Rapid Analysis of Soil Macronutrients Using Energy Dispersive X-ray Fluorescence
Determination of trace elements and macronutrients in agricultural soils is crucial for crop productivity. This study highlights the advantages, challenges, and objectives of using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence for rapid and precise analysis. The method requires minimal sample preparation, considers particle size effects, and addresses surface irregularity. Results show improved accuracy for trace elements and macronutrients, with comparisons to ICP-OES. Pressed pellet with wax binder enhances XRF analysis accuracy, particularly for aluminum and potassium.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Determination of trace elements and macronutrients in agricultural soils using energy dispersive X-ray fluorescence as a rapid and precise analytical technique Maame Croffie1, 2 (mcroffie01@qub.ac.uk) Co-authors: Paul N. Williams1, Owen Fenton2, Anna Fenelon2, Konrad Meztger2, 3, Karen Daly2 1 Institute for Global Food Security, Queen s University Belfast, Northern Ireland, BT9 5DL, UK 2 Teagasc Johnstown Castle Research Centre, Wexford, Y35 TC97, Ireland 3 International Network for Environment and Health, NUI Galway, H91 TK33, Ireland 1
Introduction Advantages Challenges Objective Minimal sample preparation Particle size effects Improve accuracy and precision for trace elements and macronutrient analysis Surface irregularity Rapid Matrix effects Inexpensive Moisture effects Portable sample X-ray tube Secondary target XRF detector XRF Spectra
Materials and Methods Cu Fe Cr Loose powder Pressed pellet Pressed pellet + wax Sample preparation Pb Al XRF analysis of ISE samples Ca P Fundamental parameters (FP) vs Matching library (ML) made up of 4 CRMs Ni S Calibration study Mn Zn Mg ISE-International Soil Exchange (reference samples for proficiency testing of labs) 3
Materials & Methods Energy-dispersive XRF Sampling sites Agreement statistics ICP-OES spectrometer 4
Results-XRF calibration study FP- fundamental parameters ML- matching library 6
Results- Comparison between XRF and ICP-OES R 2 <0.70 CCC<0.70 R 2 >0.70 CCC<0.90>0.70 R 2 >0.80 CCC>0.90 Cu Ca Zn Ni Pb Fe Mn Mg S P Al Cr K CCC-concordance correlation coefficient 7
Observed differences between XRF and ICP-OES by soil texture Teagasc Presentation Footer 8
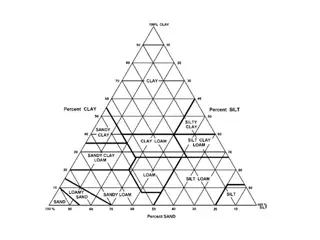
Conclusion Pressed pellet with wax binder improves accuracy of XRF analysis Matching library had varying effects on elements XRF is more accurate for Al and K than aqua regia digestion with ICP-OES analysis XRF can provide rapid determination of soil texture 9
Acknowledgements Linda Moloney Finn Owen Frahill Conor Nolan Scott Rees