Understanding the Metric System: Units, Definitions, and History
The metric system, developed in 18th-century France, offers a unified and natural approach to measurement. It includes base units like the meter for length and the gram for weight, all derived from natural properties. The modern International System of Units (SI) is widely adopted globally, with the majority of nations metricated. Despite this, the US and UK still use the English system, rooted in historical practices of body-based measurements. Efforts towards full metrication continue worldwide.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Metric System The Metric System Units, Definitions and History
The Metric System The Metric System Definition Definition The metric system is a system of units for measurement developed in late 18th century France by the chemist Lavoisier to replace the disparate systems of measures then in use with a unified, natural and universal system. In the early metric system there were several fundamental or base units, the grad or grade for angles, the metre for length, the gram for weight and the litre for capacity. These were derived from each other via the properties of natural objects, mainly water: 1 litre of water weighs 1 kg and measures 1 cubic decimetre (dm ). Other units were derived from this, such as the Celsius temperature scale, where water freezes as 0 C and boils as 100 C.
The Metric System The Metric System Definition Definition As the result of scientific progress, refinements, and different choices of base units, there have been a number of attempts at creating metric systems. The modern metric system (modern meaning post-1960) is now widely used throughout the world and is called the International System of Units (SI) ("Syst me International d'Unit s" in French).
The Metric System The Metric System Definition Definition The SI system has been adopted by nearly all the world's nations through a process called metrication. Today 95% of the world's population live in metricated countries, even though scattered use of some non-metric units may persist in some of these countries. The only, and particularly noticeable holdout to full metrication is the United States and, to a lesser degree, the United Kingdom, mainly due to public apathy. Most government business is now done fully in metric. However, efforts are underway to convert the public sphere to metric, although significant progress is likely only after more forceful legislation is passed. By the 1960s, most nations had started programs to fully convert to the metric system. As of 2005 only three countries, the United States, Liberia, and Myanmar (Burma) had not completed the changeover.
English System English System While the metric system was lawfully accepted for use in the United States in 1866, the US has not adopted the metric system as its "official" system of measurement. The US English System of measurement grew out of the manner in which people secured measurements using body parts and familiar objects. For example, shorter ground distances were measured with the human foot and longer distances were measured by paces, with one mile being 1,000 paces. Capacities were measured with household items such as cups, pails (formerly called gallons) and baskets. Obviously this system allowed for discrepancies between measurements obtained by different individuals. A standard was eventually set to ensure that all measurements represented the same amount for everyone.
English System English System Length: 1 foot (ft) = 12 inches (in) 1 yard (yd) = 3 feet 1 mile (mi) = 5280 feet 1 mile = 1760 yards
English System English System Weight: 1 pound (lb) = 16 ounces (oz) 1 ton = 2000 pounds
English System English System Capacity: 1 tablespoon (tbsp) = 3 teasponns (tsp) 1 cup (c) = 16 tablespoons 1 cup = 8 fluid ounces (oz) 1 pint (pt) = 2 cups 1 quart (qt) = 2 pints 1 gallon (gal) = 4 quarts
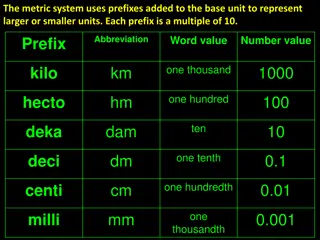
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System Multiples and submultiples of metric units are related by powers of ten; the names for these are formed with prefixes. This relationship is compatible with the decimal system of numbers and it contributes greatly to the convenience of metric units. The most commonly used prefixes for values above the base unit are hecto- (hundred), kilo- (thousand) and mega- (million); and the most commonly used for parts of the base value (i.e. below the base value) are deci- (tenth), centi- (hundredth) and milli- (thousandth). Some of the common prefixes are, however, rarely used for some units: the expressions hectometre, megametre and megagram are hardly ever heard, neither are decigram and centigram, while hectogram (often shortened to hecto), megalitre, decimetre and centimetre are commonly used measures in many countries.
