Supply Chain Preparedness for Emergency Response
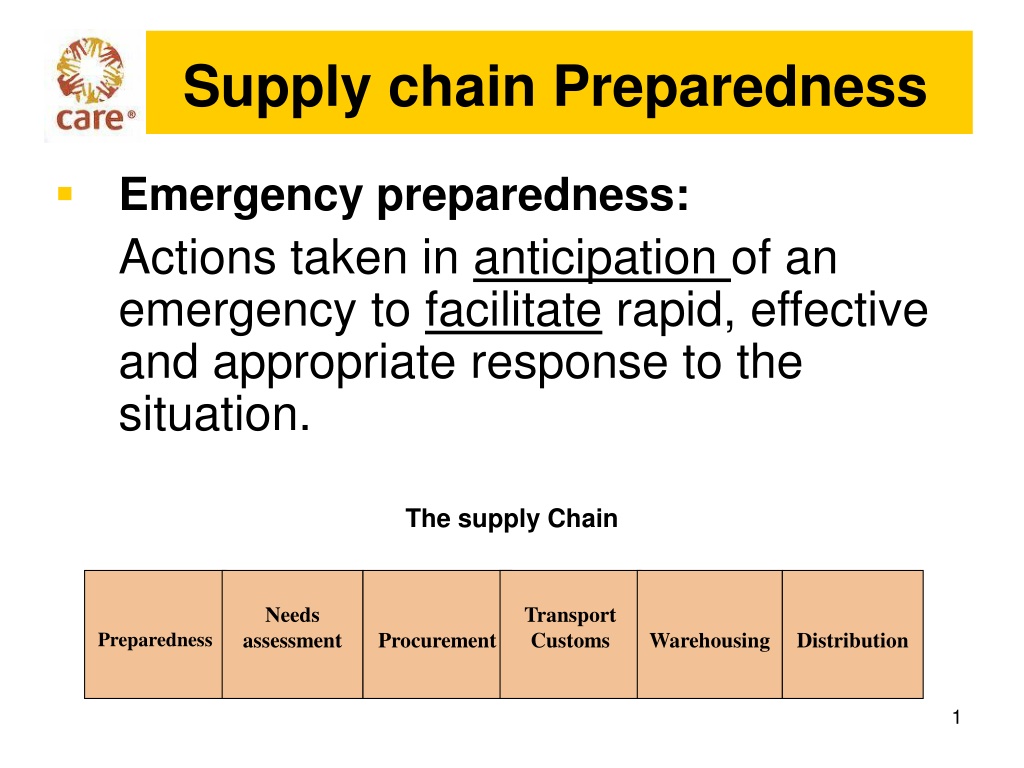
Actions are taken in anticipation of an emergency to ensure a rapid, effective, and appropriate response. This includes assessing supply chain needs, preparing transport and customs procedures, procurement, warehousing, and distribution. Elements of preparedness involve translating context, understanding internal and external capacities, identifying potential scenarios, and defining needs. Steps include establishing lists of programs and support items, sourcing options, knowing customs regulations, and assessing local infrastructure capacity.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
media_1760_care-logo Supply chain Preparedness Emergency preparedness: Actions taken in anticipation of an emergency to facilitate rapid, effective and appropriate response to the situation. The supply Chain Needs assessment Transport Customs Preparedness Procurement Warehousing Distribution 1
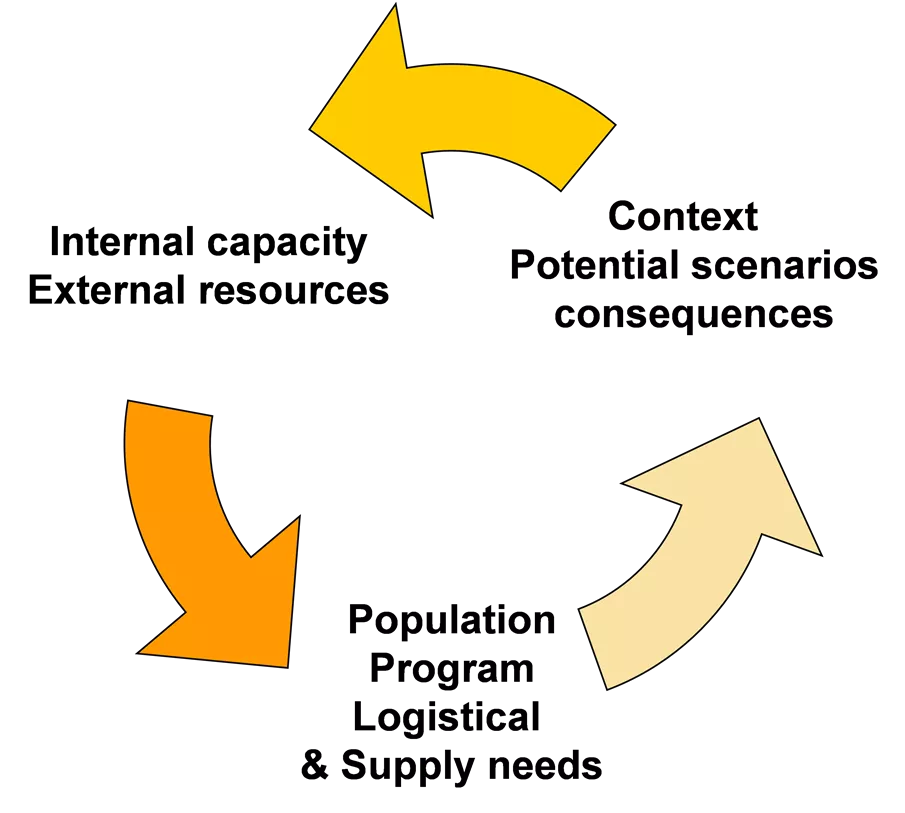
media_1760_care-logo Translating preparedness Context Internal capacity External resources Potential scenarios consequences Population Program Logistical & Supply needs 2
media_1760_care-logo Elements of the preparedness It is crucial to determine as accurately as possible: The context Define possible scenarios and consequences The needs generated Available internal capacity and resources Available external capacity and resources Complementary capabilities and resources required for meeting those needs 3
media_1760_care-logo Supply Preparedness Establish a list and specification of programs and support items required for an emergency response. Identify sourcing options: donation, purchasing, loan Knowledge of national, regional, international market (availability, cost, delivery time ) Have standard purchase contract established and adapted already prepared. Ensure that the tendering/quotes process is adapted Knowledge of majors donors guidelines for procurement. Be familiar with donor exceptions for emergency contexts. 4
media_1760_care-logo Customs Be aware of customs procedures and regulations for importing goods. Have a good freight forwarder, customs clearing agent or someone who understands customs regulations to help ease the customs process. Check the possibility of a tax exemption. Do you have the relevant documentation required if goods need to be imported? Check if some goods are prohibited or restricted (for example, communications equipment often needs licenses, some drugs might be banned) 5
