Exploring Energy Flow in Food Webs
Dive into the intricate relationships of organisms in various food chains and webs, understanding the flow of energy from producers to consumers and the impact of changes in population sizes. Discover the significance of trophic levels and the role of energy pyramids in ecosystems.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Energy Flow Rotation Make a new entry in your journal
Food Chain Quaternary Consumer Primary Consumer Secondary Producer Tertiary Consumer Consumer 1. The heron is considered a quaternary consumer. Label the trophic levels of each organism in the food chain. Sun 2. 3. Where does the cattail get its energy? Explain what the arrows represent in a food chain. The arrows point in the direction energy flows 4. Describe 2 things that would happen if all of the small fish were removed from the food chain above. Dragonfly population would increase Catfish population would decrease Bonus: What biome would this food chain be found in?Fresh water
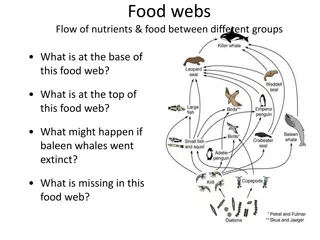
Food Web 1. Where did all energy in this food web originate from? sun 2. Place each organism in the appropriate trophic level. Quaternary Consumer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Producer Phytoplankton Zooplankton Squid Penguin Killer Whale XXXXXXX Krill Baleen Whale Killer Whale Leopard Seal XXXXXXX XXXXXXX Seal Leopard Seal XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX XXXXXXX
Food Web 3. Describe the relationship (use vocabulary) between baleen whales and krill. Whale is predator because it eats the krill - prey 4. Describe one path energy could take through this food web. Answers will vary (Sun Phytoplankton Zooplankton Baleen Whale) 5. Describe 2 things that would happen if there was an increase in the krill population. The whale, seal, and squid population would increase. The phytoplankton would decrease. Bonus: What biome would this food web be found in? saltwater (ocean)
Food Web Baleen whale Secondary Consumer Primary Consumer Killer whale Tertiary Consumer& Quaternary Consumer Primary Consumer Secondary Consumer Producer Krill Seal Secondary Consumer http://t0.gstatic.com/images?q=tbn:ANd9GcTmDhZSQJZGY9I2GtbTXqNZ9XSaCxcQmCLwHGtMU_LLQa_qdvBh_SenpTy4 Tertiary & Quaternary Consumer Tertiary Consumer Squid Penguins Leopard seal
Energy Pyramid Tertiary Consumer .1% Trophic Level 4 Secondary Consumer Trophic Level 3 1% Primary Consumer Trophic Level 2 10% Producer Trophic Level 1 Sagebrush 100%
Energy Pyramid 4. What happens to the other 90% of the energy that is not passed on from each trophic level. It escapes into the environment as heat/thermal energy 5. What consumer in the energy pyramid is going to have to eat the most food to meet their energy needs? Hawk tertiary - level 4 6. Describe in your own words why energy in an environment can be represented by a pyramid. More energy is available at the producer level so it is bigger at the bottom, less is available as you go up 7. Create a food chain with the same organisms from above, using words and arrows. Sagebrush Insects Lizard Hawk
Composting 1. Why is composting good for the environment? Composting is the healthiest fertilizer; Cuts back on garbage in landfills 2. Why is it important to have green and brown in a compost bin? So it is rich in both carbon (brown) and nitrogen (green) 3. Use the T chart to sort things that should and should NOT be in a compost bin. (on next slide) 4. What happens to the biomass of a compost bin? Biomass decreases as it is decomposed 5. What happens to the temperature of a compost bin over time? Temperature increases in a compost bin over time 6. What energy conversion happens in a compost bin? Chemical energy heat/thermal energy 7. What type of organism breaks down biomass in a compost bin? Decomposers (microorganisms, worms)
Compost Trash Wood Glass Banana peel Apple core Foil gum wrapper Soda can Leaves Worms Grass clippings Plastic bottle Meat or bones