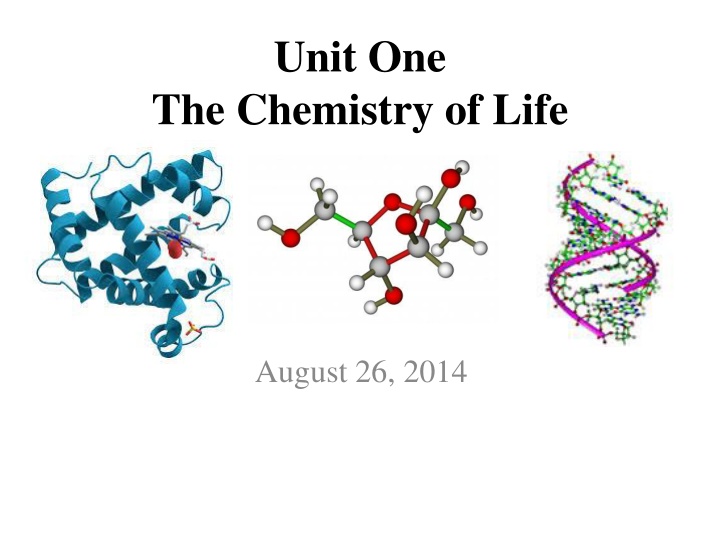
Unit One The Chemistry of Life
Explore the chemistry of life with a focus on atoms, compounds, molecular components of cells, and the significance of carbon. Understand the importance of water, cellular reactions, and macromolecules in living organisms. Delve into the composition of a living cell and the essential elements it comprises. Learn about the unique properties of carbon and its role in forming complex bio-molecules within cells. Test your knowledge with engaging questions on cell composition and compound identification.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Unit One The Chemistry of Life August 26, 2014
Lecture Outline -Chemistry review (atoms) -Components of a living cell (molecular level) -Carbon (what is so special?) -Water (what is so special?) -Cellular reactions -Macromolecule introduction
Chemistry Review __________ are positively charged particles of the atom __________ are neutral particles of an atom __________ are __________ charged particles of the atom; these ______ to other atoms
Chemistry Review Element A substance that cannot be broken down any further Periodic table of elements (Ex: hydrogen) Compound Composed of two or more different elements joined together (Ex: H2O) Ionic Bond A bond formed when one or more electrons are lost from one atom to another (Ex: NaCl-) Covalent Bond Forms when electrons are shared between atoms (Ex:CO2)
Chemistry in the Cell A living cell is composed of a selectgroup of elements, mainly: MajorElement Biomolecules (all living things have these) Carbohydrates Lipids Proteins Nucleic Acids Carbon Nitrogen Oxygen Combine to make up Hydrogen Phosphorus Sulfur
Carbon Is the Most Important Element in a Cell- Why? It has: Four bonding electrons Small size So it can: Join in rings Join in chains To make: Large/complex molecules (Bio-Molecules)
A living cell is mainly composed of all the following elements except: a. Potassium b. Phosphorus c. Oxygen d. Hydrogen
Which of the following represents a compound? a. H b. O c. C6H12O6 d. O2
Organize from smallest to largest: a. Compound atom Element biomolecule b. Element compound biomolecule c. Element atom compound biomolecule d. Biomolecule compound element
Which of the following if NOT true of biomolecules a. All living things have them b. They are larger than most elements c. Lipids are included in this category d. They are smaller than most elements
Biomolecule Formation Each goes from monomer to a polymer Separated Sub-Units; Each is a molecule Connected Sub-Units; Make up biomolecules All occurs through water and its amazing surface tension- water can form droplets!
Biomolecule Formation Dehydration Synthesis Hydrolysis -Building up the molecule -Remove water -Breaking apart molecule -Add water +H2O -H2O