Understanding the Structure of DNA
DNA, which stands for Deoxyribonucleic Acid, is a double-stranded molecule composed of nucleotides. Each nucleotide consists of a base, a phosphate, and deoxyribose sugar. These nucleotides bond together to form a sugar-phosphate backbone through chemical bonds. The DNA molecule contains four bases - Thymine, Adenine, Guanine, and Cytosine - which pair up in a complementary manner. Understanding the structure of DNA is essential for comprehending its functions and processes.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Higher Biology Unit 1: 1.1 Structure of DNA
Starter Make a mind map of the key points you remember about DNA from Nat 5 biology in your jotter
Learning Intentions Name the molecules in a DNA nucleotide and identify them in a diagram Name the type of bond on the backbone of the DNA molecule Give the names of the 4 DNA bases Describe the base pairing rule for DNA bases
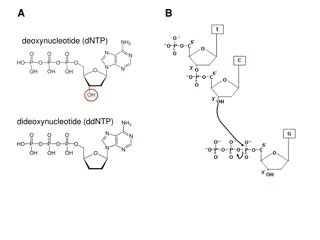
Deoxyribonucleic acid The DNA molecule is comprised of two chains of nucleotides. The nucleotides are comprised of deoxyribose sugar, a phosphate and a base.
DNA stands for Deoxyribose Nucleic Acid. It is as double stranded molecule made up of subunits called nucleotides. Each nucleotide is made of 3 parts;- A base, a phosphate and a deoxyribose sugar.
Nucleotides bond together to form a sugar- phosphate backbone. This is due to chemical bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the carbon 3 of the deoxyribose on another nucleotide.
This is what a nucleotide looks like at the molecular level
Nucleotides bond together to form a sugar-phosphate backbone. This is due to chemical bonds between the phosphate group of one nucleotide and the carbon 3 of the deoxyribose on the next nucleotide. The double helix is described as having two anti-parallel chains of nucleotides because one side goes from 5 to 3 (five prime to three prime) and the opposite side goes from 3 to 5 .
The Code There are 4 different types of base in DNA. Thymine = T Adenine = A Guanine = G Cytosine = C They have complementary base pairing T pairs with A G pairs with C
The bases pair up using hydrogen bonds to form the double helix shape. dnaribns Hydrogen bonds C and G 3 bonds T and A 2 bonds
These bases are described as being complementary to each other. This means their shapes match up.
https://www.youtube.com/watch ?v=8kK2zwjRV0M