Trade Cycles: Economic Fluctuations and Phases
Trade cycles, also known as business cycles, are fluctuations in economic activities, affecting employment, output, income, prices, and profits. These cycles consist of phases including depression, recovery, prosperity, and recession. During booms, economic activities peak, while recessions see a slowdown leading to depression. Governments often intervene during depressions to stimulate recovery and economic growth.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Module 1 Chapter 4 SHORT RUN ECONOMIC FLUCTUATIONS
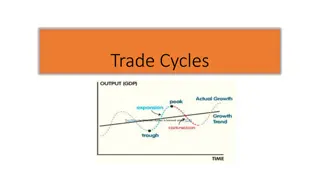
What is trade cycle ? A trade cycle refers to fluctuations in economic activities specially in employment, output and income, prices, profits etc. It has been defined differently by different economists. According to Mitchell, Business cycles are of fluctuations in the economic activities of organized communities.
Features of trade cycle A business cycle is synchronic. When cyclical fluctuations start in one sector it spreads to other sectors In a trade cycle, a period of prosperity is followed by a period of depression. Hence trade cycle is a wave like movement. Business cycle is recurrent and rhythmic; prosperity is followed by depression and vice versa Thee business cycle is not periodical. Some trade cycles last for three or four years, while others last for six or eight or even more years. The impact of a trade cycle is differential. It affects different industries in different ways.
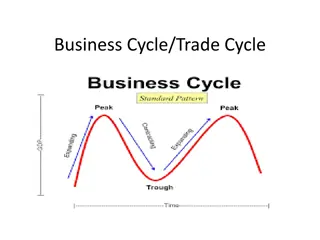
Phases of trade cycle Generally, a trade cycle is composed of four phases Depression or trough Recovery Prosperity and Recession.
Boom / Peak : This phase is also known as prosperity or peak. During this phase growth level is maximum. Income, demand, investments and profits are high. This means all the variables are at maximum Recession: This phase comes after the phase of boom when economic activities have reached the highest level it is then followed by a slow down.
Depression: The phase of recession continues to the phase of depression. There is complete slow down of all economic activities. Consumers expect lower prices and this causes a fall in demand, production, employment. Recovery: After the phase of depression which causes low level of economic activities, government may try to help and bring changes for the economy to function properly. After a while demand starts to increase slowly and so does investment and employment.