Understanding Food Webs in Aquatic Habitats
Exploring the intricate relationships within aquatic food webs, this content delves into the control of beneficial and pest species, highlighting the importance of biodiversity and the factors that influence species presence and success. From the role of frogs in the ecosystem to the impact on tadpole populations, the discussion touches on life requirements, controlling factors, and habitat variations that shape diverse aquatic environments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
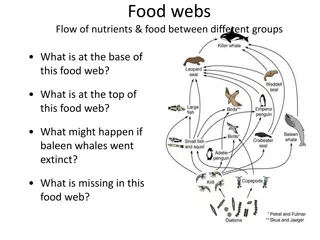
Food Web Control of Beneficial and Pest Species Food Web Control of Beneficial and Pest Species Who Eats What and Why Should We Care? Who Eats What and Why Should We Care?
What animals would you expect to find here? What are their life requirements? What factors, abiotic and biotic, are controlling factors here?
What controls frogs? What limits them? What makes them successful?
Which species in the food web promote the presence of tadpoles in this food web? Which species may prevent tadpoles from living in a pond?
Not all habitats are created equal Not all habitats are created equal What are the life requirements for your focal species to complete their life cycle in an aquatic habitat? What are some of the controlling factors that may limit your focal species? What are the abiotic differences between our two ponds: 1) 2) 3) 4) 5)
Generate your hypothesis Generate your hypothesis Generate your hypothesis Question 1: Which one of these treatments groups will have the highest and lowest biodiversity? Question 2: Which of these treatments will contain more of your focal species? Pond A: 1) 2) 3) 4) Write a hypothesis and describe the mechanism behind it. Pond B: 1) 2) 3) 4)