media_1760_care-logo Localinfrastructures Capacity of points of entry (airports, ports, borders )? Restrictions on their use? Are changes planned? State of roads, waterways and other transport infrastructure Existence & availability storage facilities Existence & availability of means of transport Identify potential bottlenecks (bridge, weather constraint ) What are the communication systems in risk area (mobile phone, radio communication, internet, none ) 6
media_1760_care-logo Transport Vehicles (cars, trucks, motorbikes) Define your possible transport requirements for personnel and the movement of supplies. Consider all transport modes, also establish alternative options. Assess the number of vehicles (type, condition) that could be available. Evaluate your potential additional requirement Assess your sourcing options to meet your requirements (for example, renting, local or international purchase, loan). In case of significant increase in the fleet size, assess the capacity to scale-up maintenance. Check what the supply of spare parts and fuel is. Consider having contingency stocks. 7
media_1760_care-logo Transport Air charter Check the possibility of chartering aircraft for cargo (type, payload, cost). Ensure that you are prepared to face the logistics involved in air Ops Know the procedure and regulations to receive charter aircraft with cargo. Sea transport Assess the sea freight entry point (warehousing, handling). Check if risk areas are reachable by boat (type of boat, payload). Identify where you can find these boats and the cost. 8
media_1760_care-logo Warehousing Assess existence & availability of storage facilities that you can hire/borrow/share at short notice. Determine what surface and volume would be needed in case of emergency. Check the possibilities of finding temporary mobile warehousing structures (Rubbhall, containers). Ensure that you have a good system to track and report on movement of supplies (waybill, bin card, stock report). Ensure you have skilled staff in warehouse management. Identify how to get additional resources (forklift... ) Consider constitution of contingency stock of non perishable relief items in High risk areas 9
media_1760_care-logo Distribution Have distribution system in place and ready to be implemented Identity Partners to support distribution Assess secondary transport and warehousing space at the distribution areas Have Monitoring system to allow accurate reporting on distribution 10
media_1760_care-logo Key Elements Knowledge Anticipation Network Scaling up capacity Systems and procedures Adaptation 11