Microbial Isolation Techniques and Methods
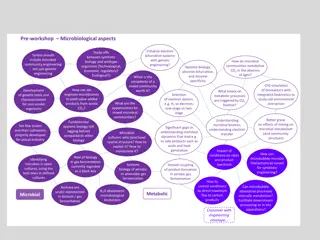
This content provides a detailed guide on the isolation of microbes from various environments using techniques such as sample introduction, inoculation, incubation, inspection, and identification. It includes information on the use of an incubator, materials, and methods required for microbial isolation. The steps for isolating bacteria and fungi are explained, along with images illustrating the process. Techniques such as agar plate preparation, sample collection, and optimal growth conditions are highlighted. The content emphasizes the importance of maintaining proper incubation conditions for successful isolation and observation of microbial growth.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
140Micro Lab 4: Isolation of microbes
The Aim Isolation of micro organisms fromvarious environments
steps : 1. Isolation introduction of a sample into a container of media to produce a culture of observable growth. 2. 2. Inoculation 3. Incubation conditions that allow growth e.g., temperature ,humidity etc.. 4. Inspection 5. Identification.
Incubator In biology, an incubator is a device used to grow and maintain microbiological cultures or cell cultures. The incubator maintains optimal temperature, humidity and other conditions such as the carbon dioxide (CO2) and oxygen content of the atmosphere inside.
Materials and methods Dettol 50%+Cotton Benzene burner Petri plate with media : - NA (for bacteria ) PDA (for fungi). Cotton swap Samples : Soil ,Rotten fruit ,Yoghurt , Mouth swab etc. Incubators
Samples Environmental Sample Normal FloraSamples Surface samples arenormally taken using sterile swabs Applying oral sample to surface ofagar
Various sources of isolation of : Bacteria Fungi
Isolation ofBacteria Put a drop of diluted yoghurt on the solid media plate of bacteria . Incubate at 37 C for 1 day. Yoghurt Take some saliva with the help of a cotton swab. Inoculate it on the media and incubate. Mouth Touch the surface of the solid media plate . Incubate 37 C for 1 day.. Hand
Agar plates are stored upside down to prevent condensation.
These plates of bacteria will be incubated at 37 C for 24 hours and then stored at refrigerator until next week when you will observe for results.
Isolation ofFungi Expose the prepared plate of solid media in air for 10 min Close the lid and incubate at 28 C. After 2-5 days fungus observe for grow Air Sprinkle a pinch of soil on the solid media plate Close the lid and incubate at 28 C After 2-3 days fungus observe for growth. Soil Clean the rotten part of fruit with alcohol Cut a piece and inoculate it on the media plate Then incubate ,after 2-5 days fungus will grow fruit
These plates of fungus will be incubated straight at 28 C for 2-5 days and then stored at refrigerator until next week when you will observe for results.
Result Bacteria Fungi Write a report