Understanding Pronouns: A Key to Language Awareness
Explore the world of pronouns in language learning, discovering how these versatile words can replace nouns and adapt to different contexts. Dive into examples and activities to enhance your grasp of pronouns and their importance in communication.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Language Awareness for Key Stage 3 4: Parts of Speech Part II 1
Roadmap In the last lesson, we began to look at the parts of speech by considering nouns and verbs Now you will see some more parts of speech: pronouns, adjectives and adverbs 2
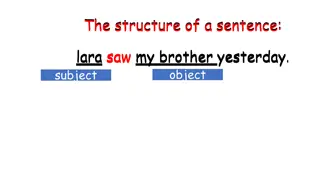
Parts of Speech Previously, we learned that you can identify nouns and verbs according to where they appear in a sentence 1. People like bikes People like dreams However, other parts of speech can also occur in the same places as nouns 2. They like them 3
Pronouns These words that can be used instead of nouns are pronouns In English, pronouns include words such as I, me, we, us, you, he, him, she, her, it, they, them, who, and whom 4
Pronouns An important difference between nouns and pronouns is that nouns have a constant meaning A noun like tree can only refer to a tree A pronoun like it can refer to any thing, depending on what you re talking about A pronoun like I always refers to the person speaking, so when a different person speaks I refers to someone different 5
Pronouns 3. John was hungry, so he ate some cake, and Bill was thirsty, so he drank some water You can see how a single form like he can refer to different people, even in the same sentence 4. John was talking to Bill and he said that he was going out with Anna Additional information is sometimes needed in order to identify the person referred to by a pronoun In this case you would have to guess who was more likely to be going out with Anna, which means you would need to know more about Anna and John and Bill 6
Activity Read the first sample text in your handout and underline all the pronouns 7
Solution 8
Solution They told me you had been to her And mentioned me to him: She gave me a good character But said I could not swim. He sent them word I had not gone (We know it to be true): If she should push the matter on, What would become of you? I gave her one, they gave him two, You gave us three or more; They all returned from him to you, Though they were mine before. If I or she should chance to be Involved in this affair, He trusts to you to set them free, Exactly as we were. 9
Adjectives Adjectives are another part of speech Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns 5. A tall tree 6. A fast bike 7. Poor you! 10
Adjectives As you will see, adjectives have many of the same properties as nouns In many languages, including French, there are singular and plural adjectives in the same way that there are singular and plural nouns 8. One good book 9. Un bon livre 10.Two good books 11.Deux bons livres 11
Adjectives In English, the adjective almost always comes before the noun 12.black cat There are some languages, such as Polish and Japanese, that use the same order as English 13.czarny kot 14.kuroi neko However, there are also languages where the noun normally comes first, such as Irish 15.cat dubh 12
Adjectives In some languages, such as French, adjectives can occur in more than one position, with different meanings 16.Un grand homme A great man 17.Un homme grand A tall man As you can see, English expresses the same distinction by using different words in the same position 13
Adjectives It is sometimes possible to use an adjective in the same way as a noun 18.I saw a rich man 19.I saw a poor man 20.I saw a French woman 21.I saw a Swiss woman 22.We discussed the rich 23.We discussed the poor 24.We discussed the French 25.We discussed the Swiss 14
Adjectives When is it possible to use adjectives in this way? Can you do this with any adjectives in English? 15
Adjectives In English it is only possible to use adjectives as nouns in certain situations, usually when referring to groups of people In other languages this can be done with almost any adjective French 26. Un m chant A naughty (person) Greek 27. T al th s The true (thing) [= the truth] 16
Adverbs Adverbs are a very diverse group of words, both in form and in function 28.Come here! 29.It was very good 30.They run quite fast 31.Unfortunately, they were late Some adverbs express location Adverbs can modify other in space or time Adverbs can modify adjectives Adverbs can modify verbs adverbs Adverbs can also modify entire sentences 17
Activity Read the second sample text in your handout and underline all the adverbs 18
Activity You can see the solution in a little while 19
Adverbs Many adverbs are formed from adjectives In English, the usual way to do this is by adding -ly 32.They are quick thinkers 33.They think quickly Some adjectives have adverbs of other types 34.They are good singers 35.They sing well However, not all words ending in -ly are adverbs 20
Adverbs In languages like German, there is no special way of forming adverbs Adverbs look just like adjectives 36.Diese S nger sind gut These singers are good 37.Sie singen gut They sing well This is also true of some adverbs in English 38.They are fast drivers 39.They drive fast 21
Adverbs There is much more choice about where to put adverbs in a sentence than for most other parts of speech 40.Often, this would happen 41.This would often happen 42.This would happen often 22
Adverbs However, sometimes changing the position of an adverb can change the meaning of a sentence 42.We want to go skiing often (We want to do a lot of skiing) 43.We often want to go skiing (We feel this way a lot) 44.He told me everything frankly (He was being frank) 45.Frankly, he told me everything (I am being frank) 23
Activity Go back to the text where you underlined adverbs Can you see any adverbs that you missed? 24
Solution 25
Solution The chief difficulty Alice found at first was in managing her flamingo. She succeeded in getting its body tucked away comfortably enough, under her arm, with its legs hanging down, but generally, just as she had got its neck nicely straightened out, and was going to give the hedgehog a blow with its head, it would twist itself round and look up in her face 26
Solution Some of these words are not always adverbs. We will discuss them more in another lesson. The chief difficulty Alice found at first was in managing her flamingo. She succeeded in getting its body tucked away comfortably enough, under her arm, with its legs hanging down, but generally, just as she had got its neck nicely straightened out, and was going to give the hedgehog a blow with its head, it would twist itself round and look up in her face 27
Conclusion Pronouns can be used in place of nouns The meaning of pronouns can change, depending on what they represent Adjectives modify nouns and pronouns Adjectives can sometimes be used like nouns Adverbs modify adjectives, verbs and other adverbs There is a lot of variety in how adverbs are formed and used 28