Comprehensive School Quality Assurance and Evaluation Process
A detailed insight into the Quality Assurance Department's role in school evaluation and improvement processes, including Whole School Evaluation (WSE), Follow-through initiatives, Teaching and Learning assessments, Resumption and Examination Monitoring. The process involves both internal self-evaluation and external evaluation to uphold educational standards and enhance learning outcomes for students.
Download Presentation
Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
Presentation Transcript
FROM THE PERSPECTIVE OF QUALITY ASSURANCE DEPARTMENT
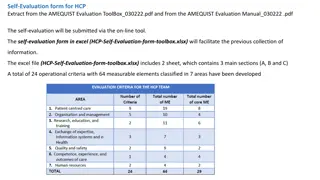
HEAD OF DEPARTMENT (HOD QA) (Government School) (PrivateSchool) School Intervention General Services Unit Unit Unit Unit WSE WSE Special Evaluation Follow-through Visit Follow-through Visit Teaching and Learning Note Monitoring and Investigation Department collaborate with Quality Assurance Department to carry out: Resumption Monitoring Examination Monitoring
Whole School Evaluation: This is targeted at validating the school s Self Evaluation. It is a systematic and objective assessment of what a school is doing, and the impact on the learners based on the criteria of the evaluation schedule. * Follow through: Underperforming schools with overall effectiveness of fair, or lower at the previous WSE requires follow-up evaluation to ensure that recommendations made for improvement are being implemented Teaching and learning: To ascertain effectiveness of teaching and learning process, ascertain Curriculum usage, usage of Lagos State Unified schemes of work and proffer solution and support to the schools. Resumption Monitoring: To ascertain readiness of school to start academic activities for the new term and encourage her to brace up for the term s activities. Examination Monitoring: To ensure schools comply with examination rules and guideline.
* Whole School Evaluation: This is targeted at validating the school s Self Evaluation. It is a systematic and objective assessment of what a school is doing, and the impact on the learners based on the criteria of the evaluation schedule. * Follow through: Underperforming schools with overall effectiveness of fair, or lower at the previous WSE requires follow-up evaluation to ensure that recommendations made for improvement are being implemented
Process of whole school evaluation
Introduction WHOLE SCHOOL EVALUATION (WSE) IS AN EDUCATION TOOL FOR THE SUPERVISION AND MONITORING OF SCHOOLS BELOW TERTIARY LEVEL. The process is a very interactive procedure which includes both school self evaluation (ss-e) and external evaluation (ee) SS-e is validated and enhanced through ee. School self evaluation is the process of the school evaluating itself using the evaluation schedule (es). External evaluation is carried out by a team of accredited evaluators drawn from the national and state education quality assurance bodies nationwide.
WSE PROCESS FLOW HIGHLIGHTED DRAW THE ITINERARY FOR SCHOOLS TO BE VISITED (SELECT SCHOOLS TO BE EVALUATED) SCHOOL IS INFORMED OF UPCOMING WSE AT LEAST 48HRS PRIOR TO THE EVALUATION. SCHOOLS PROVIDE PRE- EVALUATION DOCUMENTS AND COMPLETED SELF EVALUATION FORM. PRE -EVALUATION MEETING BY THE TEAM LEAD WITH THE EVALUATORS TO ASSIGN ROLES AND RESPONSIBILITIES AND RESOURCES (FORMS) ARE MADE AVAILABLE TO TEAM EVALUATORS. EXTERNAL EVALUATION TO VALIDATE THE INTERNAL EVALUATION USING THE EVALUATION SCHEDULE. FEEDBACK TO SCHOOL.
EXTERNAL EVALUATORS WILL JUDGE THE QUALITY OF SCHOOLS THROUGH THE EVALUATION OF : Overall effectiveness of the school; Achievement and standards; Learners personal skills and participation; The quality of teaching and learning; How well the curriculum meets learners needs; How well learners are cared for, guided and their safety provided for; The quality of the learning environment; and How well the school is led and managed.
