Viruses and Fungi: Understanding their Nature and Benefits
Delve into the realm of viruses and fungi, exploring their characteristics, classification, growth conditions, and applications. Discover the fascinating world of mycology and virology, including the study of yeast, molds, bacteriophages, and more. Uncover the crucial role these organisms play in various fields, from medicine to food production. Learn about the optimal conditions for cultivating fungi and the benefits they offer, such as baking, brewing, and antibiotic production. Visual aids complement the informative text, making the topic engaging and educational.
Uploaded on Feb 27, 2025 | 0 Views
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Viruses & fungi By:Afnan Bakhsh
Fungi: : Mycology: study of fungi. Fungi: group of heterotrophic eukaryotic cells. Fungi called saprophytes because they obtain their nutrients from dead organic material.
Classification of fungi: 1) Yeast: Oval or spherical in shape. Single cell (unicellular), one nucleus. Multiply by asexual reproduction (Budding).
2) Mold: Multicellular (multinucleated cell). Consists of branching hyphae forming Mycelium. Multiply both sexually and asexually.
What are the best conditions to grow fungi? Media: Sabouraud Dextrose Agar (SDA). PH: wide range of PH especially acidic. Moisture. Temperature
Tempreature: Room temp: causing superficial infection. 37 C: cause systemic infection, called pathogenic fungi Cold temp: cause spoilage of food. Lacto Phenol Cotton blue: Reagent used to stain fungi for microscopic examination. Use iron needle for culturing.
Benefits of fungi: Baking by using yeast. Brewing. Breaking down of dead organic material. Antibiotics. Ex: penicillin extracted from penicillium.
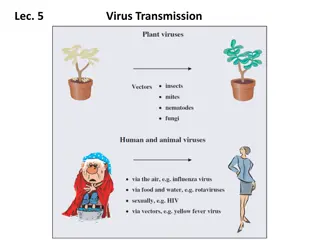
Viruses: Virology: study of viruses. Viruses are obligate intracellular agents (they can multiply only in living cell). They have single type of nucleic acid (DNA /RNA) enclosed in a capsid. Some viruses have envelop other are naked (none enveloped). Viruses size vary from 20-300 nm.
We can see it by electron microscope. Viruses infect human, plants, animals and bacteria. Viruses that infected bacteria are called: bacteriophage.
Cultivation of viruses: Inoculation of lab animals (ex: mice, hamster). Inoculation of embryonated egg. Tissue cultured cells. Use it to see Cytopathic effect: it is morphological changes in the cell caused by viruses when they multiply inside the cell. Why we do cultivation: a. Diagnosis. b. research. c. production of vaccines
Virus life cycle: Adsorption to the cell. Penetration. Multiplication. Budding outside the cell.