Understanding Bystander Intervention, Consent, and Social Conformity
Explore the concepts of bystander intervention, consent, and social conformity in this informative guide. Learn how to recognize potentially harmful situations, overcome obstacles to intervening, and navigate societal expectations. Understand the importance of obtaining consent and challenging social stereotypes to promote a safer and more inclusive environment.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author. Download presentation by click this link. If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
SAPR QUICK REFERENCE GUIDE 3/C PCA
Objectives Define bystander intervention and understand the factors that may inhibit intervention from a bystander Define consent and understand how consent can be obtained during sexual acts Understand social stereotypes of both men and women and the pressure of social conformity
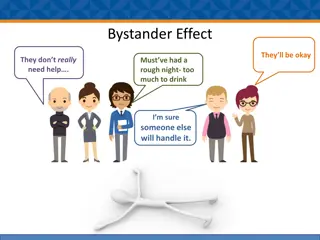
Bystander Intervention An individual or group of individuals (bystanders) witness a situation between other people developing that could turn into something bad or dangerous, and the bystanders choose to act to stop it from escalating any further (intervention) Internal Stages of Bystander Intervention Notice the event Interpret the event as a problem Determine whether or not you are responsible for dealing with the problem Determine whether or not you have the skills and resources to act Act
Obstacles to Intervening We might not know the people involved in the potentially bad situation We might not know how to intervene Nobody else is doing anything, so it must not be a big deal We might not want to be rude or interrupt something we don t think is our business We might not want our friends to be mad at us We might not want to do it alone, someone else will do something if it really is a dangerous situation We might not think anything bad will really happen
Social Conformity Adherence to a group s social patterns, standards or expectations in order to fit in with the group Individual may internally disagree, but still conforms regardless, in order to not stand out from the crowd Possible reasons for Social Conformity Individual thinks there s a logical explanation for why everyone is doing it Individual doesn t want to be embarrassed for not following along Desire to fit in Individual sees a pattern of behavior in the group, and thinks that is normal for the group, so chooses to comply and/or not change social norms
Consent Everyone is fully conscious and aware Everyone is fully participating in the event There is no physical force, threat of force, or fraud
Social Stereotypes Men/Women Set of behaviors assigned to both men and women based on assumptions for the entire gender rather than the individuals There is social pressure for women and men to act a certain way in order to fit in with the stereotypes assigned to them Could be harmful to themselves or others Social consequences for not conforming