Understanding Complex Sentences and Clauses
Complex sentences consist of an independent clause and at least one dependent clause, such as adjective, adverb, or noun clauses. They are connected using subordinate conjunctions, relative pronouns, and relative adverbs. Each has a specific role in modifying nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, or connecting dependent clauses to the main clause. Examples and explanations are provided for better comprehension.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
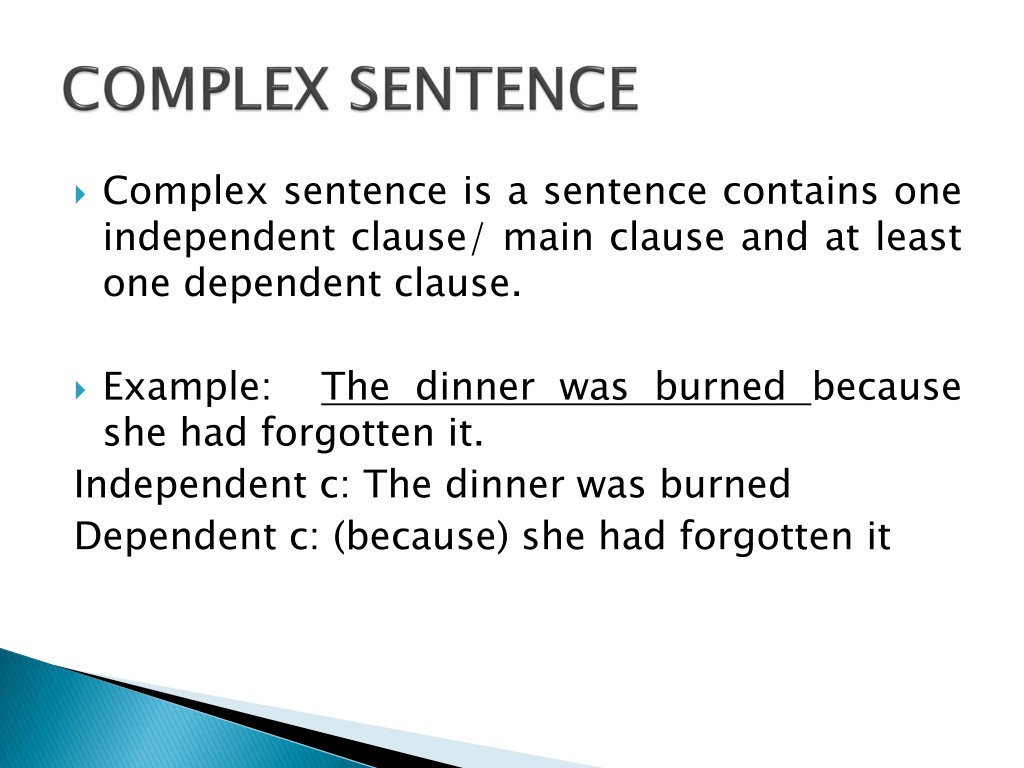
Complex sentence is a sentence contains one independent clause/ main clause and at least one dependent clause. Example: she had forgotten it. Independent c: The dinner was burned Dependent c: (because) she had forgotten it The dinner was burned because
1. Adjective clause modifies noun/ pronoun 2. Adverb Clause modifies V,ADV,ADJ in the main clause 3. Noun Clause subtitutes a noun in the main clause functioning as S, Object of preposition or appositive
subordinate conjunction (contoh: after, since, when, although, because) ketika digunakan pada adverbial clause relative pronoun (contoh: who, which, whose, whom, that) ketika digunakan pada Adjective clause question word digunakan pada noun clause subordinate conjunction adverbial clause relative pronoun Adjective clause weather, atau that noun clause question word, if if / /weather that ketika
Relative pronoun and relative adverb are used in connecting dependent clause to the main clause. Relative pronoun: who, whom, which,whose,that Relative adverb: where,when,why
Who: to modify a person as a subject Whom: to modify a person as an object Which: to modify subject/object thing Whose: is for possession Where: to relate a place When: to a time expression Why : to reason
The person who teacher The woman, who sister The manager, who worked for almost 10 years Mr. Abraham, whom my headmaster. The person whom teacher who phoned me last night is my who is very beautiful, is my who comes on time, has whom I admire so much, was whom I phoned last night is my
The car which The car which Mueeza is a cat which The mansion, whose holiday, has burned down. My brother, whose doctor. The car, whose the accident, was completely destroyed. which hit me was yellow which I drive is old. which is very faithful. whose owner is going on whose phone you just heard, is a whose driver jumped out just before
The reason why work is that more people worry than work. That's the restaurant where first time. I remember the day when There was a very hot summer the year when why worry kills more people than where we met for the when we first met. when he was born.
Adverb clause is a dependent clause that modifies a verb, adjective or adverb in the main clause.
The relation of the information in an adverb clause to the main clause is shown by subordinate conjunction. An adverb clause may come at the biginning, in the middle, or the end of the sentence. A comma is needed when the clause is placed in the beginning of a sentence.
1. Clause of time: after, before, sooner, while 2. Clause of place:nowhere,anywhere, wherever 3. Clause of contrast/concession:although, though,eventhough,whereas,even if, in spite of, as the time 4. Clause of manner: as, how, like, in that 5. Clause of purposes: in order to, that, so that, in the hope that, in case,
Because Sally kissed me, I fainted Even though Sally kissed me, I fainted Sally kissed me after I fainted Even though English teachers are boring, they still need love and respect The world would be a better place if more people respected English teachers If I were you, I would listen to my English teacher because I might learn something of life altering significance.
When? When? Where? Where? Why? Why? To what degree? To what degree? Under what circumstances? Under what circumstances?