Understanding Management Accounting and Cost Accounting
Management accounting involves planning, organizing, and controlling human efforts to achieve organizational goals, while cost accounting focuses on determining the cost of products and services. The objective of cost accounting includes cost analysis, reduction, and decision-making support.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Management accounting- this is combination of two words first management and second Accounting management is the continuous process of planning organizing staffing controlling coordinating the human efforts to achieve the predetermined goals of the organization
Accounting is an art as well as science of recording classifying and summering all the transaction and event, which are at least of a financial character and interpreting the result thereof. Thus management accounting is to redesign accounting in such a way that it is helpful to the management in formation of policy, control of execution and appreciation of effectiveness. It helps the management in carrying out its functions efficiently.
Definition of management accounting- According to Robert N. Anthony : Management accounting is concerned with accounting information that is useful to management. According to T.G. Rose management accounting is the adaptation and analysis of accounting information and its diagnosis and explanation in such a way as to assist management. According to Brown and Howard: the essential aim of management accounting should be to assist management in decision making and control
Cost accounting The word cost account has been emerged due to due to limitation of financial accounting. Cost means something that must be sacrificed to obtained a particular thing. In other word cost is amount of expenditure incurred or attributable to a given thing. In cost accounting, we use various technique, principles and method to ascertain cost of product and services.
Cost accounting is a technique to assists the management in establishing various budgets, standards, etc. cost accountancy is the practice of costing and cost accounting. According to Harold J. Wheldon, Cost accounting is the classifying and appropriate allocation of expenditure for the determination of the cost of products or services In simple world cost accounting is the application of cost control method and the ascertainment of something that has been sacrificed for the product or services and ascertainment of profitability of activities carried out or planned.
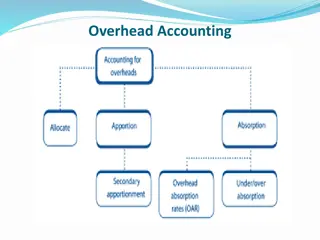
Objective and function of cost accounting- the following are the objective of cost accounting- 1) Analysis and ascertainment of costs 2) Presentation of costs for cost reduction and cost control 3) Planning and decision making
Scope of management accounting the following facts are of great significance and forms the scope of management accounting- 1) Financial Accounting- this accounting records historical data. This recorded facts about an organization are useful for planning and future course of action. The performance appraisal is based on the recorded facts and figure. So management accounting is closely related to financial accounting. 2) cost accounting- this provides various techniques and methods for determining the cost of manufacturing products or services rendered. cost accounting helps in finding out economical and non economical fields of production. Through this the efficiency of various department is judged by setting up various standards and finding out variances. So cost accounting is an essential part of management account.
3)Financial Accounting- this is concerned with the planning and controlling of financial resources of the firm. Finance has become so important for every business that all the management activity are connected to the finance. That is why management accounting includes and extends to the operation of financial management. 4) Budgeting and forecasting- Budgeting means expressing the plan policy and goals of the enterprise for a definite period in the future. The targets are set for different departments and responsibility is fixed for achieving these targets. Forecasting, on the other hand, is a prediction of what will happen as a result of a given circumstances. Both are important for management accounting in planning various activities.
5)Inventory control- inventory is used to denote stock of raw materials, goods in the process of manufacturing and finished products. Inventory has a special significance in accounting for determining correct income for a given period. Management will need effective inventory control for controlling stocks. Management accountant will guide management as to when and from where to purchases and how much to purchase. So the study of inventory control will be helpful for taking managerial decision. 6) Reporting to management- it is the duty of management accounts is to keep the management informed about the activities in the business. So various reports are sent to the management half yearly, quarterly or annually. Thus , this is also a part of management accounting.
7) Interpreting of Data- the management interprets various financial statement. This gives the idea about the financial soundness of the concern. This is interpreted in simple language to the management so that quick decision may be taken. thus, this is very important part of the management accounting. 8) Control procedure and method- this is needed to use various factors of production in a most economical way. The studies about cost, relationship of cost and profits are useful for using economic resources efficiently and economically.
9) internal audit- This system is useful to judge the performance of every department. This helps management to know the deviation in performance. It becomes able in fixing responsibly of different individual. 10) tax accounting- through this the tax liability of the concern is calculated. This helps the management in filing the return. Thus this forms the part of the management accounting. 11) Office services- management may be required to control and office. He will be expected to deal with data processing filing copying and duplicating, communicating etc.. He will be also reporting about the utility of different office machine.
Function of management Accounting- management accounting has been developed to solve the problem of management. It helps the management in taking important decision. Some of the functions of management accounting are as follow- 1. Planning & Forecasting 2. Modification of Data 3. Financial Analysis and interpretation 4. Facilitates Managerial Control. 5. Communication 6. Use of Qualitative Information
7) Co-Ordinating 8) Helpful in taking Strategic Decisions 9) Supplying Information to various Levels of management 10) Providing useful information to management for taking decision
Cost accounting According to ICMA cost accounting is technique and process of ascertainment of cost According to L.B. Dicksee- Cost accounting are accounts supplementary or subsidiary to financial accounts and are compiled for the purpose of giving additional information as to the detailed cost of working of an undertaking or any particular section thereof.
Cost According to Institute of cost and management accountants- Cost is the amount of expenditure (actual or notional)incurred on, or attributable to , an given thing. Note all the cost standards are issued by cost and works accountant of India( ICWAI) According to committee on cost concets and standards- Cost is foregoing or sacrifice , measured in monetary terms, incurred or potentially to be incurred, to achieve a special purpose. As per CAS1 - cost is a measurement , in monetary terms, of the amount of resources used for the purpose of production of goods or rendering services.
Costing is the technique and process of ascertaining costs. -------- I C M A Costing Cost Accounting the process of accounting for cost from the point at which expenditure is incurred or committed to the establishment of its ultimate relationship with cost centers and cost units. In its widest usage, it embraces the preparation of statistical data, the application of cost control methods and the ascertainment of the profitability of activities carried out or planned.
the following point must be noted: Cost centre refers to a subdivision or any part of the organization, to which costs are incurred, but does not contribute to the company's revenues directly. Cost unit implies any measurable unit of product or service, with respect to which costs are assessed. Use. It is used as a basis for classifying costs.
Scope of cost accounting scope of cost accounting are as follows= 1) Classification of cost 2) Cost allocation 3) Cost control 4) Cost comparison 5) Cost reporting 6) Cost reduction 7) Cost analysis 8) Cost audit
1) Cost is related to its cause 2) Cost is charged after it is incurred 3) Abnormal cost are excluded from its costing 4) Past costs are not charged to future period 5) The concept of conservation has no place in costing 6) Accounting for cost is based on double entry principles Principles of cost accounting
some more limitations: 1) Not applicable in trading business 2) Based on assumption 3) Only variable cost included in marginal cost 4) Based on so many technique and priciples
Method of costing can be classified in two parts 1) Specific Order costing method a) Job Costing Method b) Contract Costing Method c) Batch Costing Method d) Target Costing Method 2) Continuous Operation Costing Method a) Process costing method b) Unit Costing Method c) Operating Costing method d) Departmental Costing Method e) Multiple or Composite Costing Method Methods of costing
1) A branch of Accounting 2) Both Art and Science 3) Recognized as a profession Nature and Characteristics Of Cost Accounting: