The European Arrival in India: Exploration and Establishment
The commercial contacts between India and Europe have ancient roots through land and sea routes, with the sea route via the Cape of Good Hope being discovered by Vasco da Gama in 1498. Portuguese, Dutch, and English trading companies established settlements, with the British eventually gaining control. The decline of Portuguese power, rise of Dutch dominance, and the emergence of the English East India Company shaped European influence in India.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
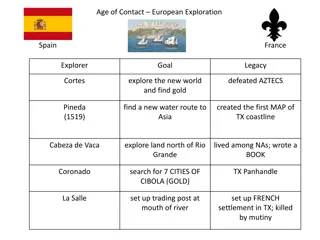
Introduction The commercial contacts between India and Europe were very old via the land route either through the Oxus Valley or Syria or Egypt . But , the new sea route via the Cape of Good Hope was discovered by Vasco da Gama in 1498 . Thereafter , many trading companies came to India and established their trading centres . They entered India as traders at the outset but by the passage of time indulged in the politics of India and finally established their colonies . The commercial rivalry among the European powers led to political rivalry . Ultimately , the British succeeded in establishing their rule in India
The Portuguese The Portuguese traveller Vasco da Gams reached the port of Calicut on 17th May 1498 and he was warmly received by Zamorin , the ruler of Calicut . He returned to Portugal in the next year . Pedro Alvarez Cabral arrived in 1500 and Vasco da Gama also made a second trip in 1502. they established trading stations at Calicut , Cannanore and Cochin . The first Governor of the Portuguese in India was Francis de Almeida .later in 1509 Albuquerque was made the governor of the Portuguese territories in India . In 1510 , he captured Goa from the ruler of Bijapur . Theresfter , Goa became the capital of the Portuguese settlements in India . Albuquerque captured Malacca and Ceylon .He also built a fort at Calicut . Albuquerque died in 1515 .
The successors of Albuquerque established Portuguese settlements at Daman , Salsette and Bombay on the west coast and at Santhome near Madras and Hugli in Bengal on the east coast . However , the Portuguese power declined in India by the end of the 16th Century . They lost all their possessions in India except Goa , Diu and Daman in the next century . The Dutch The Dutch East India Company was established in 1602 .The merchants of this company came to India and established their settlements at Masulipattinam , Pulicat , Surat, Karaikal , Nagappattinam , and Kasimbazar i. In the 17th Century they won over the Portuguese and emerged the most dominent power in European trade in the East . In the middle of the 17th Century the English began to emerge as a big colonial power . The Anglo Dutch rivalry lasted for about seven decades during that period the Dutch lost their settlements to the British one by one .
The English The English East India Company was established in 1600 and the Charter was issued by Queen Elizabeth of England Captain Hawkins arrived at the royal court of Jahangir in 1609 to seek permission to establish English trading centre at Surat . But it was refused by the Mughal Emperor due to Portuguese Pressure . Later in 1612 , Jahangir issued a farman (permission letter ) to the English and they established a trading factory at Surat in 1613 . Sir Thomas Roe came to India as ambassador of James I , the King of England to the Mughal court in 1615 . He obtained permission from Jahangir to establish English trading factories in different parts of India .
The English established their factories at Agra , Ahmadabad and Baroda by 1619 . The East India Company acquired Bombay from Charles II , the then king of England . In 1639 , Francis Day founded the city of Madras where the Fort St. George was built . in 1690 , an English factory was established at Calcutta where Fort William was built .later Calcutta became the capital of British India . Thus Bombay , Madras , Calcutta became the presidencies of the English settlements in India . The French The French East India Company was formed in 1664 by Colbert , a Minister under Louis XIV. The first French factory in India was established at Surat by Francis Caron. Later , Maracara set up a factory at Masulipattinam . Francois Martin founded Pondicherry in 1673 .
