Understanding Seedless Plants: Bryophytes and Pteridophytes
Explore the world of seedless plants through bryophytes and pteridophytes. Learn about the characteristics of green algae, the life cycles of these plants, and how vascular tissue impacts their growth. Discover the limitations and importance of vascular tissue in plants, from the small yet significant bryophytes to the fluid-moving abilities of pteridophytes like ferns. Delve into the differences between gametophytes and sporophytes in the life cycle of these fascinating plant groups.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
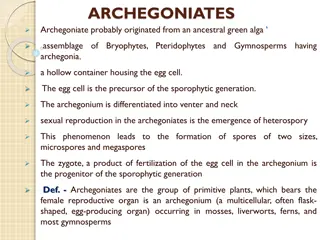
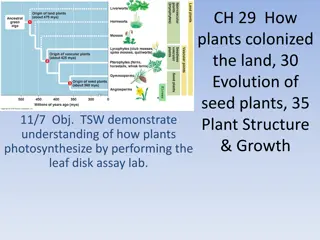
22.2 Seedless Plants P639 Identify bryophytes, pteridophytes phyte-plant type organism
Green Algae Q: What are the characteristics of green algae? A: Green algae are mostly aquatic. They are found in fresh and salt water, and in some moist areas on land.
Life Cycle- Green Algae.
Mosses types of Bryophytes Q: What factor limits the size of bryophytes? A: Bryophytes are small because they lack vascular tissue. Bryophytes: Group of plants that have specialized reproductive organs but lack vascular tissue. Vascular Tissue: specialized tissue in plants that carries water & nutrients.
Vascular Plants-ex:Pteridophytes-Ferns Q: How is vascular tissue important? A: Vascular tissues-xylem & phloem-make it possible for vascular plants to move fluids through their bodies against the force of gravity. Xylem-vascular tissue that carries water upward from roots to every part of a plant. Phloem-vascular tissue that transports solutions of nutrients & carbohydrates produce by photosynthesis through the plant. Tracheids- hollow plant cell in xylem with thick cell walls strengthened by lignin.