Respiratory System Disorders and Functions
Explore the anatomical structure, functions, and symptomatology of respiratory system disorders. Learn about dyspnea, hemoptysis, hypoxemia, orthopnea, and more. Understand asthma pathophysiology, pneumonia factors, and nursing care for asthmatic patients.
Download Presentation

Please find below an Image/Link to download the presentation.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.If you encounter any issues during the download, it is possible that the publisher has removed the file from their server.
You are allowed to download the files provided on this website for personal or commercial use, subject to the condition that they are used lawfully. All files are the property of their respective owners.
The content on the website is provided AS IS for your information and personal use only. It may not be sold, licensed, or shared on other websites without obtaining consent from the author.
E N D
Presentation Transcript
Respiratory System Disorders Respiratory System Disorders
Objectives of the lecture Objectives of the lecture At the end of the lecture the students will be able to : Realize the anatomical structure of respiratory system Describe the main function of the respiratory system List the general symptomatology of the respiratory system Discuss the pathophysiology of the asthma List the predisposing factors of pneumonia Anticipate the clinical manifestations of asthma Formulate the nursing care plan of asthmatic patients
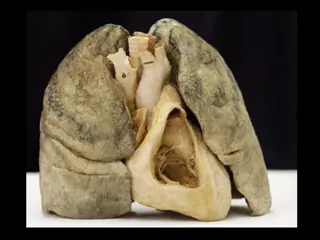
Anatomical Structure of Respiratory Anatomical Structure of Respiratory System System
Functions of Respiratory System Functions of Respiratory System The major functions of the pulmonary system (lungs and pulmonary circulation ) is to deliver oxygen to cells and remove carbon dioxide from the cells ( gas exchanges )
General Symptomatology of Respiratory General Symptomatology of Respiratory System Disorders System Disorders Dyspnea : is a subjective sensation associated with difficult breathing in any position . Hemoptysis : is the bleeding from lung main symptom is coughing up blood . Hypoxemia : Pao2 less than 80: 100 mmhg on room air , it means decrease the level of oxygen level in the blood . Hypoxia : insufficient oxygenation at the cellular level
General Symptomatology of Respiratory General Symptomatology of Respiratory System Disorders System Disorders Orthopnea : shortness of breath when in reclining position (lying position) Paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea : shortness of breathing with sudden onset occurs after going to sleep (at night ). Chest pain : chest pain related to pulmonary causes usually felt at the site where as pathology arise
General Symptomatology of Respiratory General Symptomatology of Respiratory System Disorders System Disorders Cough : dry irritative cough may indicate viral infection , cough at night related to left side heart failure , morning cough with sputum (reproductive cough )indicate bronchitis .Consider bacterial pneumonia if sputum is rusty
Physical Examination of Respiratory Physical Examination of Respiratory system system Perform a physical examination of the chest using inspection , palpation , percussion and auscultation . Diagnostic tests : Lab studies :as arterial blood gases (Pao2, Paco2 ,PH ) Sputum examination Plural fluid analysis Chest X-ray
Bronchial Asthma Bronchial Asthma Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of airways causing hypersensitivity , mucosal edema and mucus production Patients with asthma may experience symptoms free periods alternating with acute exacerbations that lasts from minutes to hours or days . Asthma , the most common chronic disease of childhood can occur at any age .
Risk Factors of Asthma Risk Factors of Asthma Family history Allergy to food , drugs .(strongest factor ) Chronic exposure to airways irritants or allergens (grass, tree, weed pollens, dust animal dander ) Common triggers for asthma symptoms and exacerbation include : Airway irritants (as: pollution , cold ,heat , weather changes strong odor , smoke ) Foods (shell , fish , nuts ) Exercise , stress, hormonal factors , medication , viral infection
Pathophesiology of Asthma Pathophesiology of Asthma Asthma is a reversible diffuse airway inflammation that leads to long-term airway narrowing exacerbated by a variety of changes in the airway including: Bronchoconstriction Airway edema Hyperresponsiveness Airway remolding(thichened)
Clinical Manifestations (S&S)of Asthma Clinical Manifestations (S&S)of Asthma Most common symptoms of asthma are cough (dry or productive ), dyspnea , wheezing (first on expiration , then during inspiration as well ) Asthma attach frequently happened at night or early morning Usually preceded by increasing symptoms over days but may being abruptly Chest tightness and dyspnea occur As exacerbation progress , diaphoresis, tachycardia,and widened pulse pressure and central cyanosis may occur
Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Assessment and Diagnostic Findings Family history , environmental and occupational related factors are essential Comorbid condition include gastro esophageal reflux, drug induced asthma and allergic Eczema , rashes , and temporary edema are allergic reaction that may accompany asthma During acute episodes ,sputum and blood test including pulse oximetry , arterial blood gases should be tested .
Prevention of Asthma Prevention of Asthma Evaluation of workplace Immediate treatment is aimed at removing or decreasing the exposure in the patient s environment and follow up Standard asthma medications may be prescribed to minimize bronchospasm and airway inflammation .
Complications of Asthma Complications of Asthma Complications of asthma include : Status asthmatics Respiratory failure Pneumonia Atelectasis Dehydration from diaphoresis
Medical Management of Asthma Medical Management of Asthma Pharmacological Therapy : there are 2 types of asthma medication : Quick relief medications , short acting beta 2 adrenergic agonist as Ventoline used to relax smooth muscle Long acting control medication : currently corticosteroids are the most potent anti-inflammatory medications effective in alleviating symptoms , improve airway functions Antibiotics may be appropriate in treatment of acute asthma exacerbations in patients with comorbid conditions (fever , purulent sputum, pneumonia )
Nursing Management of patient with Nursing Management of patient with Asthma Asthma The immediate nursing care of asthmatic patients depend on the severity of symptoms A calm approach is an important aspect of care for successful treatment both as an outpatient for mild symptoms and as a hospital patient for acute and severe symptoms .The nurse usually perform the following :
Nursing Management Nursing Management Assess the patient s respiratory status by monitoring severity of symptoms , breath sounds , pulse oximetry and vital signs . Obtains a history of allergic reactions to medication before administering medication . Identifies the medications the patient s currently taking . Administer the prescribed medication Administer fluids if patient is dehydrated Assess with intubation procedure if needed .

 undefined
undefined