Other French factories in India were Chandranagore , Mahe and Karaikal . Francois Martin was the first governor of Pondicherry , the headquarters of the French possessions in India . The Danes Denmark also established trade settlements in India . Their settlement at Tranquebar was founded in 1620 . Another important Danish settlement in India was Serampore in Bengal . Serampore was their headquarters in India . They failed to strengthen themselves in India and they sold all their settlements in India to the British in 1845 .
Anglo French Rivalry In the beginning of the 18th century , the English and the French were competing with each other to establish their supremacy in India . The Anglo French rivalry in India was manifest in the Carnatic region and in Bengal . The Carnatic Wars . The downfall of the Mughal Empire led to the independence of Deccan under Nizam ul Mulk . The Carnatic region also formed part of the Nizam s domination. In 1740 , the Austrian War of Succession broke out in Europe . In that war England and France were in the opposite camps. They came into conflict in India also .
The French governor of Pondicherry , Dupleix opened attack on the English in 1746 and thus began the First Carnatic War ( 1746 1748 ). The English sought help from the Nawab of Carnatic , Anwar ud din . But French concluded a treaty with his rival Chanda Sahib . The English army crushed a defeat on the French in the Battle of Adyar , near Madras . In the meantime , the Treaty of Aix- la- Chappelle was concluded in 1748 to end the Austrian Succession War . Thus the First Carnatic War came to an end .
But the English and French continued to take opposite sides in the internal politics of India . As a result , the Second Carnatic War ( 1749 1754 ) . Dupleix supported the cause of Muzafar Jang, who wanted to became the Nizam of Hyderabad Chanda Sahib wanted to became the Nawab of Arcot . The troops of these three defeated Anwar ud din , who was with the British in the First Carnatic War , and killed him in the Battle of Ambur im1749 . After this victory , Muzafar Jung became the Nizam and Chanda Sahib became the Nawab of Arcot . Muhammad Ali , son of Anwar ud din escaped to Tiruchirappalli . The English sent troops in support of him . In the meantime , the British commander Robert Clive captured Arcot .
Robert Clive defeated French at Kaverippakkam . Chanda Sahib was captured and beheaded in Tanjore . Meanwhile Dupleix was replaced by Godeheu as the French governor . The war came to an end by the Treaty of Pondicherry in 1754 . The outbreak of the Seven Years War ( 1756 1763) in Europe led to the Third Carnatic War ( 1758 1763 ) . Count de Lally was the commander the French troops . The British General Sir Eyre Coote defeated him at Wandiwash in 1760 . In the next year , Pondicherry was captured and destroyed by the British troops . The Seven Years War came to an end by the treaty of Paris in 1763 . The Third Carnatic War also ended .
The French agreed to confine its activities in Pondicherry , Karaikkal , Mahe and Yenam . Thus the Anglo French rivalry came to a close with British success and French failure . Causes for the French failure . 1. Commercial and naval supremacy of the English only in the Deccan but the English . 2. Lack of support from the French Government . 3. The French had support only in the Deccan but the English had a strong base in Bengal . 4. English had three important ports Calcutta , Bombay and Madras but French had only Pondicherry . 5. Difference of opinion between the French Generals . 6. England s victory in the European wars decided the destiny of the French in India
India under the East India Company The English East India Company was established on 31st December 1600 as per the Royal Charter issued by the Queen of England , Elizabeth I . After the Battle of Plassey in 1757 and the Battle of Buxar in 1764 , the Company became a political power . India was under the East India Company s rule till 1858 when it came under the direct administration of the British Crown . Robert Clive was the first Governor of Fort William under the Company s rule . He was succeeded by Verelst and Cartier . In 1772 , the Company appointed Warren Hastings as the Governor of Fort William .
Warren Hastings He assumed the administration of Bengal in 1772 , he found it lot of chaos . The financial position of the Company became worse and the difficulties were occurred by famine . Therefore , Warren Hastings realized the immediate need for introducing reforms . Abolition of Dual System The East India Company decided to act as Diwan and to undertake the collection of revenue by its own agents . Hence , the Dual System introduced by Robert Clive was abolished .in order to improve the finances of the Company , Warren Hastings reduced the Nawab s allowance of 32 Lakhs of rupees to half that amount . He also stopped the annual payment of 26 Lakhs given to the Mughal Emperor .
