Explore Space: Celestial Objects and Beyond
Dive into the wonders of the universe with this engaging lesson on space celestial objects. Discover the differences between comets and asteroids, explore planets and moons in our solar system, learn about stars, asteroids, comets, and galaxies, and unravel the mysteries of astronomy. Let your curiosity soar as you journey through the cosmos!
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
GoSkyWatch Planetarium App http://sciencenetlinks.com/tools/goskywatch- planetarium-app/ Only on apple products
21st April Lesson title: Space Celestial objects Key Words Lesson Objectives: Astronomy State the difference between a comet and an asteroid. Star Planet Moon Asteroid Comet Galaxy
Astronomy What words do you think of when you hear the word Astronomy ? Astronomy is the study of the universe beyond the Earth s atmosphere.
Celestial Bodies A celestial body is a naturally made object outside the Earth s atmosphere. We shall look at some of these bodies in our universe now..
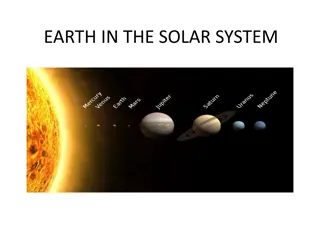
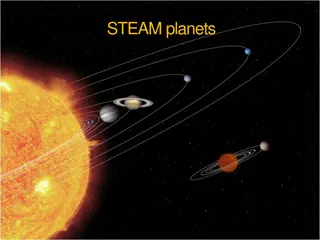
Planets M V E M J S U N Planets orbit around a star
Moon Moons orbit planets Earth has one moon A moon is a natural satellite of a planet Later we shall look at other planets in our solar system and the number of moons they each have..
Stars A star generates its own light and heat It s a big ball of burning gas! Hottest stars are blue, coldest are red Moons orbit planets Planets orbit stars. Stars are spherical in shape not star shaped.
Asteroids An asteroid is a small rocky object that orbits a star, but is too small to be considered a planet They are irregular in shape Found between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter the asteroid belt
Comets A comet is a small object made up of frozen gases, ice, rock and dust that can glow and produce a tail They orbit the sun When they come close to the sun they heat up and glow
Galaxies A galaxy is a large group of stars, dust, gas and dark matter held together by gravity They can be different shapes but most are spiral Solar systems make galaxies. Galaxies make up the Universe.
Our Solar System Our solar system is a group of planets, asteroids, comets that are in orbit around a star and held together by the star s gravity. Planets and stars make up solar systems.
Planet Data What do you think happens the surface temperature the further you move away from the planets? Celestial Bodies Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Time taken to travel around the sun (days/years) n/a Surface Temp (oC) Distance from the sun (million kms) 0
Mass [x Earth] Sun 333000 Diameter [km] 1392000 Surface Temp [ C] 6000
Mercury Mass [x Earth] 0.05 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis Surface Temp [ C] 4880 58 88 days 59 days 0 moons 350
Venus Mass [x Earth] 0.81 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis Surface Temp [ C] 12112 107.5 224 days 243 days 0 moons 460
Earth Mass [x Earth] 1 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis Surface Temp [ C] 12742 149.6 365 days 24 hours 1 moon 20
Mars Mass [x Earth] 0.11 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis Surface Temp [ C] 6790 228 687 days 24 h 37m 22 moons - 23
Jupiter Mass [x Earth] 318 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis 142600 778 11.9 years 9h 50m 16 moons [+ 1 ring] Surface Temp [ C] -120
Saturn Mass [x Earth] 95 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis 120200 1427 29.5 years 10h 14m 17 moons [+ rings] Surface Temp [ C] -180
Uranus Mass [x Earth] 14.5 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis 49000 2870 84 years 10h 49m 15 moons [+ rings] Surface Temp [ C] -210
Neptune Mass [x Earth] 17.5 Diameter [km] Distance from Sun [Million km] Time taken to travel around Sun Time taken to spin once on axis Surface Temp [ C] 50000 4497 165 years 15h 48m 8 moons -220
Planet Data What do you think happens the surface temperature the further you move away from the planets? We can now conclude the temperature decreases! Celestial Bodies Sun Mercury Venus Earth Mars Jupiter Saturn Uranus Neptune Time taken to travel around the sun (days/years) 88 224 Days 365 Days 687 Days 11.9 Years 29.5 Years 84 Years 165 Years n/a Days Surface Temp (oC) 6000 350 460 20 -23 -120 -180 -210 -220 Distance from the sun (million kms) 0 58 107.5 149.6 228 778 1427 2870 4497
Dwarf Planets A dwarf planet is a round space object that circles a star but has not cleared its own orbit They do not have enough gravity to pull the smaller objects in. Can you think of an example of a dwarf planet?
Using the information youve gathered, plot a graph of surface temperature [y] against distance from sun [x]: 500 400 300 Surface Temp. [C] 200 100 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 -100 -200 -300 Distance from Sun [Million km]
Using the information youve gathered, plot a graph of surface temperature [y] against distance from sun [x]: 500 400 300 Surface Temp. [C] 200 100 0 0 1000 2000 3000 4000 5000 6000 7000 -100 -200 -300 Distance from Sun [Million km]
A, B, C or D What was the temperature on the surface of the sun? A. 6000 oC B. 6000 K C. 60 oC D. 5700 oC
A, B, C or D What was the temperature on the surface of the sun? A. 6000 oC B. 6000 K C. 60 oC D. 5700 oC
A, B, C or D Which planet had the lowest surface temperature? A. Jupitar B. Saturn C. Neptune D. Earth
A, B, C or D Which planet had the lowest surface temperature? A. Jupitar B. Saturn C. Neptune D. Earth
A, B, C or D Which planet had the most number of moons from the data you have been given? A. Earth B. Mars C. Saturn D. Uranus
A, B, C or D Which planet had the most number of moons from the data you have been given? A. Earth B. Mars C. Saturn D. Uranus
A, B, C or D What shape are stars? A. Round B. Spherical C. Star D. Jagged
A, B, C or D What shape are stars? A. Round B. Spherical C. Star D. Jagged
Earth Facts Earth has a tilt angle about 23.5o relative to its orbit plane. It takes Earth 365 days to orbit the sun. The moon orbits the Earth every 28 days approx. This causes phases.