The Strengths and Weaknesses of the Weimar Republic
The Weimar Republic faced a turbulent period with strengths like introducing proportional representation but also weaknesses such as political instability and economic struggles. Kaiser Wilhelm II's actions, the impact of WW1, and the challenges faced by the new government are discussed in the context of the Weimar Constitution.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Thursday, 18 July 2024 LESSON TITLE: What were the strengths and weaknesses of the new Weimar Republic? 1. Which country joined WW1 which meant Germany were forced to surrender? 2. What did Kaiser Wilhelm II do? 3. What had the British Navy put around Germany? What did this cause to happen? 4. How many German civilians died of starvation? 5. How many German soldiers died during WW1? 6. Explain why Germany surrendered in WW1.
What were the strengths and weaknesses of the new Weimar Republic? To explain and judge if the Weimar Constitution was doomed from the start. Mastering To explain the strengths and weaknesses of the new Weimar Republic Securing To describe the structure of the new Weimar Republic Developing
1. In 1914 who had the most power? Explain what they could do, how do they have power? connect 2. In 1919, who had the most power? Explain what they could do. 3. Which constitution do you think was better. Why? Weimar Constitution 1914 1919
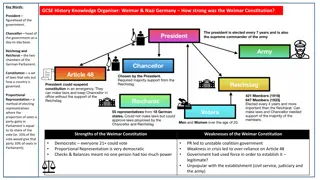
Background Information Background Information On 9th November 1918, Kaiser Wilhelm II abdicated and fled to Holland. Power was handed over to Friedrich Ebert, leader of the SPD and on the 11th November 1918 Germany surrendered to the allies. Ebert then spent the next nine months creating the new Government and trying to establish support. This included: Promising the Army the Ebert would not reform it (change it). Promising Trade Unions that he would try to achieve an 8 hour working day. Assuring industry leaders that they would not confiscate land or factories. This ensured that the businesses and the economy continued to operate. BUT Some extreme political parties were not satisfied. Demonstrations and even riots were common.
Task 1: You have a number of cards. You need to decide if they were a strength or weakness of the new Weimar Republic. You then need to place the cards on the right side of the weighing scales. Weakness of the Weimar Constitution Strengths of the Weimar Constitution Task 2: Some cards are more significant than others. Can you place the more significant cards nearer the top, the less significant at the bottom.
You have a number of cards. You need to decide if they were a strength or weakness of the new Weimar Republic. You then need to place the cards on the right side of the weighing scales. Strengths of the Weimar Constitution Weakness of the Weimar Constitution Proportional Representation meant that smaller parties won seats which often meant there was no majority in the Reichstag. This meant different parties had to join together to rule (coalition). This was a problem as they often fell out, and didn t achieve much. Between 1919-1923 there were nine coalition governments. Women for the first time in Germany, were able to vote as well as men. The Chancellor decided which laws should be passed. However in normal times, they could only pass a law if the majority of the Reichstag voted for it. Many chancellors used Article 48 to pass laws rather than getting a majority in the Reichstag. Some cards are more significant than others. Can you place the more significant cards nearer the top, the less significant at the bottom.
What were the strengths and weaknesses of the new Weimar Republic? connect On your whiteboards complete the following 1. When did Kaiser Wilhelm abdicate? 2. Identify the biggest strength of the Weimar Republic 3. Identify the biggest weakness of the Weimar Republic Overall, do you think the Weimar Constitution was a strength or a weakness? Justify your answer.
Use the information that you have learnt over the last two lessons to complete the word fill. 1. The Reichstag was the German ____________________ building 2. The new Government was headed by the ________________ who was elected for 7 years. 3. The President could make decisions without consulting the Reichstag if there was a state of ____________________ according to Article 48. 4. The Chancellor was usually the leader of the political party with the _________ seats in the Reichstag. 5. The people voted for which parties got seats in the Reichstag by the system of __________________________________. 6. Proportional Representation meant parties found it hard to get a ________________ in the Reichstag and pass laws so they formed ______________________ which often broke down.