The Importance of the Metric System
The metric system, utilized worldwide, simplifies measurements by employing a base of 10 for conversions. It consists of units like meters, grams, liters, and Celsius for length, mass, volume, and temperature. This system facilitates global communication among scientists and builders due to its standardization and ease of use.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Metric System Notes Directions First, in order to view this presentation properly you must select "Slide Show then choose From Beginning . Use the arrow keys to change slides. Next, as you go through the presentation take notes on metric measurement. DO NOT WRITE EVERYTHING. Read the information carefully, then write a summary of the important information on that page (usually only one or two sentences). Page titles are underlined . They tell you what you are learning about, so those should be the subtitles within your notes. To help you, important information is in bold. Not all pages will require note taking. Be sure to read each page carefully!
Kilometer Celsius LITER Title of your notes: Using the Metric System meter Tools Units Symbols Prefixes Converting Within the Metric System
Metric System Scientists around the world use the International System of Measurements, (SI) or Metrics, to measure distances, volumes, masses, and temperatures. In fact, most countries use the metric system of measurement. The countries in red are NOT using the metric system as a standard measurement system.
Metric System If you travel to France (or just about any other country in the world), the distances and speeds marked on the road signs will be in kilometers, not in miles. You would buy milk measured in liters
2 Metric System Liters You may be used to buying water and soda in liters, so you are already using the metric system! 1 Liter
Metric System Why do we have the metric system? Scientists and builders around the world need to be able to share information.
Metric System 10 The metric system is based on the number 10. It is easy to use because each measurement can be converted by simply multiplying or dividing by a factor of 10.
Metric System Symbols for Base Units Look at the chart below to see the basic metric units and their symbols. Base units are what all measurements are based around. Measurement Unit Symbol Length meter m Mass gram g Volume liter L Temperature Kelvin (or Celsius) K (C)
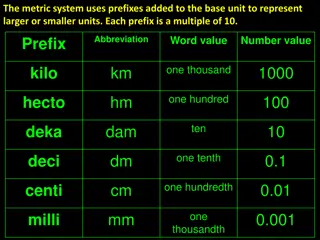
Metric System Prefixes Meter (length) Liter (liquids), and Gram (mass) are all base units. 1 base unit (no prefix) 10 Deka- 100 Hecta- 1000 - Kilo Prefixes are used with the base unit of measurement and indicate which multiple of 10 is being used. For example one dekameter is ten meters; two dekameters would be what??? Measuring in units smaller than the base unit are a fraction of the base unit. Examples are Centimeter can you tell by the fraction shown next to the prefix how many Centimeters there are in a meter???
Metric System Here are some commonly used prefixes in the metric system. Notice the multiplying factors are all based on the number 10. Prefix Symbol Multiplying Factor 1,000,000 1000 100 10 0.1 0.01 0.001 0.000001 0.000000001 Mega Kilo Hecta Deka Deci Centi Milli Micro Nano M k h da d c m u n There are 1000 meters in a kilometer. A centimeter is 0.01 of a meter meaning there are 100 centimeters in one meter.
Metric System Length Use a metric ruler or a meter stick to measure length in the Metric System.
Metric System Length The basic unit of length is meter (m). A meter is about the length of a yard in the English system. The length of a room or the length of a large animal would be measured in meters. A centimeter (cm) is one-hundredth (1/100) of a meter. 1m = 100cm The length of your finger or your silverware would be measured in cm.
Metric System - Mass Use a balance or scale to measure mass in the Metric System. Always make sure your scale or balance is on zero before measuring. To use a balance, objects are placed on the tray and then you move the riders on the beams until you get the lines on the right-side of the scale to match up (the pointer & the zero mark). To use a scale, just put the object on the tray and read the screen.
Metric System - Mass The basic unit of mass is kilogram. A kilogram is about 2.2 pounds. The mass of one of your large textbooks may be about 1 kilogram. 354.6 grams A gram is one-thousandth of a kilogram. 1 kg = 1000 g Pencils, candies, and cereal can be measured in grams.
Metric System Volume of Liquids Use a graduated cylinder to measure volume in the Metric System. Make sure you are looking at it eye level AND reading the bottom of the meniscus (curve in the liquid). This is 79 mL NOT 80 mL !!!!
Metric System Volume of Liquids The basic unit of volume is the Liter. A liter is about 1/4 of a gallon. The volume of a large bottle of soda is 2 liters. A milliliter is one-thousandth (1/1000) of a liter 1 L = 1000 mL A bottle of drinking water, a jar of spaghetti sauce, or medecine can be measured in milliliters.
