Tertiary Education Options in New Zealand
Explore the various qualifications, completion times, and providers in New Zealand's tertiary education system. Learn about the different levels of qualifications available, typical study durations, and where you can obtain these qualifications. Gain insights into the meaning of study and training, as well as the diversity of courses and training options offered by universities, polytechnics, industry training organizations, and private training establishments.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
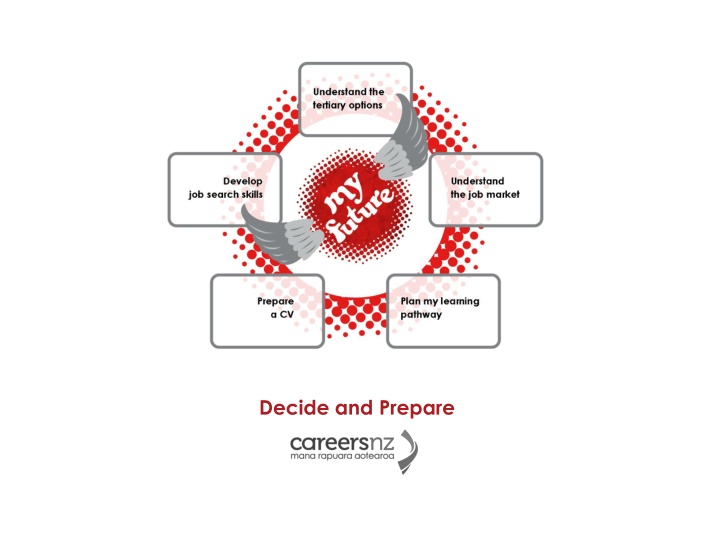
Understanding tertiary options Section 1 Decide and Prepare Careers New Zealand April 2012
Understanding tertiary options WHAT KINDS OF QUALIFICATIONS ARE THERE?
qualification types Levels 7-10 degrees, graduate and postgraduate qualifications Levels 4-6 advanced trades, technical and business qualifications Levels 1-3 senior secondary education (eg, NCEA) and basic trades training
qualification names bachelors, graduate and postgraduate certificates and diplomas honours, masters, doctorates, PhDs certificates, diplomas, national certificates, national diplomas
typical completion times for full-time study certificates general, national, graduate, postgraduate a few months, up to 1 year diplomas general, national, graduate, postgraduate 1 or 2 years, can be more bachelors degrees, honours degrees 3 or 4 years, can be 5 masters degrees 2 years doctorates, PhDs 3 years
the meaning of words study training When people talk about study they are often talking about learning at an education provider, eg, school or university. When people talk about training they are often talking about learning on the job. But, many workplace training programmes include off-the-job study. But, some study courses include on-the-job training through work placements.
Understanding tertiary options WHERE CAN I GET A QUALIFICATION?
tertiary providers 3w nanga 8universities 20polytechnics and institutes of technology (ITPs) 38industry training organisations (ITOs) +hundreds of private training establishments(PTEs)
Understanding tertiary options CAN I DO ANY COURSE I WANT?
entry requirements vary from course to course and place to place. You might need a set number of credits in particular school subjects. When there are a limited number of places in a course, meeting the minimum entry requirements might not be enough. Course providers may want to see portfolios, experience in the workplace, evidence of commitment or certain personal qualities.
entry to university Example: BA in history at Victoria University Minimum requirement is University Entrance For guaranteed entry you need a score of 150 points based on up to 80 of your best credits For example, 10 credits at excellence (40pts), 10 credits at merit (30pts) and 40 credits at achieved (80 pts). excellence=4 pts, merit=3 pts, achieved=2 pts
entry to polytech/institute Examples from Weltec: Diploma in Health Psychology Level 5 NCEA level 2 with 36 credits in three subjects. National Diploma in Architectural Technology Level 6 50 credits at NCEA Level 2, with at least 12 credits in each of Maths, Science and English. Alternatively, applicants 20 years of age or older are welcome to apply. Successful completion of selected unit standards is necessary to gain entry into the second year of this programme.
entry to workplace training Example: Retail modern apprenticeship You need to find a job in the industry and a boss willing to train you first. Requires you to successfully complete 147 credits at Levels 2 and 3 while you are working, so it helps to have NCEA Level 1 plus literacy and numeracy.
flexible options There are options that allow you to continue to explore what suits you as you go. These may be a good idea if you know the broad area you are interested in but aren t sure what sort of job you re heading for. Examples are: a general degree, eg, Bachelor of Arts or Science Pre-trade training, eg, plumbing
what you can do now Think about Start thinking about the way you might want to learn once you finish school. The tertiary study and training options available offer you different ways of learning. Think ahead When you choose your senior school subjects, check out whether your subjects will allow you to get into the tertiary study and training pathways you might want to follow.
Finding your networks Section 2 Decide and Prepare Careers New Zealand April 2012
Your network is church group . ministers . boss teachers . coach . team mates neighbours . hairdresser . vet barista . gas station guy doctor . chemist The people who know you well The people who sort of know you The people you can start a conversation with parents . sisters brothers . close friends classmates . aunts . uncles cousins . grandparents co-workers . fellow students club or group members Often it is these people who give you the best new leads
Networking is person 3 you goal person 1 person 2 X X
Networking example Jo wants to explore nursing as a career option cousin friend (nursing home manager) Jo doctor family friend colleague (nurse) colleague (nursing agency) minister friend aunt (case manager) church member (social worker)
Doing it right Think about how you can make a good first impression Prepare yourself to emphasize your positive qualities MUST DO #1 Create a positive impression of yourself appearance People say I m friendliness I ve had curiosity good feedback about honesty
Doing it right You can tell people about what you are looking for without directly asking for help. Decide what is reasonable to ask of people. How strong is your connection? MUST DO # 2 Tell people about your interests and goals How willing is the person? This may lead you to someone who could help you. How much hassle is your request?
www.careers.govt.nz Career Kete, Decide and Prepare section, April 2012 The information on networks in this presentation is based on ideas in Teaching Networking Skills: Paving a Way to Jobs and Careers, Aug 2008, Institute for Community Inclusion, UMass Boston. Downloaded December 2010 from http://www.communityinclusion.org/article.php?article_id=251