Understanding Key Geometric Concepts in Mathematics
Explore the fundamental concepts of geometry in mathematics, including points, lines, line segments, rays, polygons, circles, circumference, radius, diameter, and co-centric circles. Learn about different types of polygons such as triangles, quadrilaterals, pentagons, hexagons, heptagons, octagons, nonagons, and decagons. Enhance your knowledge of geometric shapes and their properties to improve your understanding of mathematical principles.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
MATHS CLASS 4 CH3- GEOMETRY
LINES Point A point shows an exact location or position. It has no length and width. It is represented by a dot (.) and is denoted by a capital letter like P and Q. examples : . P, .Q Line A line is a straight path that has no end points and extends endlessly in both directions. Examples :- <------.------.-----> <----> or <----> P Q QP PQ
Line segment A line segment is a fixed length with 2 definite points. Example: P Q PQ or QP Ray A ray originates from one point and extends endlessly in other direction. Example : P Q PQ
POLYGON Closed figures formed by joining 3 or more line segments are called polygons. A polygon of three sides is called triangle. A polygon of four sides is called quadrilateral. Similarly, a polygon of 5, 6, 7, 8, 9 and 10 sides are called pentagon, hexagon, heptagon, octagon, nonagon and decagon.
TYPES OF POLYGON Triangle (3 sided polygon.) Quadrilateral (4 sided polygon.) Pentagon (5 sided polygon.) Hexagon (6 sided polygon.)
Heptagon (7 sided polygon.) Octagon (8 sided polygon.) Nonagon (9 sided polygon.) Decagon (10 sided polygon.)
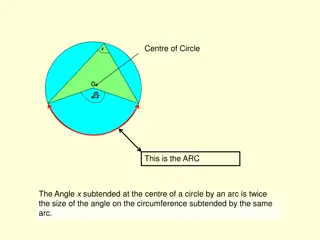
CIRCLE Circle - A circle is a curved figure. Centre It is a point in the circle from which all the points on the boundary of the circle are at the equal distance.
Circumference The length of the boundary of the circle is called its circumference. Radius It is a distance between the centre of a circle and any point on its boundary. Radius is the half of the diameter. r = d/2 or d 2
Diameter It is the longest line segment passing through the centre and joining any 2 points on a circle. A diameter is twice the radius. d = 2 r
Co centric circles The circles which have same centre but different radii and diameter are called co centric circles.