Metric System Volume of Regular Shapes (boxes) Use a ruler or meter stick to find the volume of a regular shaped object.
Metric System Volume of Regular Shapes (boxes) cm cm cm cm3 To calculate the volume of a regular shape, multiply the length times the width times the height. The unit for solid volume is m3 or cm3.
Metric System Volume of Irregular Shapes Use a graduated cylinder and water displacement to determine the volume of odd shaped objects like rocks or toys. To find the volume of an odd shaped item: 1. add water to graduated cylinder 2. add the object and note the new volume 3. Subtract the original volume of just water
Metric System Volume of Irregular Shapes The unit for the volume for all solids is m3 or cm3. Because 1 mL = 1 cm3it is easy to convert. The water in the diagram increased 10 mL when the rock was added. That means the rock has a volume of 10 cm3.
Metric System - Temperature You use a thermometer to measure temperature. Always check the increments on your thermometer so you know what the reading is. Wait a minute or two for the red liquid to stop moving so you get an accurate reading.
Metric System - Temperature One of two units may be used in the Metric System when measuring temperature. Kelvins are used for extreme temperatures so we will only be using Celsius in class. IMPORTANT JUST SO YOU KNOW CELSIUS 0 Celsius = freezing point of water 0 Celsius = 273 Kelvin 100 Celsius = boiling point of water 310 Kelvin = body temperature 37 Celsius = body temperature
Metric System Once you learn how to measure in the Metric System, you will need to convert from one unit to another on occasion. For instance, you may have a balance that measures in grams, but your lab directions call for you to record the mass in kilograms. You will need to know how to convert the units.
Metric System - Conversions An easy way to convert between the commonly used measurements is to simply move the decimal. But How many places do you move the decimal? Which direction do you move it? Here s an easy method to converting measurements within the Metric System which uses a mnemonics chart.
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 Here are some prefixes and their corresponding values. Reading from left to right: each prefix is 10 times smaller than the value on its left. Reading from right to left: each prefix is 10 times larger than the value on its right.
Metric System Conversions The following pages are conversion practice. Only take notes you feel you need.
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 A kilometer is 10 times longer than a Hectometer. A kilometer is 1000 times longer than a meter. 1 km = 1000 m
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 K H D B D C M King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk A mnemonic can help you with conversions within the Metric System. Each letter of the mnemonic begins with the first letter of the metric prefix.
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk You will always be able to rebuild this chart if you memorize the mnemonic!
Metric System - Conversions Since the Metric System is based on factors of 10, we need only worry about moving the decimal when converting between metric measurements. Let s try a conversion: How many milliliters are in 1.25 Liters? OR 1.25 L = ? mL
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Start with the mnemonic: King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk. Now add the prefixes that start with the first letter of the mnemonic. They will be in the correct order!
Each Prefix along the chart is a Place or Spot . Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Now we are ready to make the conversion: 1.25 L = ? mL Step 1: Since Liter has no prefix, we will place our pencil on the Base-No Prefix spot. Step 2: Find Milli- on the chart.
Metric System - Conversions King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Step 3: Start at Base-No Prefix and jump your pencil to the right towards Milli- . You moved 3 places to the right to arrive at Milli . Step 4: Now move the decimal in 1.25 L to the right 3 places. This matches what you just did on the chart.
Metric System - Conversions Move the decimal to the right 3 places. Add a zero in the last place. You need not keep the decimal visible it is understood to be to the right of 1250 ml.
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 Try another conversion: 247 meters = ? kilometers Follow the previous steps: Place your pencil on Base-No Prefix and move to Kilometers by jumping 3 spaces to the left.
Metric System - Conversions Now move the decimal point 3 spaces to the left. The decimal is understood to be to the right of 7 . Add a zero in front of the decimal. Remember: Meter m, kilometer km
Metric System - Conversions King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Move the decimal one place to the right. Convert 56.2 cm to mm.
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Use the chart on your paper and try these conversions: Answers are revealed on the next slide. 93.2 mL = _____ L 845.34 g = _____ Kg 0.56 m = _____ cm
Metric System - Conversions 1000 100 10 1 1/10 1/100 1/1000 King Henry Died By Drinking Chocolate Milk Answers: Remember to add zeroes as placeholders where necessary. 1. 93.2 mL = 0.0932 L 2. 845.34 g = 0.84534 Kg 3. 0.56 m = 56 cm