Understanding Coordination Compounds and Ligands in Chemistry
Coordination compounds involve ligands that donate electron pairs to central metal ions. Ligands can be categorized based on the number of donor atoms they contain, such as mono-, bi-, tri-, tetra-, penta-, and hexadentate ligands. Each type of ligand has the ability to form bonds with the central metal ion at specific positions, influencing the coordination number of the complex. Dr. Atul Kumar Singh, an Assistant Professor at M.L. Arya College in India, provides valuable insights into the concepts of coordination compounds and ligands.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Coordination Compounds Course Instructor: Dr. Atul Kumar Singh Assistant Professor Department of Chemistry M. L. Arya College, Kasba Purnia -854330 India
Ligands The molecules, anions or cations which are directly linked with the central metal atom or ion by coordinate bond in a complex ion are called ligands. The ligand acts as a donor as it donates one or more electron pairs to the central metal atom thus should have lone pair or pairs of electrons. The centre ion acts as an acceptor as it accept electrons from ligands thus should have vacant orbitals.
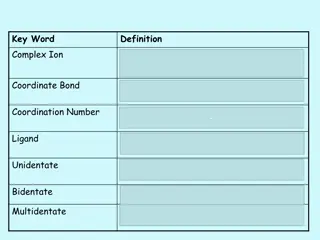
Types of ligands Depending on the number of donor atoms present ligands can be divided into following types a. Mono- or unidentate ligands b. Bidentate ligands c. Tridentate ligands d. Tetradentate ligands e. Pentadentate ligands f. Hexadentate ligands g. Chelating ligands
Mono- or unidentate ligands Ligands which donate a single pair of electron to a metal atom. Examples
Bidentate ligands Ligands which donate two pairs of electron i.e, have the ability to link with central metal ion at two positions Examples
Tridentate ligands Ligands which donate three pairs of electron i.e. have the ability to link with central metal ion at three positions Examples
Tetradentate ligands Ligands which donate four pairs of electron i.e. have the ability to link with central metal ion at four positions Examples
Pentadentate ligands Ligands which donate five pairs of electron i.e. have the ability to link with central metal ion at five positions Examples
Hexadentate ligands Ligands which donate six pairs of electron i.e. have the ability to link with central metal ion at six positions Examples
Coordination Number The number of ligands that are directly attached to the central metal atom or ion by coordinate bonds is known as the coordination number of the metal atom or ion i.e, the total number of coordination bond ligands form with the central metal atom or ion.
Coordination Sphere The central metal atom or ion and the ligands that are directly attached to it are enclosed in a square bracket is known as coordination sphere.
Charge on the complex ion The charge on the complex ion is the algebraic sum of the charges carried by central metal ion and the ligands coordinated to it.