Understanding the Intricacies of the Nervous System
Delve into the intricate workings of the nervous system, encompassing the brain, spinal cord, and nerves. Explore key components such as neurons, neurotransmitters, and reflexes, essential for perceiving and responding to stimuli. Uncover the vital role of this control system in interpreting the external world.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Nervous System By: Sonia Espinosa, Matt Marchisotta, and Jillian Abizadeh
The Nervous Systems Main Function Your body s control system, it sends, receives, and processes nerve impulses all throughout the body The nervous system is comprised of nerves made up of specialized cells known as neurons The nervous system is essential when it comes to perceiving and comprehending the external world
Where is the nervous system in your body?...everywhere!
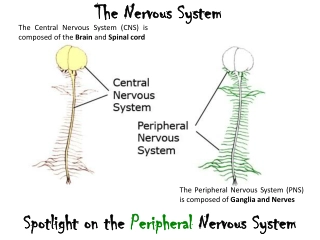
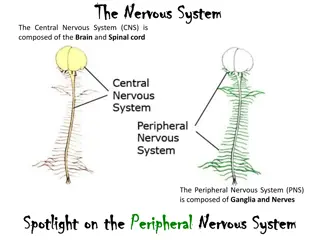
Main parts of the System and vocabulary Brain- An organ of soft nervous tissue contained in the skull of vertebrates, functioning as the coordinating center of sensation and intellectual and nervous activity Cerebrum- The principal and most anterior part of the brain in vertebrates Cerebellum- The part of the brain at the back of the skull in vertebrates, it also coordinates and regulates muscular activity Medulla- The inner region of an organ or tissue, especially when it is distinguishable from the outer region or cortex Spinal Cord- The cylindrical bundle of nerve fibers and associated tissue that is enclosed in the spine and connects nearly all parts of the body to the brain Nerves- A whitish fiber or bundle of fibers that transmits impulses of sensation to the brain or spinal cord, and impulses from these to the muscles and organs Neurons- A specialized cell transmitting nerve impulses Impulses- A sudden strong and unreflective urge or desire to act Neurotransmitter- A chemical substance that is released at the end of a nerve fiber by the arrival of a nerve impulse and, by diffusing across the synapse or junction Reflexes- An action that is performed as a response to a stimulus and without conscious thought Stimulus- a thing or event that evokes a specific functional reaction in an organ or tissue Response- an behavior of a living organism that results from an external or internal stimulus
What each part does: Central nervous system- consists of the brain and spinal cord, sends out nerve impulses and analyzes information from the sense organs, it is the main control center in your body, and the center of thought. Peripheral nervous system- includes the craniospinal nerves that branch off from the brain and spinal cord; from the central nervous system, it carries nerve impulses to the muscles and glands Autonomic nervous system- regulates involuntary action, such as a heart beat and digestion.
Describe the path a nerve impulse travels throughout the body from stimulus to response They pass through the thoracic region to innervate the internal organs Image result for nerve cells
How the system affects other body systems Receptors in muscles provide the brain with information about body position and movement. The brain controls the contraction of skeletal muscle. The nervous system regulates the speed at which food moves through the digestive tract.
How other body systems affect the system Bones from the skeletal system provide calcium that is essential for the proper functioning of the nervous system. In the endocrine system, reproductive hormones affect the development of the nervous system. The digestive system sends sensory information to the brain. Reproductive hormones from the reproductive system affect brain development and sexual behavior.
Two diseases of the nervous system Epilepsy, in which abnormal electrical discharges from brain cells can seize which means they can cause seizures, epilepsy is triggered by bright and or flashing lights. That is why there are caution signs in movies or television shows that have bright and or flashing lights Huntington s disease, which is an inherited condition that causes the nerve cells in the brain to degenerate.
Effects of outside/environmental factors on the system Lead in the nervous system causes Kidney damage Learning disabilities Attention deficit disorder Decreased intelligence
Fun Facts! There are millions of nerve cells in the human body. This number even exceeds the number of stars in the Milky Way. The human brain consists of about 100 billion neurons. If all these neurons were to be lined up, it would form a 600 mile long line. In humans, the right side of the brain controls the left side of the body, while the left side of the brain controls the right side.
Resources http://artdistrictchiropractic.com/new-patient-center/fun-facts.html http://www.livescience.com/22665-nervous-system.html https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/brain https://faculty.washington.edu/chudler/organ.html http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/bb/neuro/neuro00/web2/Patel.html http://kidshealth.org/en/kids/brain.html http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/medulla-oblongata https://www.uab.edu/medicine/sci/faqs-about-spinal-cord-injury-sci/what-does-the- spinal-cord-do https://www.reference.com/science/nerves-5c6f4991b82d6b73 http://www.brainfacts.org/brain-basics/neuroanatomy/articles/2012/the-neuron/