term Things to be Considered during review of Advances Compliance of RBI Norms & Bank Policy Track Record of Customer Credit Rating Authorization Level Authorization Limit
Things to be Considered during review of Advances Parameters of Interest & Penalties Review of Advances on a Regular Intervals Value of Securities Creation of Charges on securities Drawing Power
Things to be Considered during review of Advances Terms for Consortium Advances Stock Audit or Physical Verification Credit Summation against interest debited Valuation of Security Ad hoc Provision in case of Fraud
Frequent MOC s reported by Auditors Change in Date of NPA Details in deduction Column ECGC/CGTMSE/IRRD etc. Addition to NPAs Change in Provision Addition to NPA s Reversal of Un-realized Interest identified as FRAUD Unexpired Discount/Processing Change in Status of NPA Charges/Short/Excess interest Changes in Security Value Charged Apportioning of common Reversal of Interest wrongly security available to all the debited to NPA account credit facilities in case of Rectification of wrong accounting group accounts. of Recovery in NPA accounts
IRAC Norms (Income Recognition and Asset Classification) Asset Classification Income Recognition
KEY HIGHLIGHTS Simplest Definition : An Asset, including a leased asset, when it ceases to generate income for the bank is Non Performing Asset (NPA) Record of Recovery is the Thumb Rule & Not security available NPA Date is of Utmost Important : To ensure Actual Date of NPA is used. However, if restructuring fails, original date of NPA (As if No restructuring is done)
Definitions Income Recognition Asset Classification Provisioning Norms Writing Off NPAs, etc.. Most Important
Stress Test Accounts remain mostly above limit Frequent cheque bouncing/dishonour Frequent TOD sanctioned and outstanding Turnover in loan account much lower than purchase/sale of stock Discounted bills remain unrealised Frequent LC devolvement Non submission of stock statements/financials on time Submitted stock statements are not proper and mismatch between audited figures/ stock audit reports Ad hoc limits/ Delay in renewal of limits Undue delay in commencement of projects Funded/unfunded limits not commensurate with operations Bills discounting disproportionate to operations (accommodation) Specific economic conditions affecting the borrower
NPA Nature of Facility Term Loan Overdraft/ Cash Credit Bills Purchased/Discounted Parameters Interest and/or instalment of principal remain overdue beyond 90 days Remains out of order as indicated above Remains overdue beyond 90 days Agriculture Loan (Short Duration Crops) Instalment of principal or interest thereon remains overdue for 2 crop seasons Agriculture Loan (Long Duration Crops) Instalment of principal or interest thereon remains overdue for 1 crop seasons Securitization Transaction Amount of liquidity facility remains outstanding beyond 90 days Overdue receivables representing positive mark-to-market value of a derivative contract which remains unpaid beyond 90 days from specified due date for payment Derivative Transactions
Classification of Advances Standard Assets Sub-Standard Assets Doubtful Assets Loss Assets Regular repayment interest and/or instalments in of Loss identified by : Remained NPA Remained in the sub-standard category period of months for a period for a >12 1. The bank less than or Does not carry more normal risk equal to 12 than 2. The internal or external auditors Collection liquidation in full is improbable questionable & months highly 3. inspection The RBI Not a non performing asset or
Asset Classification to be borrower-wise and not facility-wise It is difficult to envisage a situation when only one facility to a borrower becomes a problem credit and not others. Therefore, all the facilities granted by a bank to a borrower will have to be treated as NPA and not the particular facility which has become irregular.
Debits out of Devolvement of LCs invoked If the debits arising out of devolvement of letters of credit or invoked guarantees are parked in a separate account, the balance outstanding in that account also should be treated as a part of the borrower s principal operating account for the purpose of application of prudential norms on income recognition, asset classification and provisioning.
Treatment of Bill Discounting under LC The bills discounted under LC favoring a borrower may not be classified as a Non- performing assets (NPA), when any other facility granted to the borrower is classified as NPA. However, in case documents under LC are not accepted on presentation or the payment under the LC is not made on the due date by the LC issuing bank for any reason and the borrower does not immediately make good the amount disbursed as a result of discounting of concerned bills, the outstanding bills discounted will immediately be classified as NPA with effect from the date when the other facilities had been classified as NPA.
FITL (Funded Interest term loan) The FITL / debt or equity instrument created by conversion of unpaid interest will be classified in the same asset classification category in which the restructured advance has been classified. Further movement in the asset classification of FITL / debt or equity instruments would also be determined based on the subsequent asset classification of the restructured advance.
Provisioning norms Sub - Standard Assets 1 A general provision of 15 percent on total outstanding should be made without making any allowance for ECGC guarantee cover and securities available.
Provisioning norms Doubtful Assets 100 percent of the extent to which the advance is not covered by the realizable value of the security to which the bank has a valid recourse, and the realizable value is estimated on a realistic basis. Regarding the secured portion, provision may be made on the following basis, at the rates ranging from 25 percent to 100 percent of the secured portion depending upon the period for which the asset has remained doubtful: Period for which the advance has remained in doubtful category Secured Advance % Upto 1 Year 25 1-3 Year 40 More than 3 Year 100
Loss ASSETS Loss assets should be written off. If loss assets are permitted to remain in the books for any reason, 100 percent of the outstanding should be provided for
Assessment of Provision Ensure that the balance included in the statement is as per GLB/ software as at the year end Ensure that all collateral properties have been valued once in three years In most NPA, primary security consisting of hypothecated stock of raw materials, finished goods, etc and book debts should be ignored unless the same is backed by a recent stock audit/ book debt/ receivables audit
Assessment of Provision Review provisioning gaps pointed out by the branch auditors in the previous year as per their MOC/ LFAR Team members need to check and ensure that the amount of provision held by the branches for diminution of fair value of restructured advances has been netted off from the borrowers balance outstanding
Assessment of Provision In case of NPAs with balance of Rs. 5 crore and above, stock audit at annual intervals by external agencies is mandatory. In case stock audit has not been carried out, stock valuation as per the auditors assessment may be considered for the purpose of provisioning. Ensure that bank has legal charge on all the properties whose values are being considered for arriving at the secured portion of the borrowers outstanding
Sub-categories of SMA ( Special Mention Accounts ) Banks have been advised to create the following 3 sub- categories prior to the loan turning into a NPA : Points to be Considered SMA Sub- categories Basis for Classification SMA 0 Principal or interest payment not overdue for more than 30 days but account showing signs of incipient stress SMA 1 Principal or interest payment overdue between 31-60 days SMA - 2 Principal or interest payment overdue between 61-90 days
Thank You ! CA Hitesh Pomal hp@msglobal.co.in (M) +91 9824049402