Revenue Reforms After the abolition of the Dual System , the responsibility of collecting the revenue fell on the shoulders of the Company . For that purpose , a Board of Revenue was established at Calcutta to supervise the collection of revenue . English collectors were appointed in each district . The Treasury was removed from Murshidabad to Calcutta and an Accountant General was appointed . Calcutta became the capital of Bengal in 1772 and shortly after of British India .
The Board of Revenue farmed out the lands by auction for a period of five years . The Zamindars were given priority in the auction . However , certain good measures were taken to safeguard the interests of the peasants . Arbitrary cesses and unreasonable fines were abolished . Besides , restrictions were imposed on the enhancement of rent , Yet , the system was a failure . Many Zamindars defaulted and the arrears of revenue accumulated . Reorganisation of the Judicial System : The Judicial system during his period was a store house of abuses . The Nawab who hitherto the chief administrator of Justice , misused his powers . Often , his judgements were careless . The Zamindars who acted as judges at lower levels within their own areas were highly corrupt and prejudiced .
On the whole , the judicial institution suffered from extreme corruption . He felt that the necessity of reorganising the judicial system . Each district was provided with a civil court under the Collector and a Criminal court under an Indian Judge . To hear appeals from the district courts to two appellate courts , one for civil cases and another for criminal cases , were established at Calcutta . The the highest civil court of appeal was Sadar Diwani Adalat which was to be presided over by the Governor and two Judges recruited from the members of his council. The highest appellate criminal court was known as Sadar Nizamat Adalat under an Indian Judge appointed by the Governor in council . Experts in Hindu and Muslim laws were provided to assist the Judges .
The Hindu law was prepared in Sanskrit by learned Pandits and it was translated into Persian . An English translation of it Code of Hindu Laws was prepared by Halhed . Trade Regulations and Other Reforms : He abolished the system of Dastaks or free Passes and regulated the internal trade . He reduced the number of custom houses and enforced a uniform tariff of 2.5 % for Indian and non Indian goods . Private trade by the Company s servants continued buy within enforceable limits . Weavers were given better treatment and facilities were made to improve their condition . He introduced a uniform system of pre- paid postage system . A bank was started in Calcutta . He improved the police in Calcutta .
The Regulating Act of 1773 : The Regulating Act of 1773 opened a new chapter in the constitutional history of thr Company . Previously , the Home government in England consisted of the Court of Directors and the Court of Proprietors . The Court of Directors were elected annually and practically managed the affairs of the Company . In India , each of the three presidencies was independent and responsible only to the Home Government . The government of the presidency was conducted by a Governor and a Council .
The East India Company became a territorial power when it acquired a wide dominion in India and also the Diwani rights . Its early administration was in Corrupt . The disastrous famine which broke out in Bengal in 1770 affected the agriculturists . As a result , the revenue collection was poor . In short , the Company was on the brink of Bankruptcy . In 1773 , the Company approached the British government for an immediate loan . It was under these circumstances that the Parliament of England resolved to regulate the affairs of the Company . Lord North , the Prime Minister of England , appointed a select committee to inquire into the affairs of the Company . The report submitted by the Committee paved the way for the enactment of the Regulating Act .
Provisions of the Act 1. The term of office of the members of the Court of Directors was extended from one year to four years . One fourth of them were to retire every year and the retiring Directors were not eligible for re- election . 2. The Governors of Bengal was styled the Governor General of Fort William whose tenure of office was for a period of five years . 3. A Council of four members was appointed to assist the Governor General .the Government was to be conducted in accordance with the decision of the majority. .the Governor General had casting vote in case of a tie . 4. The Governor General in Council was made supreme over the other Presidencies in matters of war and peace . 5. Supreme Court was established at Calcutta consisting of a Chief Justice and three Junior Judges. It was to be independent of the Governor General in Council . In 1774 , the Supreme Court was established by a Royal Charter .
