Understanding Transposon Insertion Orientation and Its Impact on Gene Expression
This detailed guide explores the orientation of transposon insertions relative to their inherent asymmetry, like the P-element’s 5’ and 3’ ends, and how it influences constructs for driving ectopic gene expression. Using FlyBase resources, it explains the significance of orientation in constructs like EP and EPg for driving transcription away from genes of interest. Detailed steps and diagrams help track down information about construct elements and their orientations. This comprehensive resource delves into the molecular intricacies of transposon-driven gene expression regulation.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
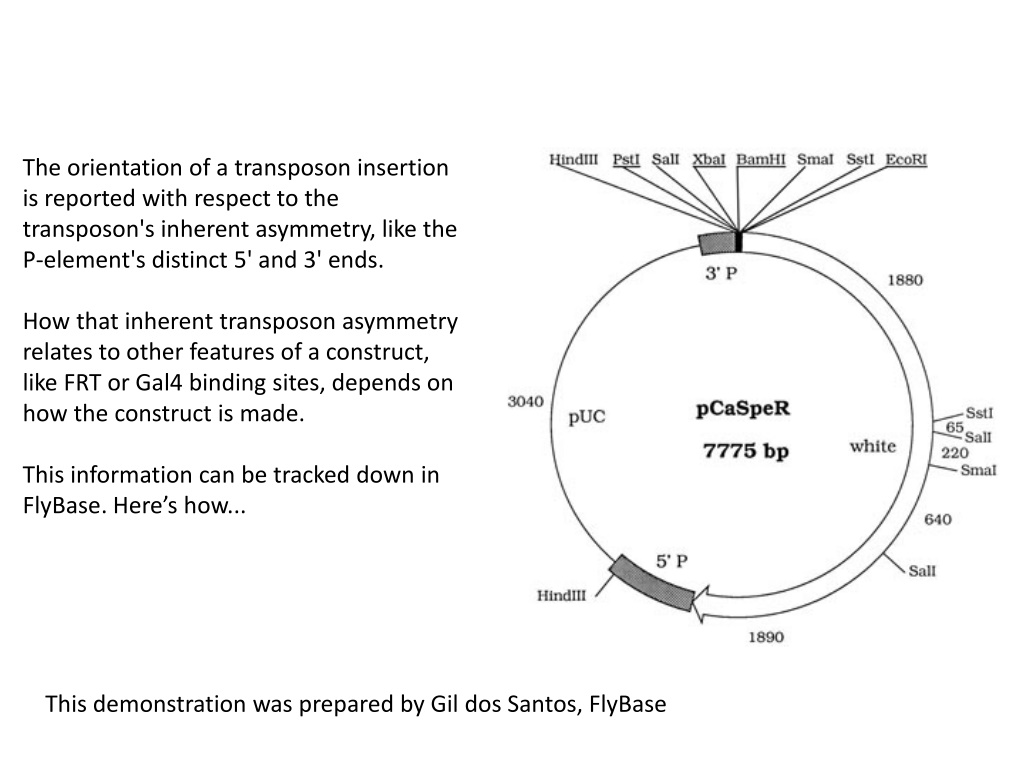
The orientation of a transposon insertion is reported with respect to the transposon's inherent asymmetry, like the P-element's distinct 5' and 3' ends. How that inherent transposon asymmetry relates to other features of a construct, like FRT or Gal4 binding sites, depends on how the construct is made. This information can be tracked down in FlyBase. Here s how... This demonstration was prepared by Gil dos Santos, FlyBase
I want to drive ectopic cbs expression: 3 5 HP21640 There are 2 EP/EP-like insertions in the region. If the triangle points up, it means that the P5 -to-P3 direction is oriented on the minus strand, relative to the genomic scaffold. We ll need to track down info about each kind of construct, {EPg} vs {EP} in FlyBase. Click on the blue triangle for the insertion of interest...
Clicking on the triangle for HP21640 takes you to the transposon insertion report. From there, look for the Inserted element link. Follow that to get info about the construct itself. The Segments & Size section of the construct report describes what s in the EP element, relative to the P5 and P3 ends. Click on each segment to get more info: e.g., CaSpeR_P5 has the mini-white cassette. e.g., The GAGA and UAS sites are nested just inside of the P3 . I would infer that EP-driven transcription proceeds through P3 . See references for more info. You may find the GDP s maps of commonly used constructs helpful.
Figuring out P{EPg}HP21640 {EPg}-driven transcription EP-driven 3 5 HP21640 From the info about the EPg construct, I would infer that transcription of this HP21640 insertion proceeds through the P3 ends, away from the cbs gene.
Figuring out P{EP}G2391 {EP}-driven transcription EP-driven 3 5 G2391 There s another EP-type element in the region: G2391. Following the same procedure, I figured out that the GAGA and UAS sites are nested just within P3 end. The blue triangle points down, meaning the 5 -to-3 orientation of the P-element is along the plus strand (relative to the genome). This is the one I want.