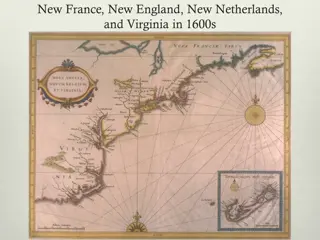
The British Exploration and Colonization Journey
British exploration and colonization efforts were motivated by various factors such as internal problems in England, surplus population, and the quest for new opportunities. Despite initial challenges and failed attempts, the British eventually began to spread their influence in the New World through ventures like Jamestown, facing obstacles like poor living conditions and conflicts with Native Americans.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Causes of British Exploration A lot of problems in England Ireland Henry VIII Primogeniture Surplus Population Debtors Enclosure
Why didnt the British spread out to the New World?
British Begin to Spread 1588- Defeat of the Spanish Armada by the British (and the Protestant Wind ) Spanish no longer had a stronghold on the Atlantic Ocean Failed Attempts at Colonization Newfoundland Too cold, people starve and froze Roanoke Whole colony disappeared
Settling the Southern Colonies
Jamestown (1607) Joint Stock Company Virginia Company VERY IMPORTANT - The charter of the Virginia Company guaranteed settlers the same rights as Englishmen in Britain Problems for Jamestown The swampy site of Jamestown meant poor drinking water Mosquitoes caused malaria and yellow fever Men wasted time looking for gold rather than doing useful tasks (digging wells, building shelter, planting crops) There were zero women on the initial ship Supply ship wrecked in the Bahamas in 1609
Captain John Smith At one point, he was kidnapped by local Indians and forced into a mock execution by the chief Powhatan and had been saved by Powhatan s daughter, Pocahontas. Meant to show that Powhatan wanted peaceful relations with the colonists. John Smith s main contribution was that he gave order and discipline, highlighted by his no work, no food policy. Starving Time - Colonists had to eat cats, dogs, rats, even other people. One fellow wrote of eating powdered wife. Gun powder accident
Settler/ Native Relations After Smith Lord De La Warr was appointed governor of Virigina Caused problems with the Powhatans Pocahantas married John Rolfe Pocahontas died Rolfe blamed by the Natives Anglo-Powhatan Wars
Tobacco John Rolfe King Nicotine Land Depletion Labor Intensive 1619- Dutch ship brings 20 African laborers to Virginia 1619 House of Burgesses 1stself-government in the New World King James hates tobacco and the House of Burgesses Revokes Charter to make Virginia a royal colony (1624)
Maryland: A Catholic Haven Lord Baltimore Catholics Tobacco White Indentured Servants Freedom of Worship until it was flooded by Protestants Act of Toleration
West Indies Sugar Plantations African Slaves (sugar needed a lot of land cleared) Strict Slave Codes (Barbados 1661) Poorer farmers were pushed out, moved to what becomes South Carolina (called Carolina) Takes the slave codes with them First tried slave codes on Natives, but the Natives died, so they were replaced by Africans
Colonization Hiatus Civil War in England King Charles I dismisses Parliament for 11 years, but is then beheaded Oliver Cromwell rules (harshly) for 10 years 1660 King Charles II takes the thrown to begin the Restoration Period
Carolina (1670) Close ties to British West Indies Savanna Natives help wipe out and enslave the other tribes in the area As Natives die and become less in number, Savanna decide to leave before they are next Carolinians decide to thin the Natives before they leave, so they cannot come back and cause problems Rice Africans have knowledge resistance to malaria
North Carolina (1712) Squatters Geographically Isolated Resistance to Authority Many similarities between North Carolina and Rhode Island Most democratic Most independent minded people Least aristocratic of colonies
Georgia (1733) Buffer James Oglethorpe Debtors Religious toleration for all Christians EXCEPT Catholics
Southern Colony Similarities Church of England Dominate Plantations Cash Crop Slavery Aristocracy Slow growth of cities, churches and schools Some religious toleration Conflicts with Native Americans
Protestant Reformation 1517 Martin Luther 95 Thesis starts the Protestants 1536 John Calvin Basis of Puritanism 1530s King Henry VIII Splits England from the Roman Catholic Church and the Pope
Puritans vs. Separatists Wanted to purify or get rid of all Roman Catholic influence in the Anglican Church Since all British subjects were members of the Anglican church, Saints and Damned had to sit together in the same church Wanted only visible saints to be in the church Wanted to separate from the Anglican church
Pilgrims in the New World Fled King James I Went to Holland (The Netherlands) Dutchification Virginia Storm Plymouth Mayflower Compact
New England is Built on God and Cod Starving Squanto Thanksgiving Economy built on fur, fish and lumber
William Bradford Elected governor 30 times New settlers for fishing 1629 colony was officially recognized in England as the Massachusetts Bay Colony with the largest scale start of any colony (1,000 settlers and 11 supply ships) Worried Non-Puritans would ruin his godly experiment
The Great Migration 1630s 70,000 people left England for the Americas (20,000 Puritans) Massachusetts elected John Winthrop 1stgovernor (served as governor or deputy governor for 19 years) Democracy is the meanest and worst form of government. If the people be governors, who shall be governed? A City Upon a Hill
Franchise in Massachusetts Freemen adult, white, male, members of the Congregational Church Only about 2/5 of the men Town Meetings General Court Government was to enforce God s Laws (applied to believers and non- believers) Taxes to support the church
Clergymen in Massachusetts Religious leaders had power because they controlled admission to church membership Congregations could hire and fire their ministers There were laws to limit Earthly pleasures Fine of twenty shillings (about $100) for couples caught kissing in public. The Puritan concept of Hell was very serious, frightening, and very real. Michael Wigglesworth s Day of Doom, written in 1662, sold one copy for every twenty people.