6. This Act prevented the servants of the Company including the Governor General , members of his council and the judges of the Supreme Court from receiving directly or indirectly any gifts in kind or cash . Expansionist Policy of Warren Hastings He was known for his expansionist policy . His administration witnessed the Rohilla War , the First Anglo Maratha War and the Second Anglo Mysore War . The Rohilla War 1774 : Rohilkand was a small kingdom situated in between Oudh and the Marathas . Its ruler was Hafiz Rahmat Khan . He concluded a defensive treaty in 1772 with the Nawab of Oudh fearing an attack by the Marathas . But no such attack took place . But , the Nawab demanded money .
When Rahmat refused , the Nawab with the help of the British invaded Rohilkand . Warren Hastings , who sent the British troops against Rohilkand was severely criticised for his policy on Rohilla affair . First Anglo Maratha War ( 1775- 82 ) The Marathas were largely remained disunited since the Third Battle of Panipet (1761) The internal conflict among the Marathas was best utilized by the British in their expansionist policy . In 1775, there was a dispute for the post of Peshwa between Madhav Rao and his uncle Ragunatha Rao. The British authorities in Bombay concluded the Treaty of Surat with Ragunatha Rao in March 1775 .
Ragunatha Rao promised to cede Bassein and Salsette to the British but later when he was unwilling to fulfil his promise , the British captured them . This action of the Bombay Government was not approved by Warren Hastings . In 1776, Warren Hastings sent Colonel Upton to settle the issue . He cancelled the Treaty of Surat and concluded the Treaty of Purander with Nana Fadnavis , another Maratha leader . According to this Treaty Madhava Rao II was accepted as the new Peshwa and the British retained Salsette along with a heavy war indemnity .
However , the Home authorities rejected the Treaty of Purander . Warren Hastings sanctioned operations against the Marathas . In meantime , the Britiah force sent by the Bombay Government was defeated by the Marathas . In 1781 , warren Hastings sent British troops under the command of Captain Popham . He defeated the Maratha chief , Mahadaji Scindia , and captured Gwaloor . Later in May 1782 , the Treaty of Salbai was signed between Warren Hastings and Mahadaji Scindia . Accordingly , Salsette and Bassein were given to the British . Raghunath Rao was pensioned off and Madhav Rao II was accepted as the Peshwa .
The Treaty of Salbai established the British influence in Indian Politics . It provided the British twenty years of peace with the Marathas . The Treaty also enabled the British to put pressure on Mysore with the help of the Marathas in recovering their territories from Haider Ali . Thus , the British , seved themselves from the combined opposition of Indian powers and dividing the Indian powers . The 2nd Anglo Mysore War ( 1780 84 ). The first Anglo Mysore War took place in 1767 69 . Haider Ali emerged victorious against the British and at the end of the war a defensive treaty was concluded between Haider Ali and the British . After eleven years , the Second Mysore War broke.
Major Causes 1. The British failed to fulfil the terms of the defensive treaty with Haider when he was attacked by the Marathas in 1771 . 2. There was an outbreak of hostilities between the English and the French during the American War of Independence . 3. The British captured Mahe , a French settlement within Haider's territories . 4. Haider Ali formed a grand alliance with the Nizam of Hyderabad and the Marathas against the British in 1779 The War began when the British led their forces through Haider s territory without his permission to capture Guntur in the Northern Sarkars . Haider Ali defeated colonel Baillie and captured Arcot in 1780 . In the next year , Warren Hastings , by a clever diplomacy , divided the Confederacy .
He made peace with the Nizam , won the friendship of Bhonsle and came to an understanding with the Scindia ( both Marathas ) As a result , Haider was isolated without any alliance . He was defeated by Sir Eyre Coote at Porto Novo in March 1781 . In December 1782 , Haider died of Cancer at the age of Sixty and his death was kept secret till his son Tipu Sultan assumed power . The Second Mysore War came to an end by the Treaty of Mangalore in 1783 . Accordingly , all conquests were mutually restored and the prisoners on both side were liberated .