Understanding Carbon Movement in the Environment
Explore the intricate processes of carbon movement in the biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and geosphere. Learn how plants absorb carbon dioxide, animals utilize carbon for tissue building, and the impacts of human activities like burning fossil fuels on carbon distribution. Discover the critical role of carbon in regulating Earth's temperature and the consequences of increased greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
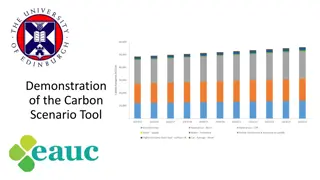
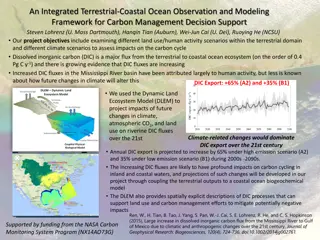
Movement of carbon between the biosphere, atmosphere, oceans, and geosphere. Series of complex processes through which all of the carbon atoms in existence rotate. Plants absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere and combine it with water they get from the soil to make the substances they need for growth. The process of photosynthesis turns carbon atoms from carbon dioxide into sugars. Animals, such as rabbits, eat plants and use the carbon to build their own tissues.
Carbon moves from fossil fuels to the atmosphere when fuels are burned. When humans burn fossil fuels to power factories, power plants, cars and trucks, most of the carbon enters the atmosphere as carbon dioxide gas. Each year, five and a half billion tons of carbon is released by burning fossil fuels. That s the weight of 100 million adult African elephants! Of the huge amount of carbon that is released from fuels, 3.3 billion tons enters the atmosphere. The rest mostly becomes dissolved in seawater.
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to the oceans. The oceans, and other bodies of water, soak up some of the carbon from the atmosphere. Carbon dioxide is a greenhouse gas and traps heat in the atmosphere. Without it and other greenhouse gases, Earth would be a frozen world. Humans have burned so much fuel that there is approximately 30% more carbon dioxide in the air today than there was about 150 years ago. More greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide in our atmosphere can cause our planet to become warmer.