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System Examples: Examples: Convert 10.25 kilometers to meters. Notice in the listing above that meter is three places to the right of the prefix kilo. This tells us to move the decimal point three places to the right. The answer is: 10.25 km = 10,250 m
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System Examples: Examples: Convert 650 mL to daL. [mL is milliliters and daL is decaliters]. Notice in the listing above that the prefix deca is four places to the left of the prefix milli. This tells us to move the decimal point four places to the left. (Note: dL is deciliters, daL is decaliters.) The answer is: 650 mL = 0.0650 daL
Conversion of Units in English System Conversion of Units in English System Examples: Examples: Convert 84 inches to feet. A proportion can be set up using the appropriate conversion ratio. In a proportion the product of the means equals the product of the extremes. Use this "cross multipy" concept to find the answer.
Conversion of Units in Metric System Conversion of Units in Metric System Examples: Examples: Convert 750 grams to milligrams. Notice in the listing above that the prefix milli is three places to the right of gram. This tells us to move the decimal point three places to the right. The answer is: 750 g = 750,000 mg
Conversion of Units in English System Conversion of Units in English System Examples: Examples: Find the number of cups in two gallons. There is no stated conversion for cups to gallons, so we have to be a bit more creative. Since there are 4 cups in 1 quart, and 4 quarts in 1 gallon, we can set up the conversion ratio based on "quarts". Two gallons is 8 quarts.
Conversion of Units in English System Conversion of Units in English System Examples: Examples: Convert 16 ton to pounds. Set up the conversion ratio and solve for the missing value.
Metric System Base Units Metric System Base Units
Metric System Derived (Compound) Units Metric System Derived (Compound) Units
Metric System Derived (Compound) Units Metric System Derived (Compound) Units
Metric System Metric System Meter ( Meter (Metre Metre) ) Closeup of National Prototype Metre Bar No. 27, made in 1889 by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures (BIPM) and given to the United States, which served as the standard for defining all units of length in the US from 1893 to 1960.
Metric System Metric System Meter ( Meter (Metre Metre) ) By 1983 it was accepted that the speed of light in vacuum was constant and that this constant provided a more reproducible procedure for measuring length. Therefore, the metre was redefined in terms of the speed of light. These definitions give a much better reproducibility and also allow anyone, anywhere with a suitably equipped laboratory, to make a standard metre.
Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Story 1: On September 23, 1999 NASA lost the $125 million Mars Climate Orbiter spacecraft after a 286-day journey to Mars. Miscalculations due to the use of English units instead of metric units apparently sent the craft slowly off course -- 60 miles in all. Thrusters used to help point the spacecraft had, over the course of months, been fired incorrectly because data used to control the wheels were calculated in incorrect units. Lockheed Martin, which was performing the calculations, was sending thruster data in English units (pounds) to NASA, while NASA's navigation team was expecting metric units (Newtons). Problem 1 - A solid rocket booster is ordered with the specification that it is to produce a total of 10 million pounds of thrust. If this number is mistaken for the thrust in Newtons, by how much, in pounds, will the thrust be in error? (1 pound = 4.5 Newtons)
Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Story 2: On January 26, 2004 at Tokyo Disneyland's Space Mountain, an axle broke on a roller coaster train mid-ride, causing it to derail. The cause was a part being the wrong size due to a conversion of the master plans in 1995 from English units to Metric units. In 2002, new axles were mistakenly ordered using the pre-1995 English specifications instead of the current Metric specifications. Problem 2 - A bolt is ordered with a thread diameter of 1.25 inches. What is this diameter in millimeters? If the order was mistaken for 1.25 centimeters, by how many millimeters would the bolt be in error?
Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Some Famous Unit Conversion Errors! Story 3: On 23 July 1983, Air Canada Flight 143 ran completely out of fuel about halfway through its flight from Montreal to Edmonton. Fuel loading was miscalculated through misunderstanding of the recently adopted metric system. For the trip, the pilot calculated a fuel requirement of 22,300 kilograms. There were 7,682 liters already in the tanks. Problem 3 - If a liter of jet fuel has a mass of 0.803 kilograms, how much fuel needed to be added for the trip?
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System foot meter 1 meter = 0.28084 feet
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System mile kilometer 1 mile = 1.60934
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System pound kilogram 1 kg = 2.20462
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System quart liter 1 quart = 0.946353 liter
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System second second
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System Kelvin Degree Fahrenheit 1 Kelvin = -459.67 Fahrenheit
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System mi/h km/h
Lets Test Your Knowledge. Let s Test Your Knowledge . English System Metric System foot meter mile pound quart liter second Kelvin Degree Fahrenheit mi/h kilometer kilogram second km/h