Problems in Massachussets Quakers were fined, flogged, and/or banished. Anne Hutchinson Very intelligent, strong-willed, talkative woman Claimed that a holy life was no sure sign of salvation The truly saved need not bother to obey the law of either God or man - antinomianism . Banished Roger Williams Radical idealist Hounded his fellow clergymen to make a clean and complete break with the Church of England. Denied that civil government could and should not govern religious behavior Banished Founded Rhode Island
Rhode Island Little Rhody The Sewer The Traditional Home of the Otherwise Minded People had nothing in common except that they weren t wanted anywhere else
Connecticut Reverend Thomas Hooker Puritans 1639 Fundamental Orders of Connecticut
New Hampshire Originally part of Connecticut Separated in 1679 because the king wanted the granite
New England Confederation 1643 - four colonies banded together to form the New England Confederation. Almost all Puritan Weak, but still a notable milestone toward American unity Colonies were semiautonomous commonwealths Charles II hoped to control colonies more firmly, but was shocked to find how much his orders were ignored by Massachusetts. Sea-to-sea charter was given to rival Connecticut (1662), and a charter was given to Rhode Island (1663). Finally, in 1684, Massachusetts charter was revoked.
Dominion of New England 1686- Created to bolster the colonial defense against Indians Tied the colonies closer to Britain Enforced the hated Navigation Acts. Forbade American trade with countries other than Britain Smuggling became common Sir Edmund Andros Governor of the Dominion Establishing headquarters in Boston Openly showed association with the hated Church of England His soldiers were vile-mouthed (in Puritan land) Curbed town meetings, restricted the courts and the press, and revoked all land titles. Taxed the people without their consent
Glorious Revolution Charles II William and Mary Sir Edmund Andros Massachusetts got a new charter (1691) - charter allowed all landowners to vote, as opposed to the previous law of voting belonging only to the church members
New York New Netherlands New Sweden Wall Street Peter Stuyvesant Duke of York Dutch Influence
Pennsylvania Quakers William Penn Native American Interaction Freedom of Worship No Slavery
Middle Colonies Similarities New York, New Jersey, Delaware, and Pennsylvania Fertile soil and broad expanse of land All except for Delaware exported lots of grain The Susquehanna River tapped the fur trade of the interior, and the rivers were gentle, with little cascading waterfalls. Landholdings were generally intermediate in size. The middle colonies were more ethnically mixed than other colonies. A considerable amount of economic and social democracy prevailed. Benjamin Franklin, born in Boston, entered Philadelphia as a seventeen-year-old in 1720 with a loaf of bread under each arm and immediately found a congenial home in the urbane, open atmosphere of the city. Americans began to realize that not only were they surviving, but that they were also thriving.
Chesapeake Area Issues Life in the American wilderness was harsh. Diseases like malaria, dysentery, and typhoid killed many. Few people lived to 40 or 50 years. In the early days of colonies, women were so scarce that men fought over all of them. The Chesapeake region had fewer women and a 6:1 male to female ratio is a good guide. Few people knew any grandparents. A third of all brides in one Maryland county were already pregnant before the wedding (scandalous). Virginia, with 59,000 people, became the most populous colony.
Headright System Tobacco Headright System Problems of the system Indentured servants
Bacons Rebellion Problems of freed indentured servants Nathaniel Bacon William Berkeley Bacon s men attacks on Indian settlements Bacon s Death Berkeley s win Ideas of rebellion and paranoia
Colonial Slavery By 1700 only about 400,000 African slaves were brought over to the US By 1680 landowners feared mutinous white servants Mid 1680s, for the first time, black slaves outnumbered white servants among the plantation colonies new arrivals. 1750 - blacks accounted for nearly half of the Virginian population. Some of the earliest black slaves gained their freedom and some became slaveholders themselves. Slave Codes Harsh Laws Many Contributions to American society Revolts
New England Society Most people owned small farms or businesses Less disease Average life expectancy of 70 years. Tended to migrate as a family Women usually married in their early twenties and gave birth every two years until menopause. Less rights for women Law was very severe, strict and based on Puritan religious beliefs New towns were legally chartered by colonial authorities. Education Meeting Houses Harvard College Religion was central to everything they did Economy based on trading Most settlers were from England Little Slavery Southern Society Few families owned most of the land, money and slaves The largest social group was subsistence farmers. Drunkenness Swampy land Disease (malaria, yellow fever) Low life expectancy Few women, many single men Women had more power Few cities Schools and churches were slow to develop Economy based on agriculture Settlers from all over Europe Wide Spread Slavery
Half Way Covenant (1662) Worry about Children Jeremiads Salem Witch Trials Salem Accusations Deaths Europe