The Balanced Scorecard and Its Performance Metrics
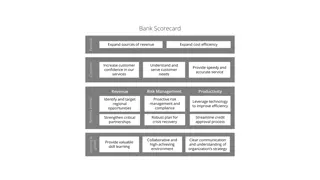
The balanced scorecard, developed by Dr. Robert Kaplan and David Norton in the early 1990s, offers a strategic framework beyond traditional financial measures. It focuses on four perspectives: Customers, Internal Processes, Financial, and Learning & Growth. Each perspective includes objectives, measures, targets, and initiatives. Key performance indicators cover areas like process efficiency, financial performance, and learning and growth indicators.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
The Balance scorecard Measures that drive performance
What is the balanced scorecard? Developed in the early 1990 s by Dr. Robert Kaplan and David Norton "The balanced scorecard retains traditional financial measures. But financial measures tell the story of past events, an adequate story for industrial age companies for which investments in long-term capabilities and customer relationships were not critical for success. These financial measures are inadequate, however, for guiding and evaluating the journey that information age companies must make to create future value through investment in customers, suppliers, employees, processes, technology, and innovation."
What is the balanced scorecard? The balanced scorecard is centered on four performance metrics or perspectives: Customers Internal processes Financial Learning and growth When implemented properly, each one of these perspectives contains four subparts consisting of Objectives Measures Targets Initiatives
Internal Process/Process efficiency Cost Throughput Quality Multiple productivity measures may include Labour cost as a % of sales dollars Sales per employee Machinery & equipment investments per employee Total labour cost per hour Production lead time Wastage percentage Efficiency WIP % % of defects
Financial perspective The financial performance perspective of the balanced scorecard addresses the question of how shareholders view the firm and which financial goals are shareholder s perspective. desired from the
Financial Performance The table below outlines possible financial performance objectives and their metrics. Objective Specific Measure Growth Revenue Growth Profitability Return on equity Cost Leadership Unit Cost
Key performance indicators include: Illness rate/days of absence Employee turnover Gender/racial ratios Internal promotion %
Customer perspective Many companies today have a corporate mission that focuses on the customer. To be number one in delivering value to customers is a typical mission statement. How a company is performing from its customers perspective has become, therefore, a priority for top management. The balanced scorecard demands that managers translate their general mission statement on customer service into specific measures that reflect the factors that really matter to customers.
Sustainability Indicators Social performance indicators: labor practices, human rights, and broader issues affecting consumers, community, and other stakeholders in society. Environmental performance indicators (KePI): greenhouse gas emissions, water consumption, waste output
Question 01 Expected outcome of the strategy should be evaluated not only through financial indicators. Explain the Balance scorecard system to strategic performance evaluation as opposed to rigid financial evaluation using possible key performance indicators. What are the possible factors that can drive the performance gap in KPI s?