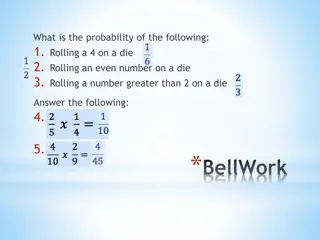Probability Calculations for Events with Cards, Dice, and More
Explore various scenarios involving probabilities with standard decks of cards, dice, and other items. From determining the likelihood of pulling specific cards from a deck to rolling dice and flipping coins, learn about independent and dependent events, as well as the rules governing their probabilities.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
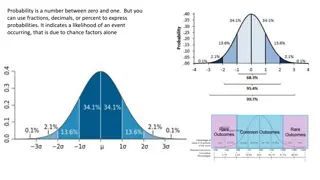
Bell Ringer What is the probability of pulling the following from a standard deck of cards? The Ace of Spades A heart A red queen A black number card The ten of clubs A card higher than 2
Probability of Compound Events Mr. Haupt CC.2.1.8.E.1
Independent Events Independent Events Events that do NOT influence one another. What are the odds of rolling a 2 on a dice and flipping a coin and getting heads? Most of the time, you can tell if it is independent if you are replacing your first choice before choosing the second. Example: The probability of choosing a heart from a deck of cards, replacing it, and then choosing a spade. The rule for finding probability of independent events. P(A and B) = P(A) * P(B)
Dependent Events Events that influence one another. You do not replace the first choice before picking the second one, and so the odds of your second pick are altered. You have a box of chocolates (are you Gump?), there are 21 and there are 7 each of three kinds, PB, Coconut, and Carmel. Find the probability of picking a PB, eating it, and then picking a Carmel. Don t eat the coconut ones, they re gross. The rule for dependent events: P(A then B) = P(A) * P(B after A)
Example Time! It s like Adventure Time but with more math! (And less adventure ) You have a blue dice and a green dice, what is the probability of: P(blue 1 and green 1) P(blue even green even) P(blue and green both less than 6) P(blue 6 and green 7) P(blue 1 or 2 and green 1 or 2)
Example Time! 2.0 The same great quality you trust with an all new flavor! Find the probability of selecting letter tiles from the word below. You do NOT replace the tile before picking a second one. P R O B A B I L I T Y P(vowel then vowel) P(I then I) P(consonant then vowel) P(A then A)