ACHIEVEMENT AND STANDARD KEY ISSUES Consistency of Learners achievement across all subjects and grade level Learners achievement in public Examinations (BECE, SSCE, NABTEB, etc) Learners achievement in internal examinations and tests Schools achievement in relation to National Learning targets/State benchmark (using Curriculum & Scheme of work) Learners written works compared to other Schools Performance of Schools in external competition in the last 3 years Continuous Assessment exercise Learners proficiency in the language of instruction (oral and written)
LEARNERS PERSONAL SKILLS AND PARTICIPATION KEY ISSUES Learners conduct at break time and movement in the School Bullying and other forms of harassment Learner/learner and Staff/learner relationship Learners attendance in School Learners Representative Council Learners participation in co and extra-curricular activities to build their skills Giving Gifted learners and those with Special talents and abilities room to thrive Contribution to the community beyond the School Learners opportunities to work with staff and SBMC to solve problems Roles of learners in the development of School rules and decision that affect them
CURRICULUM AND OTHER ACTIVITIES KEY ISSUES Extent of use of current National Curriculum and teachers guide (Scrutiny of lesson plans) Evidence of Scheme of work for all subjects drawn from the National Curriculum Access to all curricular options by learners including learners with special needs Use, appropriateness and availability of textbooks and other instructional materials Promotion and participation in sports, the arts and other co and extracurricular activities
CARE, GUIDANCE AND SAFETY KEY ISSUES Learners healthy lives and safety Availability of Sickbay, fire extinguisher and sand bucket Learners supervision when they are not in class Learners access to medical facilities Programme on awareness/sensitization of HIV & AIDS, Ebola, Lassa fever, COVID-19 etc. Procedure for responding to and reporting issues related to learners protection, violence and conflict Guidance and counseling unit Open day and parent attendance Support to learners from disadvantaged and challenged families to join school life fully Documented School rules with appropriate sanction for erring learners Posters for cautions as regards safety within the school premises Learners spiritual, emotional, moral and social wellbeing
LEARNING ENVIRONMENT KEY ISSUES Perimeter fencing, School building Sporting facilities and equipment Physic, Chemistry and Biology laboratories Library, IT Facility Toilet facilities School farm/gardens Separate toilet facilities for male and female learners and teachers Access to all areas of the School for learners with special needs Fire extinguishers
MANAGEMENT KEY ISSUES Clear vision and mission relevant to National Education goals; shared publicly; consistent with the specified goals for the level the school operates. School has a regularly updated, functional SDP to improve quality & standard. Analyses and uses performance data (exam and test results) for improvement stakeholders to inform planning. and shared with all Parents help the school in solving academic and social problems of learners Involves staff and learners in decision making, setting school goals and reviewing them.
Continuation Effective committees and staffing structures in place that contribute to improvement Supervision and monitoring of lesson activities by Principal, Head teacher, Supervisor. Headteacher/Principal/ empowers and motivates Assistants to perform leadership roles Leadership motivates teachers and learners to improve and perform leadership duties. Leadership promotes and protects staff welfare. The performance appraisal of staff is focused on bringing about improvement. There is professional development for teachers. Tackles discrimination and resolves conflicts promptly. Provision is made to cater for learners with special needs. Record keeping is in line with statutory financial regulations and SBMC advice. Partnership in school events by parents, SBMC and community members Extent of compliance with and reports in the last 3 years.
Stages in external evaluation There are three stages in external evaluation namely: i. pre school evaluation (planning external school evaluation) Ii. The ee proper /on-site visit; and Iii. Post evaluation
DOCUMENTS TO COLLECT FOR EXTERNAL EVALUATION THE RECENT COMPLETED AND SIGNED SEF WHICH SHALL BE USED AS FOCUS FOR THE EE; COPY OF THE SCHOOL DEVELOPMENT PLAN (SDP) COPY OF THE SCHOOL IMPROVEMENT PLAN (sip) A COPY OF THE SCHOOLS RECENT EE REPORT (IF AVAILABLE); PROSPECTUS or brief history of the school stating vision and mission statement; Nominal rolls showing qualifications with dates, teaching experience and date of appointment, classes/subject taught etc.; ANALYSIS OF INTERNAL AND EXTERNAL EXAMINATION RESULTS;
DOCUMENTS TO COLLECT FOR EXTERNAL EVALUATION CONTINUED List of awards won by the school in the last three years; List of societies and clubs; Learners enrolment by sex and class; Programme of activities and games fixtures for the term/year. Recent medical certificate of fitness by authorized healthcare provider to be produced by kitchen staff and other food handlers in the school.
PROCESS OUTPUT REPORT IS COLLATED WITH ALL AVAILABLE EVIDENCES. CRITIQUED IN THE OFFICE BY THE QA READER AND APPROVED BY DG, OEQA. THE EVALUATION REPORT IS SHARED WITH STAKEHOLDERS. SUMMARY OF GRADING AND OVERALL EFFECTIVENESS IS SUBMITTED TO PRS DEPARTMENT.
Conclusion OEQA compliments schools for higher achievements and learners improved performance OEQA does not witch-hunt